正在加载图片...
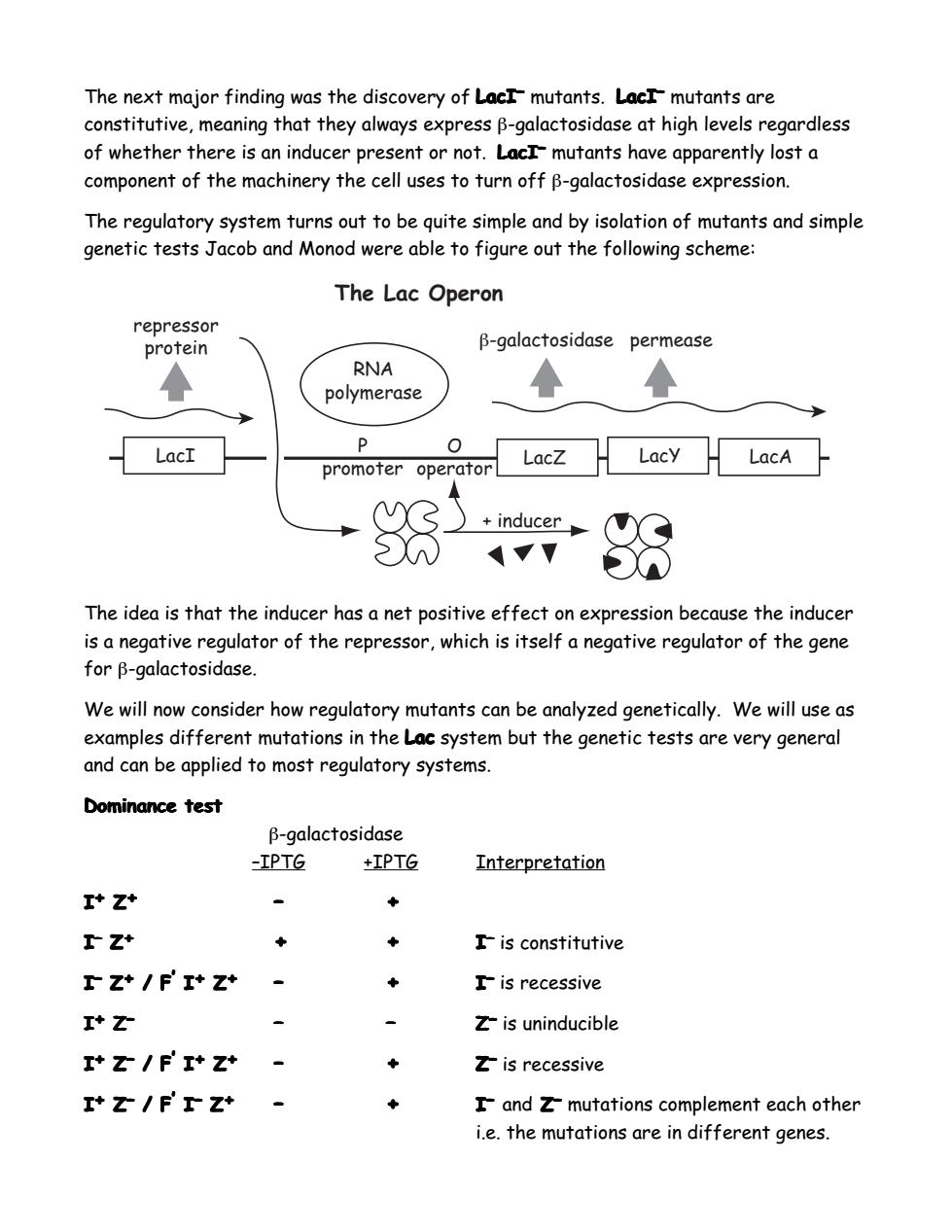
The next major finding was the discovery of LacI mutants.LacI mutants are constitutive,meaning that they always express B-galactosidase at high levels regardless of whether there is an inducer present or not.LacI-mutants have apparently lost a component of the machinery the cell uses to turn off B-galactosidase expression. The regulatory system turns out to be quite simple and by isolation of mutants and simple genetic tests Jacob and Monod were able to figure out the following scheme: The Lac Operon repressor protein B-galactosidase permease RNA polymerase LacI P 0 Lacy promoter operator LacZ LacA inducer The idea is that the inducer has a net positive effect on expression because the inducer is a negative regulator of the repressor,which is itself a negative regulator of the gene forβ-galactosidase. We will now consider how regulatory mutants can be analyzed genetically.We will use as examples different mutations in the Lac system but the genetic tests are very general and can be applied to most regulatory systems. Dominance test β-galactosidase -IPTG +IPTG Interpretation I+Z+ 工Zt Iis constitutive 工Z*/F'I+Z+ Iis recessive I+Z Zis uninducible I'Z/F'I+Z* Zis recessive I Z/F T Z+ Iand Z-mutations complement each other i.e.the mutations are in different genes.The next major finding was the discovery of LacI– mutants. LacI– mutants are constitutive, meaning that they always express β-galactosidase at high levels regardless of whether there is an inducer present or not. LacI– mutants have apparently lost a component of the machinery the cell uses to turn off β-galactosidase expression. The regulatory system turns out to be quite simple and by isolation of mutants and simple genetic tests Jacob and Monod were able to figure out the following scheme: The Lac Operon LacI LacZ LacY LacA P promoter O operator repressor protein β-galactosidase permease + inducer RNA polymerase The idea is that the inducer has a net positive effect on expression because the inducer is a negative regulator of the repressor, which is itself a negative regulator of the gene for β-galactosidase. We will now consider how regulatory mutants can be analyzed genetically. We will use as examples different mutations in the Lac system but the genetic tests are very general and can be applied to most regulatory systems. Dominance test β-galactosidase –IPTG +IPTG Interpretation I+ Z+ – + I– Z+ + + I– Z+/ F’I+Z+ – + I+ Z– – – I+ Z–/ F’I+Z+ – + I+ Z–/ F’I–Z+ – + I– is constitutive I– is recessive Z– is uninducible Z– is recessive I–and Z– mutations complement each other i.e. the mutations are in different genes