正在加载图片...
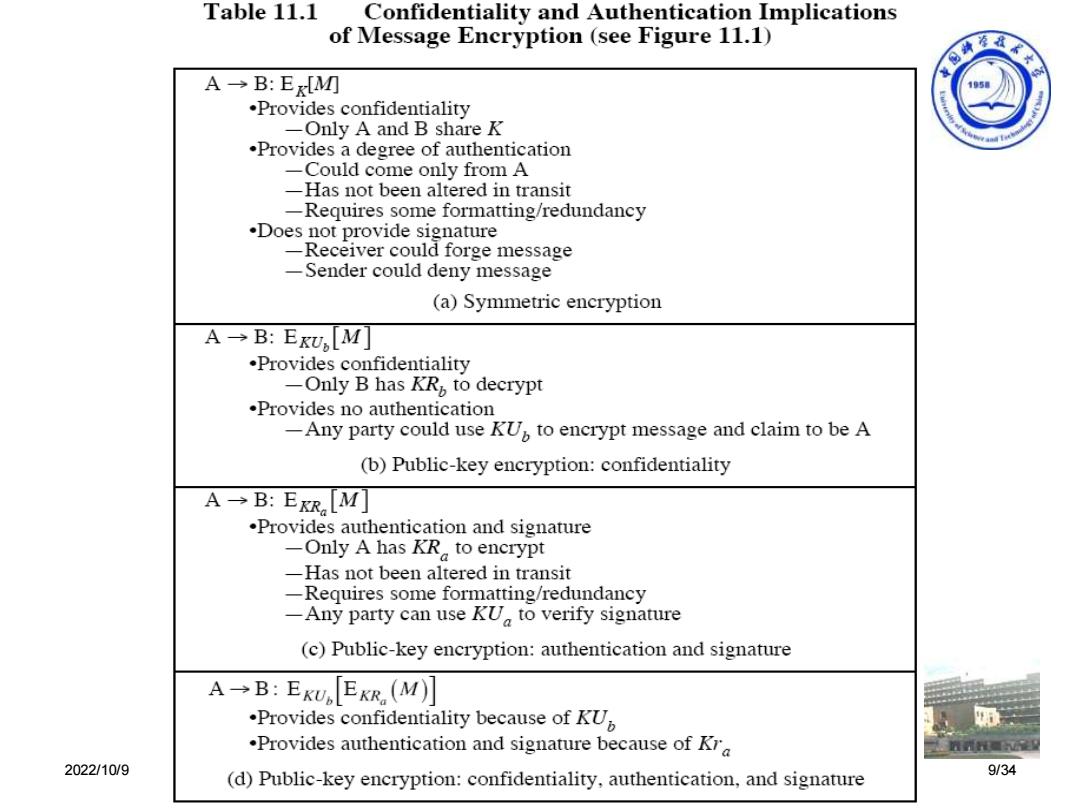
Table 11.1 Confidentiality and Authentication Implications of Message Encryption(see Figure 11.1) 海车柔大 A→B:E[MM 105 .Provides confidentiality -Only A and B share K .Provides a degree of authentication -Could come only from A -Has not been altered in transit -Requires some formatting/redundancy .Does not provide signature -Receiver could forge message Sender could deny message (a)Symmetric encryption A→B:ExU,M] .Provides confidentiality -Only B has KR,to decrypt .Provides no authentication -Any party could use KUp to encrypt message and claim to be A (b)Public-key encryption:confidentiality A→B:E,M] .Provides authentication and signature -Only A has KR to encrypt Has not been altered in transit -Requires some formatting/redundancy -Any party can use KU to verify signature (c)Public-key encryption:authentication and signature A→B:EKU[EKR(M] .Provides confidentiality because of KU .Provides authentication and signature because of Kra 2022/10/9 (d)Public-key encryption:confidentiality,authentication,and signature 9/342022/10/9 现代密码学理论与实践-11 9/34