正在加载图片...
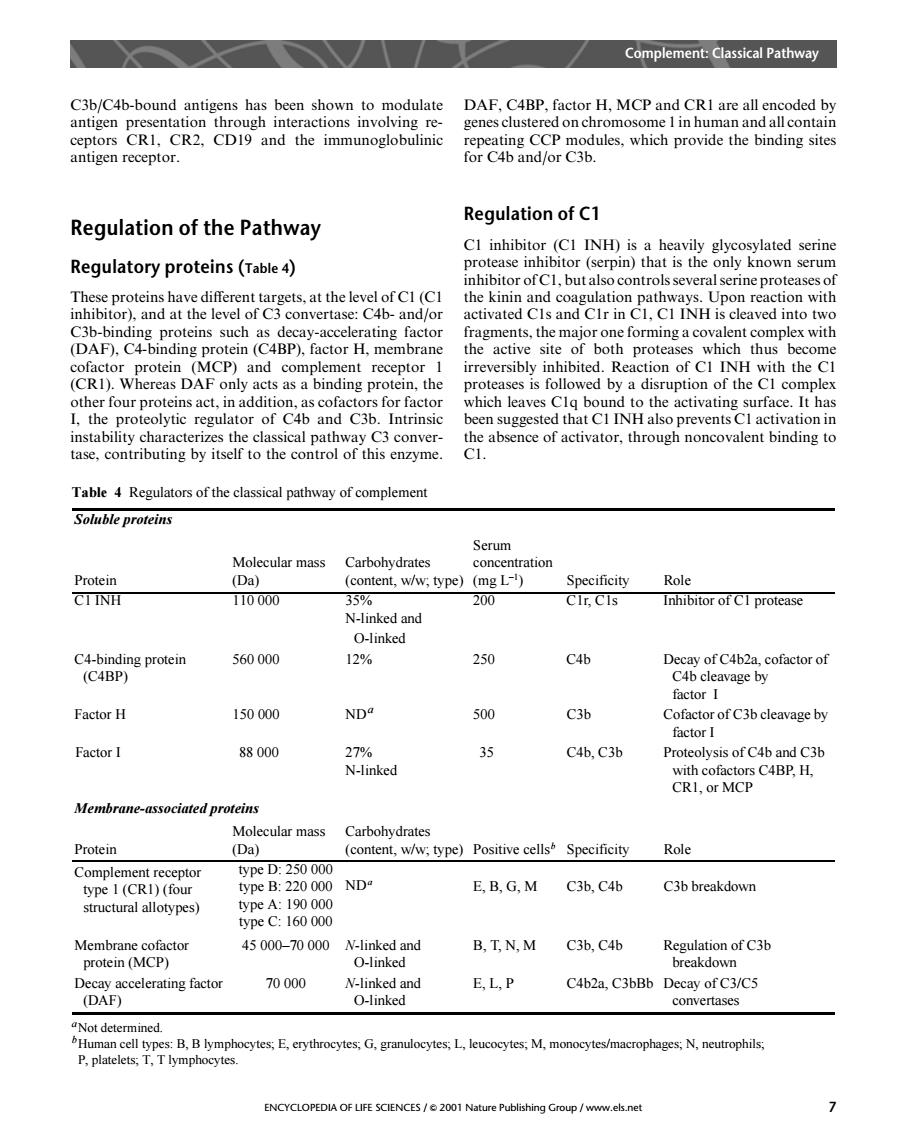
Complement:Classical Pathway C3b/C4b-bound antigens has been shown to modulate DAF,C4BP,factor H.MCP and CRI are all oded ng CCP dules.which r antigen receptor. Regulation of the Pathway Regulation of C1 CI inhibitor (CI INH)is a heavily glycosylated serine Regulatory proteins(Table 4) ease inhibitor(serpin)that is the only known serum itor of Cl,butalso contro ssever serne protease activated Cis and Cir in is cleaved into tw C3b-binding proteins such as decay-accelerating factor fragments,the major one forming a covalent complex with the active site of both proteases whicl thus CP)an bite 0n0 th the C the other four proteins act in addition which leaves Clq bound to the activatir g surface it has I.the proteolytic regulator of C4b and C3b.Intrinsic been suggested that CI INH also prevents Cl activation in instability aract tabsecnceofactinatogthronghnoancoralenlbndingt8 Table 4 Regulators of the classical pathway of complement Soluble proteins Serum Molecular mass Carbohydrates concentration (Da (content,w/w;type)(mg L) Specificity 110000 N-ikedand <00 Inhibitor of CI protease 560000 12% 250 DeipaftCab2acoaciorof vage by Factor H 150000 C3b r of C3b cleavage by 88000 27% 35 C4b,C3b Proteolysis of C4b and C3b N-linked with cofactors C4BP.H. CRI or MCP Membrane-associated proteins Protein Molecular mass (Da) type)Positive cells Specificity Role 250000 eB:220000ND1 E.B,G,M C3b,C4b C3b breakdown ctural alloty pes) ypeA:190000 type C:160000 Membrane cofactor 45 000-70 000 N-linked and B.T.N.M C3b.C4b Regulation of C3b protein (MCP) O-linked breakdown Decay accelerating factor 70000 N-linked and E,L.P C4b2a.C3bBb Decay of C3/C5 (DAF) O-linked convertases P.plateletsT.Tlymphocvtes ocytes,E,erythrocytes,G,granulocytes,L leu ocytes,M,monoeytes/macrophages,N.neutrophils ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES/2001 Nature Publishing Group /www.els.net C3b/C4b-bound antigens has been shown to modulate antigen presentation through interactions involving receptors CR1, CR2, CD19 and the immunoglobulinic antigen receptor. Regulation of the Pathway Regulatory proteins (Table 4) These proteins have different targets, at the level of C1 (C1 inhibitor), and at the level of C3 convertase: C4b- and/or C3b-binding proteins such as decay-accelerating factor (DAF), C4-binding protein (C4BP), factor H, membrane cofactor protein (MCP) and complement receptor 1 (CR1). Whereas DAF only acts as a binding protein, the other four proteins act, in addition, as cofactors for factor I, the proteolytic regulator of C4b and C3b. Intrinsic instability characterizes the classical pathway C3 convertase, contributing by itself to the control of this enzyme. DAF, C4BP, factor H, MCP and CR1 are all encoded by genes clustered on chromosome 1 in human and all contain repeating CCP modules, which provide the binding sites for C4b and/or C3b. Regulation of C1 C1 inhibitor (C1 INH) is a heavily glycosylated serine protease inhibitor (serpin) that is the only known serum inhibitor of C1, but also controls several serine proteases of the kinin and coagulation pathways. Upon reaction with activated C1s and C1r in C1, C1 INH is cleaved into two fragments, the major one forming a covalent complex with the active site of both proteases which thus become irreversibly inhibited. Reaction of C1 INH with the C1 proteases is followed by a disruption of the C1 complex which leaves C1q bound to the activating surface. It has been suggested that C1 INH also prevents C1 activation in the absence of activator, through noncovalent binding to C1. Table 4 Regulators of the classical pathway of complement aNot determined. bHuman cell types: B, B lymphocytes; E, erythrocytes; G, granulocytes; L, leucocytes; M, monocytes/macrophages; N, neutrophils; P, platelets; T, T lymphocytes. Soluble proteins Protein Molecular mass (Da) Carbohydrates (content, w/w; type) Serum concentration (mg L–1 ) Specificity Role C1 INH 110 000 35% N-linked and 200 C1r, C1s Inhibitor of C1 protease O-linked C4-binding protein (C4BP) 560 000 12% 250 C4b Decay of C4b2a, cofactor of C4b cleavage by factor I Factor H 150 000 NDa 500 C3b Cofactor of C3b cleavage by factor I Factor I 88 000 27% N-linked 35 C4b, C3b Proteolysis of C4b and C3b with cofactors C4BP, H, CR1, or MCP Membrane-associated proteins Protein Molecular mass (Da) Carbohydrates (content, w/w; type) Positive cellsb Specificity Role Complement receptor type 1 (CR1) (four structural allotypes) type D: 250 000 type B: 220 000 type A: 190 000 type C: 160 000 NDa E, B, G, M C3b, C4b C3b breakdown Membrane cofactor protein (MCP) 45 000–70 000 N-linked and O-linked B, T, N, M C3b, C4b Regulation of C3b breakdown Decay accelerating factor (DAF) 70 000 N-linked and O-linked E, L, P C4b2a, C3bBb Decay o C3/C5 convertases f Complement: Classical Pathway ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www.els.net 7