正在加载图片...
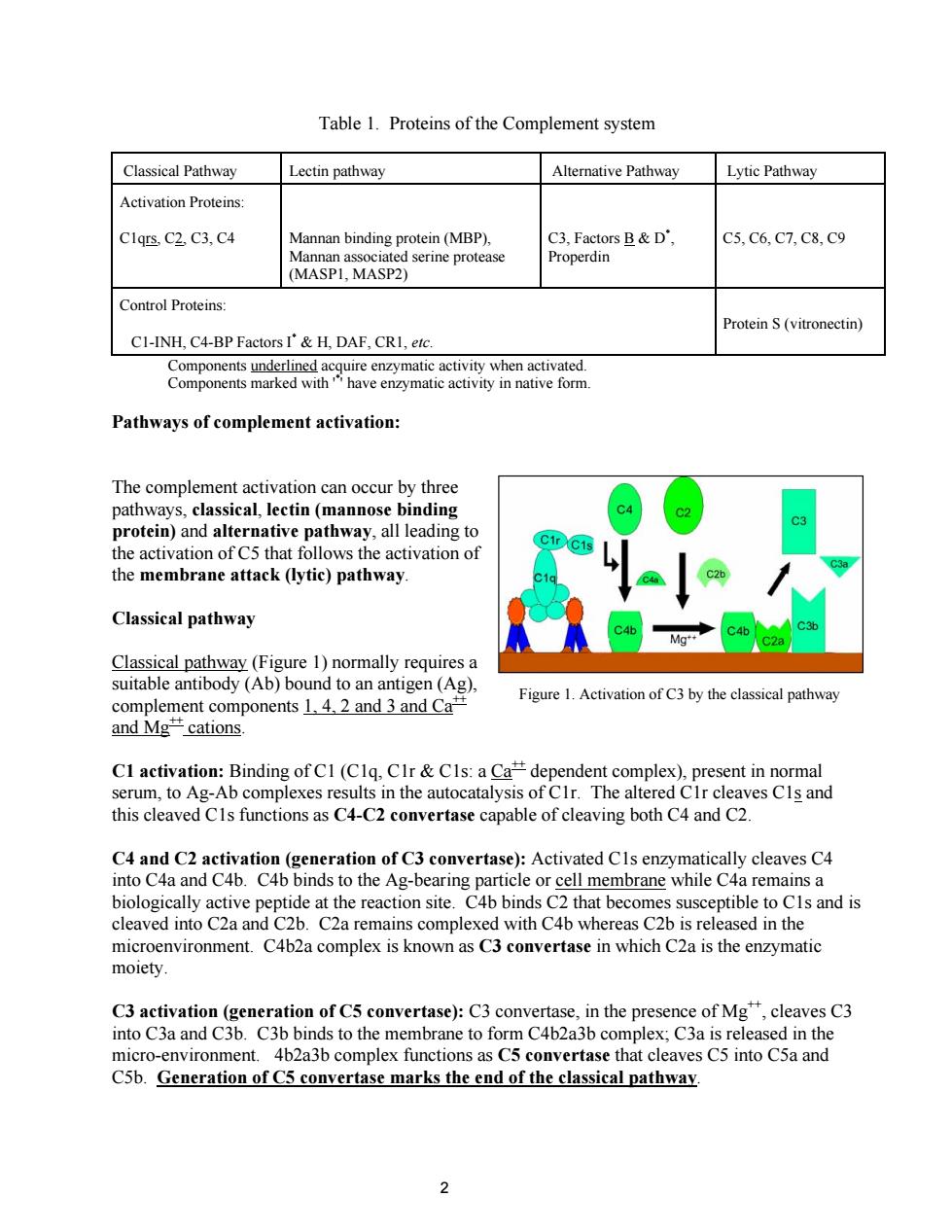
Table 1.Proteins of the Complement system Classical Pathway Lectin pathway alternative pathway Lytic Pathway Activation Proteins Clqrs,C2 C3,C4 nnan bindin g protein(MBP) C5,C6,C7,C8,C9 enne protea (MASPI MASP2) Control Proteins: Protein S(vitronectin) C1-INH,C4-BP FactorsI'&H,DAF,CR1,etc. Pathways of complement activation: binding protein)and alternative pathway,all leading to the activation of C5 that follows the activation of the membrane attack(lytic)pathway. Classical pathway Classical pathway(Figure 1)normally requires a suitable antibody (Ab)bound to an antigen(Ag) nponents 1.4.2 and 3 and Ca Figure 1.Activation of C3 by the classical pathway endent complex sent in norma aves CIs and this cleaved CIs functions as C4-C2 convertase capable of cleaving both C4 and C2 C4 and C2 activation(generation of C3 convertase):Activated CIs enzymatically cleaves C4 into C4a and C4b.C4b binds to the Ag-bearing particle or cell membrane while C4a remains a biologically active peptide at the reaction site.C4b binds C2 that becomes susceptible to Cls and is cleaved into C2a and C2b.C2a remains complexed with C4b whereas C2b is released in the microenvironment.C4b2a complex is known as C3 convertase in which C2a is the enzymatic moiety C3activation (generation ofC5 convertase):C converta in the presence of Mg,cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b.C3b binds to the membrane to form C4b2a3b complex;C3a is released in th micro-environment. 4b2a3b complex functions as C5 convertase that cleaves C5 into CSa and C5b.Generation of C5 convertase marks the end of the classical pathwav. Table 1. Proteins of the Complement system Classical Pathway Lectin pathway Alternative Pathway Lytic Pathway Activation Proteins: C1qrs, C2, C3, C4 Mannan binding protein (MBP), Mannan associated serine protease (MASP1, MASP2) C3, Factors B & D* , Properdin C5, C6, C7, C8, C9 Control Proteins: C1-INH, C4-BP Factors I* & H, DAF, CR1, etc. Protein S (vitronectin) Components underlined acquire enzymatic activity when activated. Components marked with '* ' have enzymatic activity in native form. Pathways of complement activation: Figure 1. Activation of C3 by the classical pathway The complement activation can occur by three pathways, classical, lectin (mannose binding protein) and alternative pathway, all leading to the activation of C5 that follows the activation of the membrane attack (lytic) pathway. Classical pathway Classical pathway (Figure 1) normally requires a suitable antibody (Ab) bound to an antigen (Ag), complement components 1, 4, 2 and 3 and Ca++ and Mg++ cations. C1 activation: Binding of C1 (C1q, C1r & C1s: a Ca++ dependent complex), present in normal serum, to Ag-Ab complexes results in the autocatalysis of C1r. The altered C1r cleaves C1s and this cleaved C1s functions as C4-C2 convertase capable of cleaving both C4 and C2. C4 and C2 activation (generation of C3 convertase): Activated C1s enzymatically cleaves C4 into C4a and C4b. C4b binds to the Ag-bearing particle or cell membrane while C4a remains a biologically active peptide at the reaction site. C4b binds C2 that becomes susceptible to C1s and is cleaved into C2a and C2b. C2a remains complexed with C4b whereas C2b is released in the microenvironment. C4b2a complex is known as C3 convertase in which C2a is the enzymatic moiety. C3 activation (generation of C5 convertase): C3 convertase, in the presence of Mg++, cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b. C3b binds to the membrane to form C4b2a3b complex; C3a is released in the micro-environment. 4b2a3b complex functions as C5 convertase that cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b. Generation of C5 convertase marks the end of the classical pathway. 2