正在加载图片...
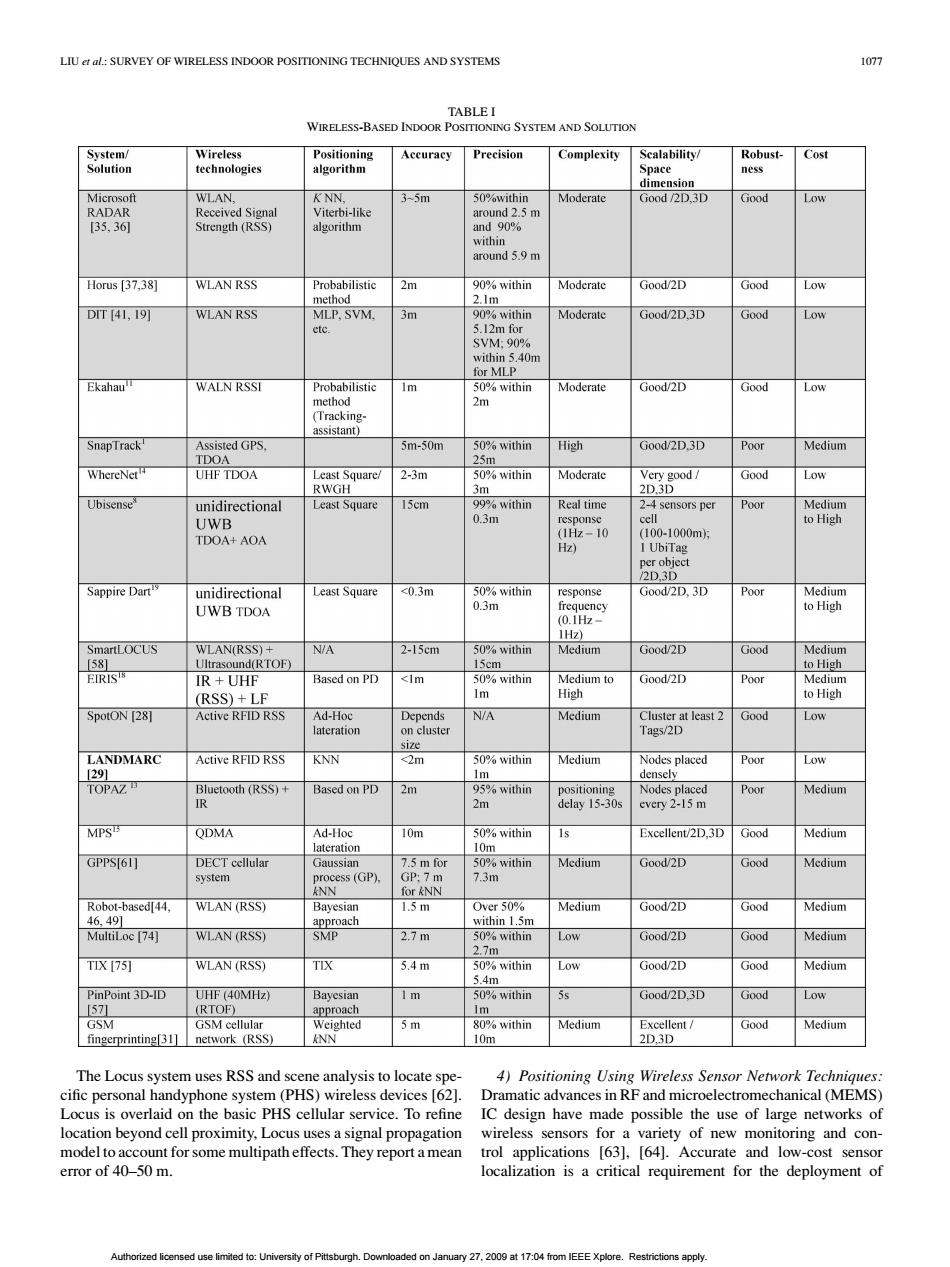
LIU:SURVEY OF WIRELESS INDOOR POSITIONING TECHNIQUES AND SYSTEMS 1077 TABLE I WIRELESS-BASED INDOOR POSITIONING SYSTEM AND SOLUTION System/ Wireless Positioning Accuracy Precision Complexity Scalability/ Robust- Cost Solution technologies algorithm Space ness dimension Microsoft WLAN. K NN, 3-5m 50%within Moderate Good/2D,3D Good Low RADAR Received Signal Viterbi-like around 2.5 m [35,36 Strength (RSS) algorithm and 90% within around 5.9 m Horus [37.38] WLAN RSS Probabilistic 2m 90%within Moderate Good/2D Good Low method 2.1m DT[41,19] WLAN RSS MLP,SVM. 3m 90%within Moderate Good/2D.3D Good Low ctc. 5.12m for SVM:90% within 5.40m for MLP Ekahau WALN RSSI Probabilistic Im 50%within Moderate Good/2D Good Low method 2m (Tracking- assistant) SnapTrack Assisted GPS. 5m-50m 50%within High Good/2D.3D Poor Medium TDOA 25m WhereNet UHF TDOA Least Square/ 2-3m 50%within Moderate Very good/ Good Low RWGH 3m 2D.3D Ubisense unidirectional Least Square 15cm 99%within Real time 2-4 sensors per Poor Medium UWB 0.3m response cell to High (1Hz-10 TDOA+AOA (100-1000m: Hz) I UbiTag per object /2D3D Sappire Dart unidirectional Least Square <0.3m 50%within response Good/2D.3D Poor Medium UWB TDOA 0.3m frequency to High (0.1Hz 1Hz) SmartLOCUS WLAN(RSS)+ N/A 2-15cm 50%within Medium Good/2D Good Medium [581 Ultrasound(RTOF) 15cm to High EIRISTW IR UHF Based on PD <1m 50%within Medium to Good/2D Poor Medium (RSS)+LF 1m High to High SpotON [28] Active RFID RSS Ad-Hoc Depends N/A Medium Cluster at least 2 Good Low lateration on cluster Tags/2D sie LANDMARC Active RFID RSS KNN <2m 50%within Medium Nodes placed Poor Low [291 1m densely TOPAZ Bluetooth (RSS)+ Based on PD 2m 95%within positioning Nodes placed Poor Medium 2m delay 15-30s every 2-15 m MPS QDMA Ad-Hoc 10m 50%within Excellent/2D.3D Good Medium lateration 10m GPPS[61] DECT cellular Gaussian 7.5 m for 50%within Medium Good/2D Good Medium system process (GP). GP:7 m 7.3m ANN for &NN Robot-based[44. WLAN(RSS) Bayesian 1.5m Over 50% Medium Good/2D Good Medium 46.491 approach within 1.5m MultiLoc [74] WLAN(RSS) SMP 2.7m 50%within Low Good/2D Good Medium 2.7m TIX [75] WLAN(RSS) TIX 5.4m 50%within Low Good/2D Good Medium 5.4m PinPoint 3D-ID UHF (40MHz) Bayesian 50%within 5s Good/2D.3D Good Low [571 (RTOF) approach Im GSM GSM cellular Weighted 5m 80%within Medium Excellent Good Medium fingerprinting[31] network (RSS) ANN 10m 2D,3D The Locus system uses RSS and scene analysis to locate spe- 4)Positioning Using Wireless Sensor Network Technigues: cific personal handyphone system(PHS)wireless devices [62]. Dramatic advances in RF and microelectromechanical(MEMS) Locus is overlaid on the basic PHS cellular service.To refine IC design have made possible the use of large networks of location beyond cell proximity,Locus uses a signal propagation wireless sensors for a variety of new monitoring and con- model to account for some multipath effects.They report a mean trol applications [63],[64].Accurate and low-cost sensor error of 40-50 m. localization is a critical requirement for the deployment of Authorized licensed use limited to:University of Pittsburgh.Downloaded on January 27.2009 at 17:04 from IEEE Xplore.Restrictions apply.LIU et al.: SURVEY OF WIRELESS INDOOR POSITIONING TECHNIQUES AND SYSTEMS 1077 TABLE I WIRELESS-BASED INDOOR POSITIONING SYSTEM AND SOLUTION The Locus system uses RSS and scene analysis to locate specific personal handyphone system (PHS) wireless devices [62]. Locus is overlaid on the basic PHS cellular service. To refine location beyond cell proximity, Locus uses a signal propagation model to account for some multipath effects. They report a mean error of 40–50 m. 4) Positioning Using Wireless Sensor Network Techniques: Dramatic advances in RF and microelectromechanical (MEMS) IC design have made possible the use of large networks of wireless sensors for a variety of new monitoring and control applications [63], [64]. Accurate and low-cost sensor localization is a critical requirement for the deployment of Authorized licensed use limited to: University of Pittsburgh. Downloaded on January 27, 2009 at 17:04 from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply