正在加载图片...
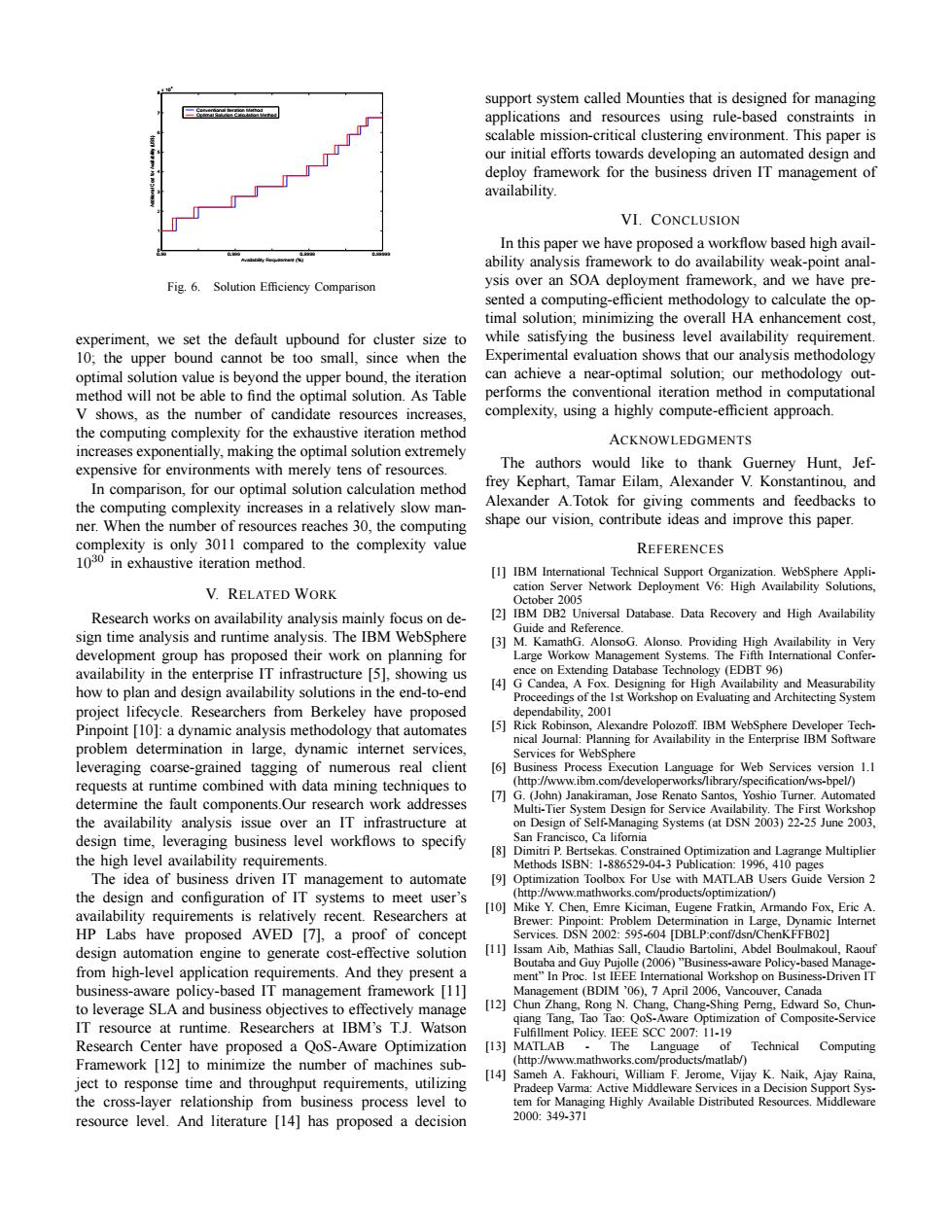
support system called Mounties that is designed for managing applications and resources using rule-based constraints in scalable mission-critical clustering environment.This paper is our initial efforts towards developing an automated design and deploy framework for the business driven IT management of availability VI.CONCLUSION In this paper we have proposed a workflow based high avail- ability analysis framework to do availability weak-point anal- Fig.6.Solution Efficiency Comparison ysis over an SOA deployment framework,and we have pre- sented a computing-efficient methodology to calculate the op- timal solution;minimizing the overall HA enhancement cost. experiment,we set the default upbound for cluster size to while satisfying the business level availability requirement. 10;the upper bound cannot be too small,since when the Experimental evaluation shows that our analysis methodology optimal solution value is beyond the upper bound,the iteration can achieve a near-optimal solution;our methodology out- method will not be able to find the optimal solution.As Table performs the conventional iteration method in computational V shows,as the number of candidate resources increases, complexity,using a highly compute-efficient approach. the computing complexity for the exhaustive iteration method ACKNOWLEDGMENTS increases exponentially,making the optimal solution extremely expensive for environments with merely tens of resources. The authors would like to thank Guerney Hunt.Jef- In comparison,for our optimal solution calculation method frey Kephart,Tamar Eilam,Alexander V.Konstantinou,and the computing complexity increases in a relatively slow man- Alexander A.Totok for giving comments and feedbacks to ner.When the number of resources reaches 30,the computing shape our vision,contribute ideas and improve this paper. complexity is only 3011 compared to the complexity value REFERENCES 1030 in exhaustive iteration method [1]IBM International Technical Support Organization.WebSphere Appli- V.RELATED WORK cation Server Network Deployment V6:High Availability Solutions, October 2005 Research works on availability analysis mainly focus on de- [2]IBM DB2 Universal Database.Data Recovery and High Availability sign time analysis and runtime analysis.The IBM WebSphere Guide and Reference. [3]M.KamathG.AlonsoG.Alonso.Providing High Availability in Very development group has proposed their work on planning for Large Workow Management Systems.The Fifth International Confer- availability in the enterprise IT infrastructure [5],showing us ence on Extending Database Technology (EDBT 96) [4]G Candea,A Fox.Designing for High Availability and Measurability how to plan and design availability solutions in the end-to-end Proceedings of the Ist Workshop on Evaluating and Architecting System project lifecycle.Researchers from Berkeley have proposed dependability,2001 Pinpoint [10]:a dynamic analysis methodology that automates [5]Rick Robinson,Alexandre Polozoff.IBM WebSphere Developer Tech- nical Journal:Planning for Availability in the Enterprise IBM Software problem determination in large,dynamic internet services, Services for WebSphere leveraging coarse-grained tagging of numerous real client [6]Business Process Execution Language for Web Services version 1.1 requests at runtime combined with data mining techniques to (http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/library/specification/ws-bpel/) [7]G.(John)Janakiraman,Jose Renato Santos,Yoshio Turner.Automated determine the fault components.Our research work addresses Multi-Tier System Design for Service Availability.The First Workshop the availability analysis issue over an IT infrastructure at on Design of Self-Managing Systems(at DSN 2003)22-25 June 2003. design time,leveraging business level workflows to specify San Francisco,Ca lifomia the high level availability requirements. [8]Dimitri P.Bertsekas.Constrained Optimization and Lagrange Multiplier Methods ISBN:1-886529-04-3 Publication:1996,410 pages The idea of business driven IT management to automate [9]Optimization Toolbox For Use with MATLAB Users Guide Version 2 the design and configuration of IT systems to meet user's (http://www.mathworks.com/products/optimization/) (10]Mike Y.Chen,Emre Kiciman,Eugene Fratkin,Armando Fox,Eric A. availability requirements is relatively recent.Researchers at Brewer:Pinpoint:Problem Determination in Large,Dynamic Internet HP Labs have proposed AVED [7],a proof of concept Services.DSN 2002:595-604 [DBLP:conf/dsn/ChenKFFB02] design automation engine to generate cost-effective solution [11]Issam Aib,Mathias Sall,Claudio Bartolini,Abdel Boulmakoul,Raouf Boutaba and Guy Pujolle(2006)"Business-aware Policy-based Manage- from high-level application requirements.And they present a ment"In Proc.Ist IEEE Interational Workshop on Business-Driven IT business-aware policy-based IT management framework [11] Management (BDIM '06),7 April 2006,Vancouver,Canada to leverage SLA and business objectives to effectively manage [12]Chun Zhang,Rong N.Chang,Chang-Shing Perng,Edward So,Chun- IT resource at runtime.Researchers at IBM's T.J.Watson qiang Tang,Tao Tao:QoS-Aware Optimization of Composite-Service Fulfillment Policy.IEEE SCC 2007:11-19 Research Center have proposed a QoS-Aware Optimization [13]MATLAB The Language of Technical Computing Framework [12]to minimize the number of machines sub- (http://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab/) ject to response time and throughput requirements,utilizing [14]Sameh A.Fakhouri,William F.Jerome,Vijay K.Naik,Ajay Raina, Pradeep Varma:Active Middleware Services in a Decision Support Sys- the cross-layer relationship from business process level to tem for Managing Highly Available Distributed Resources.Middleware resource level.And literature [14]has proposed a decision 2000:349.3710.99 0.999 0.9999 0.99999 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 x 104 Availability Requirement (%) Additional Cost for Availability (US$) Conventional Iteration Method Optimal Solution Calculation Method Fig. 6. Solution Efficiency Comparison experiment, we set the default upbound for cluster size to 10; the upper bound cannot be too small, since when the optimal solution value is beyond the upper bound, the iteration method will not be able to find the optimal solution. As Table V shows, as the number of candidate resources increases, the computing complexity for the exhaustive iteration method increases exponentially, making the optimal solution extremely expensive for environments with merely tens of resources. In comparison, for our optimal solution calculation method the computing complexity increases in a relatively slow manner. When the number of resources reaches 30, the computing complexity is only 3011 compared to the complexity value 1030 in exhaustive iteration method. V. RELATED WORK Research works on availability analysis mainly focus on design time analysis and runtime analysis. The IBM WebSphere development group has proposed their work on planning for availability in the enterprise IT infrastructure [5], showing us how to plan and design availability solutions in the end-to-end project lifecycle. Researchers from Berkeley have proposed Pinpoint [10]: a dynamic analysis methodology that automates problem determination in large, dynamic internet services, leveraging coarse-grained tagging of numerous real client requests at runtime combined with data mining techniques to determine the fault components.Our research work addresses the availability analysis issue over an IT infrastructure at design time, leveraging business level workflows to specify the high level availability requirements. The idea of business driven IT management to automate the design and configuration of IT systems to meet user’s availability requirements is relatively recent. Researchers at HP Labs have proposed AVED [7], a proof of concept design automation engine to generate cost-effective solution from high-level application requirements. And they present a business-aware policy-based IT management framework [11] to leverage SLA and business objectives to effectively manage IT resource at runtime. Researchers at IBM’s T.J. Watson Research Center have proposed a QoS-Aware Optimization Framework [12] to minimize the number of machines subject to response time and throughput requirements, utilizing the cross-layer relationship from business process level to resource level. And literature [14] has proposed a decision support system called Mounties that is designed for managing applications and resources using rule-based constraints in scalable mission-critical clustering environment. This paper is our initial efforts towards developing an automated design and deploy framework for the business driven IT management of availability. VI. CONCLUSION In this paper we have proposed a workflow based high availability analysis framework to do availability weak-point analysis over an SOA deployment framework, and we have presented a computing-efficient methodology to calculate the optimal solution; minimizing the overall HA enhancement cost, while satisfying the business level availability requirement. Experimental evaluation shows that our analysis methodology can achieve a near-optimal solution; our methodology outperforms the conventional iteration method in computational complexity, using a highly compute-efficient approach. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors would like to thank Guerney Hunt, Jeffrey Kephart, Tamar Eilam, Alexander V. Konstantinou, and Alexander A.Totok for giving comments and feedbacks to shape our vision, contribute ideas and improve this paper. REFERENCES [1] IBM International Technical Support Organization. WebSphere Application Server Network Deployment V6: High Availability Solutions, October 2005 [2] IBM DB2 Universal Database. Data Recovery and High Availability Guide and Reference. [3] M. KamathG. AlonsoG. Alonso. Providing High Availability in Very Large Workow Management Systems. The Fifth International Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT 96) [4] G Candea, A Fox. Designing for High Availability and Measurability Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Evaluating and Architecting System dependability, 2001 [5] Rick Robinson, Alexandre Polozoff. IBM WebSphere Developer Technical Journal: Planning for Availability in the Enterprise IBM Software Services for WebSphere [6] Business Process Execution Language for Web Services version 1.1 (http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/library/specification/ws-bpel/) [7] G. (John) Janakiraman, Jose Renato Santos, Yoshio Turner. Automated Multi-Tier System Design for Service Availability. The First Workshop on Design of Self-Managing Systems (at DSN 2003) 22-25 June 2003, San Francisco, Ca lifornia [8] Dimitri P. Bertsekas. Constrained Optimization and Lagrange Multiplier Methods ISBN: 1-886529-04-3 Publication: 1996, 410 pages [9] Optimization Toolbox For Use with MATLAB Users Guide Version 2 (http://www.mathworks.com/products/optimization/) [10] Mike Y. Chen, Emre Kiciman, Eugene Fratkin, Armando Fox, Eric A. Brewer: Pinpoint: Problem Determination in Large, Dynamic Internet Services. DSN 2002: 595-604 [DBLP:conf/dsn/ChenKFFB02] [11] Issam Aib, Mathias Sall, Claudio Bartolini, Abdel Boulmakoul, Raouf Boutaba and Guy Pujolle (2006) ”Business-aware Policy-based Management” In Proc. 1st IEEE International Workshop on Business-Driven IT Management (BDIM ’06), 7 April 2006, Vancouver, Canada [12] Chun Zhang, Rong N. Chang, Chang-Shing Perng, Edward So, Chunqiang Tang, Tao Tao: QoS-Aware Optimization of Composite-Service Fulfillment Policy. IEEE SCC 2007: 11-19 [13] MATLAB - The Language of Technical Computing (http://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab/) [14] Sameh A. Fakhouri, William F. Jerome, Vijay K. Naik, Ajay Raina, Pradeep Varma: Active Middleware Services in a Decision Support System for Managing Highly Available Distributed Resources. Middleware 2000: 349-371