正在加载图片...
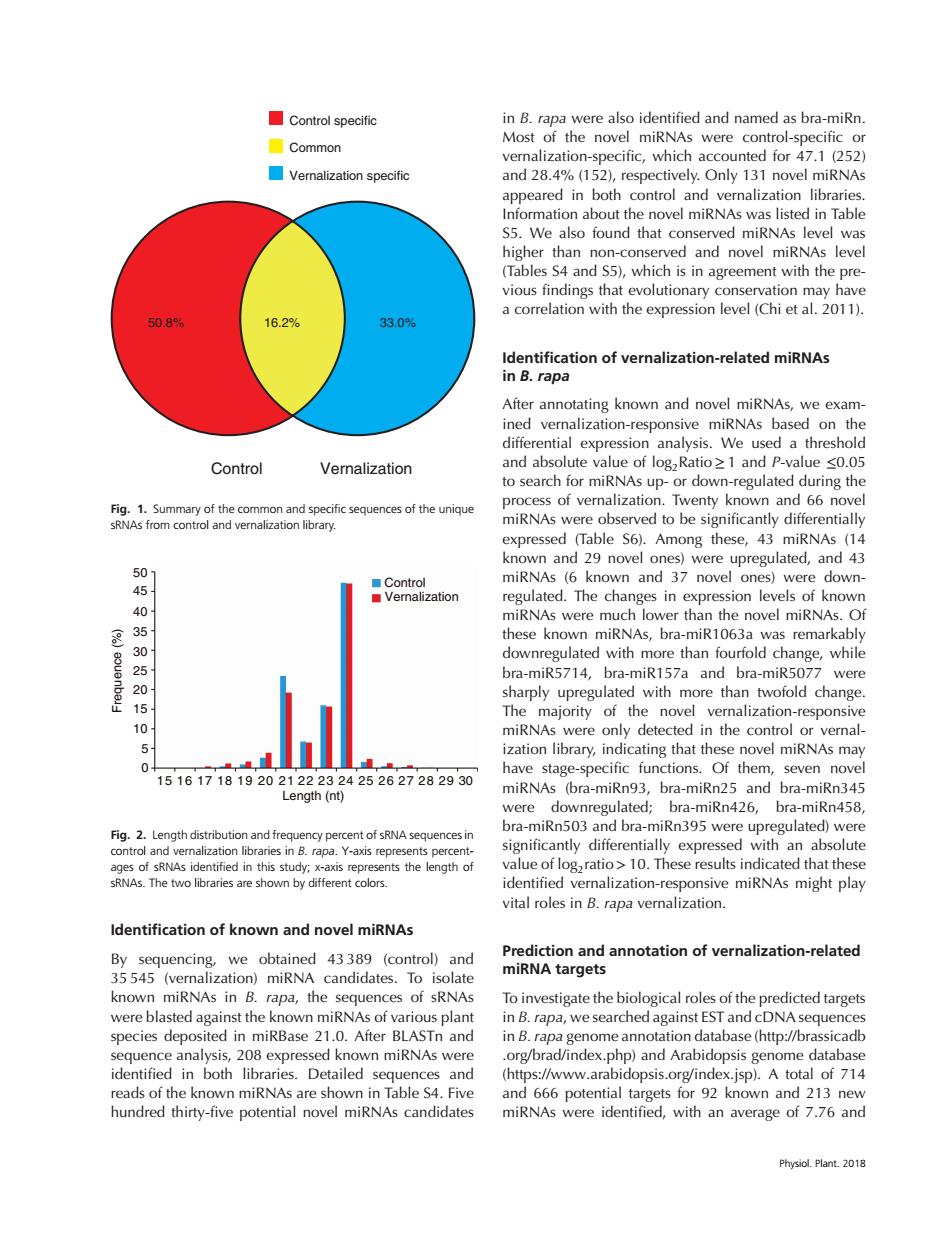
■Control specific in B.rapa were also identified and named as bra-miRn. ☐Common Most of the novel miRNAs were control-specific or vernalization-specific,which accounted for 47.1 (252) Vernalization specific and 28.4%(152),respectively.Only 131 novel miRNAs appeared in both control and vernalization libraries. Information about the novel miRNAs was listed in Table S5.We also found that conserved miRNAs level was higher than non-conserved and novel miRNAs level (Tables S4 and S5),which is in agreement with the pre- vious findings that evolutionary conservation may have a correlation with the expression level(Chi et al.2011). 50.89 16.2% 33.0% Identification of vernalization-related miRNAs in B.rapa After annotating known and novel miRNAs,we exam- ined vernalization-responsive miRNAs based on the differential expression analysis.We used a threshold Control Vernalization and absolute value of logzRatio >1 and P-value <0.05 to search for miRNAs up-or down-regulated during the process of vernalization.Twenty known and 66 novel Fig.1.Summary of the common and specific sequences of the unique sRNAs from control and vernalization library. miRNAs were observed to be significantly differentially expressed (Table S6).Among these,43 miRNAs (14 known and 29 novel ones)were upregulated,and 43 01 ■Control miRNAs (6 known and 37 novel ones)were down- 5 ■Vernalization regulated.The changes in expression levels of known 40 miRNAs were much lower than the novel miRNAs.Of 50050 these known miRNAs,bra-miR1063a was remarkably downregulated with more than fourfold change,while bra-miR5714,bra-miR157a and bra-miR5077 were sharply upregulated with more than twofold change. 15 The majority of the novel vernalization-responsive 10 miRNAs were only detected in the control or vernal- 5 ization library,indicating that these novel miRNAs may 0 have stage-specific functions.Of them,seven novel 15161718192021222324252627282930 miRNAs (bra-miRn93,bra-miRn25 and bra-miRn345 Length (nt) were downregulated;bra-miRn426,bra-miRn458, bra-miRn503 and bra-miRn395 were upregulated)were Fig.2.Length distribution and frequency percent of sRNA sequences in control and vernalization libraries in B.rapa.Y-axis represents percent- significantly differentially expressed with an absolute ages of sRNAs identified in this study:x-axis represents the length of value of logzratio>10.These results indicated that these sRNAs.The two libraries are shown by different colors. identified vernalization-responsive miRNAs might play vital roles in B.rapa vernalization ldentification of known and novel miRNAs By sequencing,we obtained 43389 (control)and Prediction and annotation of vernalization-related 35 545 (vernalization)miRNA candidates.To isolate miRNA targets known miRNAs in B.rapa,the sequences of sRNAs To investigate the biological roles of the predicted targets were blasted against the known miRNAs of various plant in B.rapa,we searched against EST and cDNA sequences species deposited in miRBase 21.0.After BLASTn and in B.rapa genome annotation database(http://brassicadb sequence analysis,208 expressed known miRNAs were .org/brad/index.php)and Arabidopsis genome database identified in both libraries.Detailed sequences and (https://www.arabidopsis.org/index.jsp).A total of 714 reads of the known miRNAs are shown in Table S4.Five and 666 potential targets for 92 known and 213 new hundred thirty-five potential novel miRNAs candidates miRNAs were identified,with an average of 7.76 and Physiol.Plant.2018Control Vernalization 50.8% 16.2% 33.0% Control specific Common Vernalization specific Fig. 1. Summary of the common and specific sequences of the unique sRNAs from control and vernalization library. Frequence (%) 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Control Vernalization 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Length (nt) Fig. 2. Length distribution and frequency percent of sRNA sequences in control and vernalization libraries in B. rapa. Y-axis represents percentages of sRNAs identified in this study; x-axis represents the length of sRNAs. The two libraries are shown by different colors. Identification of known and novel miRNAs By sequencing, we obtained 43 389 (control) and 35 545 (vernalization) miRNA candidates. To isolate known miRNAs in B. rapa, the sequences of sRNAs were blasted against the known miRNAs of various plant species deposited in miRBase 21.0. After BLASTn and sequence analysis, 208 expressed known miRNAs were identified in both libraries. Detailed sequences and reads of the known miRNAs are shown in Table S4. Five hundred thirty-five potential novel miRNAs candidates in B. rapa were also identified and named as bra-miRn. Most of the novel miRNAs were control-specific or vernalization-specific, which accounted for 47.1 (252) and 28.4% (152), respectively. Only 131 novel miRNAs appeared in both control and vernalization libraries. Information about the novel miRNAs was listed in Table S5. We also found that conserved miRNAs level was higher than non-conserved and novel miRNAs level (Tables S4 and S5), which is in agreement with the previous findings that evolutionary conservation may have a correlation with the expression level (Chi et al. 2011). Identification of vernalization-related miRNAs in B. rapa After annotating known and novel miRNAs, we examined vernalization-responsive miRNAs based on the differential expression analysis. We used a threshold and absolute value of log2Ratio≥1 and P-value ≤0.05 to search for miRNAs up- or down-regulated during the process of vernalization. Twenty known and 66 novel miRNAs were observed to be significantly differentially expressed (Table S6). Among these, 43 miRNAs (14 known and 29 novel ones) were upregulated, and 43 miRNAs (6 known and 37 novel ones) were downregulated. The changes in expression levels of known miRNAs were much lower than the novel miRNAs. Of these known miRNAs, bra-miR1063a was remarkably downregulated with more than fourfold change, while bra-miR5714, bra-miR157a and bra-miR5077 were sharply upregulated with more than twofold change. The majority of the novel vernalization-responsive miRNAs were only detected in the control or vernalization library, indicating that these novel miRNAs may have stage-specific functions. Of them, seven novel miRNAs (bra-miRn93, bra-miRn25 and bra-miRn345 were downregulated; bra-miRn426, bra-miRn458, bra-miRn503 and bra-miRn395 were upregulated) were significantly differentially expressed with an absolute value of log2ratio>10. These results indicated that these identified vernalization-responsive miRNAs might play vital roles in B. rapa vernalization. Prediction and annotation of vernalization-related miRNA targets To investigate the biological roles of the predicted targets in B. rapa, we searched against EST and cDNA sequences in B. rapa genome annotation database (http://brassicadb .org/brad/index.php) and Arabidopsis genome database (https://www.arabidopsis.org/index.jsp). A total of 714 and 666 potential targets for 92 known and 213 new miRNAs were identified, with an average of 7.76 and Physiol. Plant. 2018