正在加载图片...
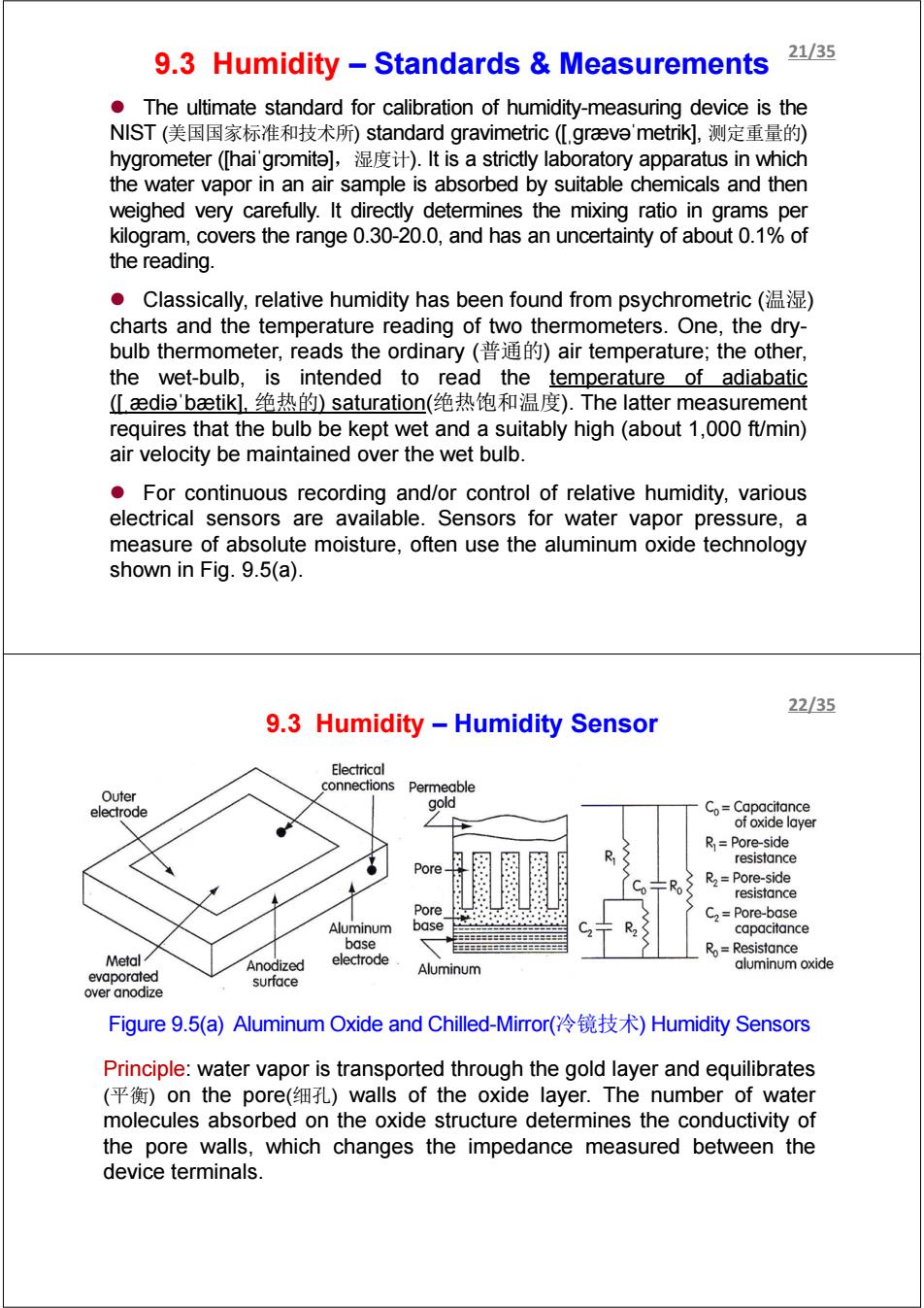
9.3 Humidity Standards Measurements 21/35 The ultimate standard for calibration of humidity-measuring device is the NIST(美国国家标准和技术所)standard gravimetric(L,graeva'metrik],测定重量的) hygrometer([hai'gromite],).It is a strictly laboratory apparatus in which the water vapor in an air sample is absorbed by suitable chemicals and then weighed very carefully.It directly determines the mixing ratio in grams per kilogram,covers the range 0.30-20.0,and has an uncertainty of about 0.1%of the reading. Classically,relative humidity has been found from psychrometric ( charts and the temperature reading of two thermometers.One,the dry- bulb thermometer,reads the ordinary air temperature;the other, the wet-bulb,is intended to read the temperature of adiabatic (Ldie'baetik].绝热的)saturation(绝热饱和温度).The latter measurement requires that the bulb be kept wet and a suitably high(about 1,000 ft/min) air velocity be maintained over the wet bulb. For continuous recording and/or control of relative humidity,various electrical sensors are available.Sensors for water vapor pressure,a measure of absolute moisture,often use the aluminum oxide technology shown in Fig.9.5(a). 22/35 9.3 Humidity -Humidity Sensor Electrical connections Permeable Outer gold electrode Co=Capacitance of oxide layer R=Pore-side resistance Pore R2=Pore-side resistance Pore C2=Pore-base Aluminum base capacitance base Ro=Resistance Metal Anodized electrode evaporated Aluminum aluminum oxide surface over anodize Figure9.5(a)Aluminum Oxide and Chilled-Mirror(冷镜技术)Humidity Sensors Principle:water vapor is transported through the gold layer and equilibrates (平衡)on the pore(细孔)walls of the oxide layer..The number of water molecules absorbed on the oxide structure determines the conductivity of the pore walls,which changes the impedance measured between the device terminals.z The ultimate standard for calibration of humidity-measuring device is the NIST (美国国家标准和技术所) standard gravimetric ([ˌgrævəˈmetrik], 测定重量的) hygrometer ([haiˈgrɔmitə],湿度计). It is a strictly laboratory apparatus in which the water vapor in an air sample is absorbed by suitable chemicals and then weighed very carefully. It directly determines the mixing ratio in grams per kilogram, covers the range 0.30-20.0, and has an uncertainty of about 0.1% of the reading. z Classically, relative humidity has been found from psychrometric (温湿) charts and the temperature reading of two thermometers. One, the drybulb thermometer, reads the ordinary (普通的) air temperature; the other, the wet-bulb, is intended to read the temperature of adiabatic ([ˌædiəˈbætik], 绝热的) saturation(绝热饱和温度). The latter measurement requires that the bulb be kept wet and a suitably high (about 1,000 ft/min) air velocity be maintained over the wet bulb. z For continuous recording and/or control of relative humidity, various electrical sensors are available. Sensors for water vapor pressure, a measure of absolute moisture, often use the aluminum oxide technology shown in Fig. 9.5(a). 9.3 Humidity – Standards & Measurements 21/35 9.3 Humidity – Humidity Sensor Figure 9.5(a) Aluminum Oxide and Chilled-Mirror(冷镜技术) Humidity Sensors Principle: water vapor is transported through the gold layer and equilibrates (平衡) on the pore(细孔) walls of the oxide layer. The number of water molecules absorbed on the oxide structure determines the conductivity of the pore walls, which changes the impedance measured between the device terminals. 22/35