正在加载图片...
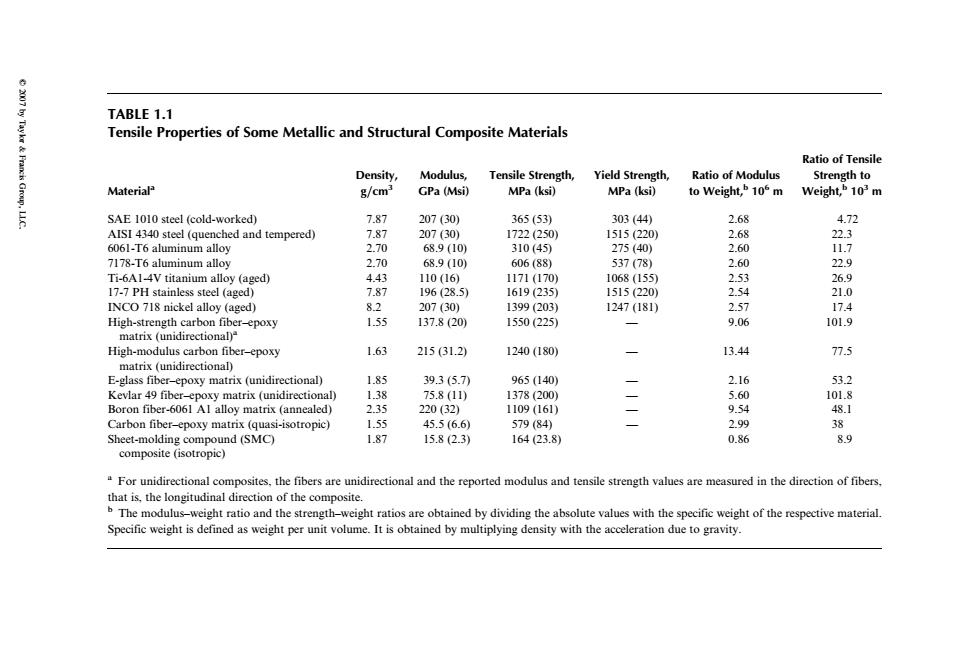
TABLE 1.1 Taykr Francis Group. Tensile Properties of Some Metallic and Structural Composite Materials Ratio of Tensile Density, Modulus, Tensile Strength, Yield Strength, Ratio of Modulus Strength to Material g/cm3 GPa (Msi) MPa(ksi) MPa (ksi) to Weight,b 105 m Weight,b 103m SAE 1010 steel (cold-worked) 7.87 207(30) 365(53) 303(44) 2.68 4.72 AISI 4340 steel (quenched and tempered) 7.87 207(30) 1722(250) 1515(220) 2.68 22.3 6061-T6 aluminum alloy 2.70 68.9(10) 310(45) 275(40) 2.60 11.7 7178-T6 aluminum alloy 2.70 68.9(10) 606(88) 537(78) 2.60 22.9 Ti-6A1-4V titanium alloy (aged) 4.43 110(16) 1171(170) 1068(155 2.53 26.9 17-7 PH stainless steel (aged) 7.87 196(28.5) 1619(235) 1515(220) 2.54 21.0 INCO 718 nickel alloy (aged) 8.2 207(30) 1399(203) 1247(181) 2.57 17.4 High-strength carbon fiber-epoxy 1.55 137.8(20) 1550(225) 9.06 101.9 matrix (unidirectional)" High-modulus carbon fiber-epoxy 1.63 215(31.2) 1240(180) 13.44 77.5 matrix (unidirectional) E-glass fiber-epoxy matrix(unidirectional) 1.85 39.3(5.7) 965(140) 2.16 53.2 Kevlar 49 fiber-epoxy matrix (unidirectional) 1.38 75.8(11) 1378(200) 5.60 101.8 Boron fiber-6061 Al alloy matrix (annealed) 2.35 220(32) 1109(161) Carbon fiber-epoxy matrix (quasi-isotropic) 1.55 45.5(6.6) 579(84) 二 9.54 48.1 2.99 38 Sheet-molding compound(SMC) 1.87 15.8(2.3) 164(23.8) 0.86 89 composite (isotropic) "For unidirectional composites,the fibers are unidirectional and the reported modulus and tensile strength values are measured in the direction of fibers. that is,the longitudinal direction of the composite. The modulus-weight ratio and the strength-weight ratios are obtained by dividing the absolute values with the specific weight of the respective material Specific weight is defined as weight per unit volume.It is obtained by multiplying density with the acceleration due to gravity.TABLE 1.1 Tensile Properties of Some Metallic and Structural Composite Materials Materiala Density, g=cm3 Modulus, GPa (Msi) Tensile Strength, MPa (ksi) Yield Strength, MPa (ksi) Ratio of Modulus to Weight,b 106 m Ratio of Tensile Strength to Weight,b 103 m SAE 1010 steel (cold-worked) 7.87 207 (30) 365 (53) 303 (44) 2.68 4.72 AISI 4340 steel (quenched and tempered) 7.87 207 (30) 1722 (250) 1515 (220) 2.68 22.3 6061-T6 aluminum alloy 2.70 68.9 (10) 310 (45) 275 (40) 2.60 11.7 7178-T6 aluminum alloy 2.70 68.9 (10) 606 (88) 537 (78) 2.60 22.9 Ti-6A1-4V titanium alloy (aged) 4.43 110 (16) 1171 (170) 1068 (155) 2.53 26.9 17-7 PH stainless steel (aged) 7.87 196 (28.5) 1619 (235) 1515 (220) 2.54 21.0 INCO 718 nickel alloy (aged) 8.2 207 (30) 1399 (203) 1247 (181) 2.57 17.4 High-strength carbon fiber–epoxy matrix (unidirectional)a 1.55 137.8 (20) 1550 (225) — 9.06 101.9 High-modulus carbon fiber–epoxy matrix (unidirectional) 1.63 215 (31.2) 1240 (180) — 13.44 77.5 E-glass fiber–epoxy matrix (unidirectional) 1.85 39.3 (5.7) 965 (140) — 2.16 53.2 Kevlar 49 fiber–epoxy matrix (unidirectional) 1.38 75.8 (11) 1378 (200) — 5.60 101.8 Boron fiber-6061 A1 alloy matrix (annealed) 2.35 220 (32) 1109 (161) — 9.54 48.1 Carbon fiber–epoxy matrix (quasi-isotropic) 1.55 45.5 (6.6) 579 (84) — 2.99 38 Sheet-molding compound (SMC) composite (isotropic) 1.87 15.8 (2.3) 164 (23.8) 0.86 8.9 a For unidirectional composites, the fibers are unidirectional and the reported modulus and tensile strength values are measured in the direction of fibers, that is, the longitudinal direction of the composite. b The modulus–weight ratio and the strength–weight ratios are obtained by dividing the absolute values with the specific weight of the respective material. Specific weight is defined as weight per unit volume. It is obtained by multiplying density with the acceleration due to gravity. 2007 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC