正在加载图片...
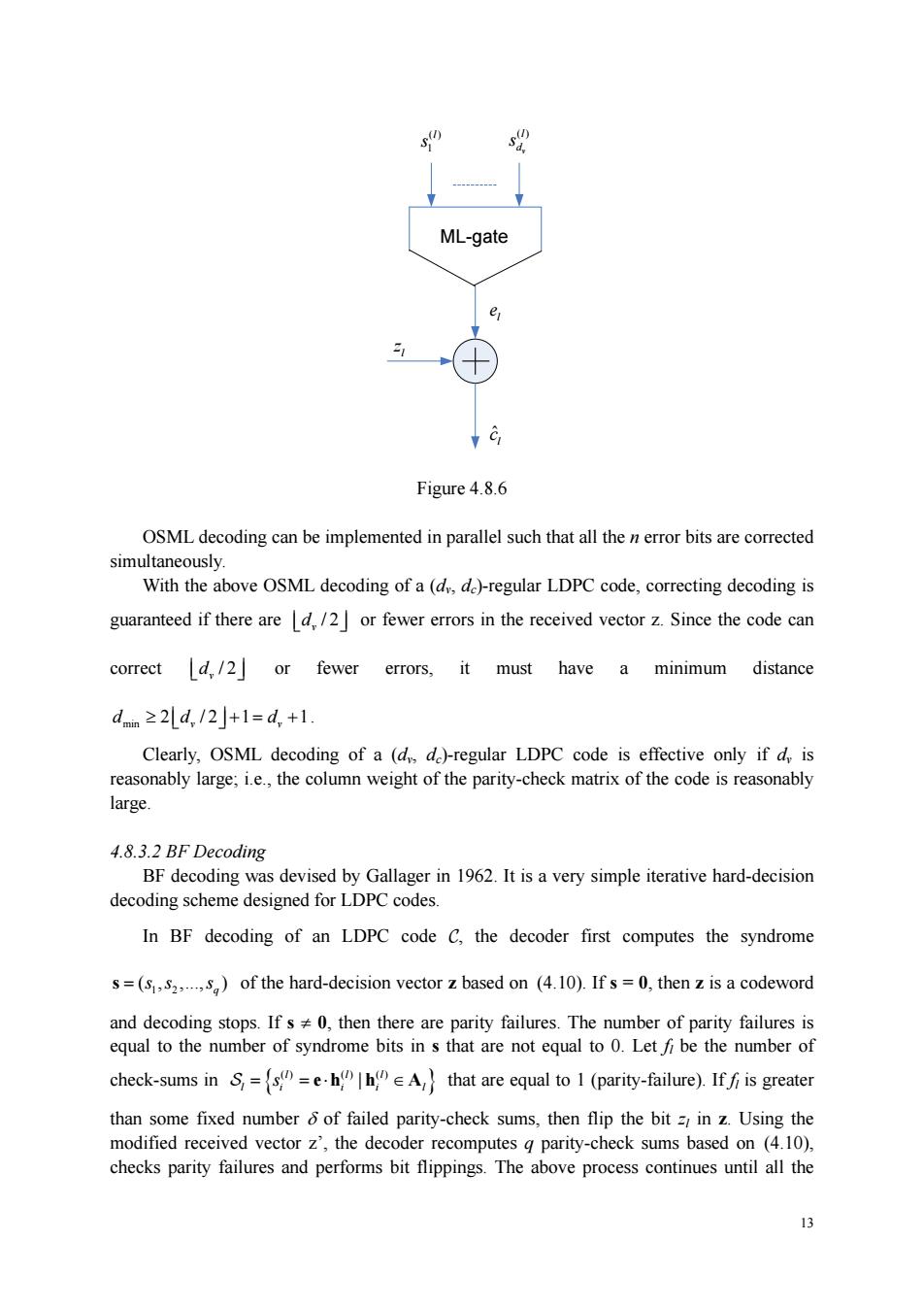
ML-gate Figure 4.8.6 OSML decoding can be implemented in parallel such that all bits are corrected simultaneously. With the above OSML decoding of a(dd)-regular LDPC code,correcting decoding is guaranteed if there ared,/2 or fewer errors in the received vector z.Since the code can correct d,/2]or fewer errors,it must have a minimum distance d≥2Ld,/2j+1=d+1 Clearly,OSML decoding of a (d de)-regular LDPC code is effective only if d,is reasonably large;i.e.,the column weight of the parity-check matrix of the code is reasonably large. 4.8.3.2 BF Decoding BF decoding was devised by Gallager in 1962.It is a very simple iterative hard-decision decoding scheme designed for LDPC codes. In BF decoding of an LDPC code C.the decoder first computes the syndrome s=(s.)of the hard-decision vector z based on (4.10).Ifs=0,then z is a codeword and decoding stops.If s0,then there are parity failures.The number of parity failures is equal to the number of syndrome bits in s that are not equal to 0.Letfi be the number of check-sums in==eA that are equal to 1(parity-failure).If is greater than some fixed number of failed parity-check sums,then flip the bit=in z.Using the modified received vector z',the decoder recomputes g parity-check sums based on (4.10), checks parity failures and performs bit flippings.The above process continues until all the 313 ( ) 1 l s ( ) v l d s ML-gate l z ˆ l c l e Figure 4.8.6 OSML decoding can be implemented in parallel such that all the n error bits are corrected simultaneously. With the above OSML decoding of a (dv, dc)-regular LDPC code, correcting decoding is guaranteed if there are / 2 v ⎢ ⎥ d⎣ ⎦ or fewer errors in the received vector z. Since the code can correct / 2 v ⎢ ⎥ d⎣ ⎦ or fewer errors, it must have a minimum distance min 2 /2 1 1 v v dd d ≥ += + ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ ⎦ . Clearly, OSML decoding of a (dv, dc)-regular LDPC code is effective only if dv is reasonably large; i.e., the column weight of the parity-check matrix of the code is reasonably large. 4.8.3.2 BF Decoding BF decoding was devised by Gallager in 1962. It is a very simple iterative hard-decision decoding scheme designed for LDPC codes. In BF decoding of an LDPC code C, the decoder first computes the syndrome 1 2 ( , ,., ) q s = ss s of the hard-decision vector z based on (4.10). If s = 0, then z is a codeword and decoding stops. If s ≠ 0, then there are parity failures. The number of parity failures is equal to the number of syndrome bits in s that are not equal to 0. Let fl be the number of check-sums in { } () () () | l ll l i ii l S = =⋅ ∈ s eh h A that are equal to 1 (parity-failure). If fl is greater than some fixed number δ of failed parity-check sums, then flip the bit zl in z. Using the modified received vector z’, the decoder recomputes q parity-check sums based on (4.10), checks parity failures and performs bit flippings. The above process continues until all the