正在加载图片...
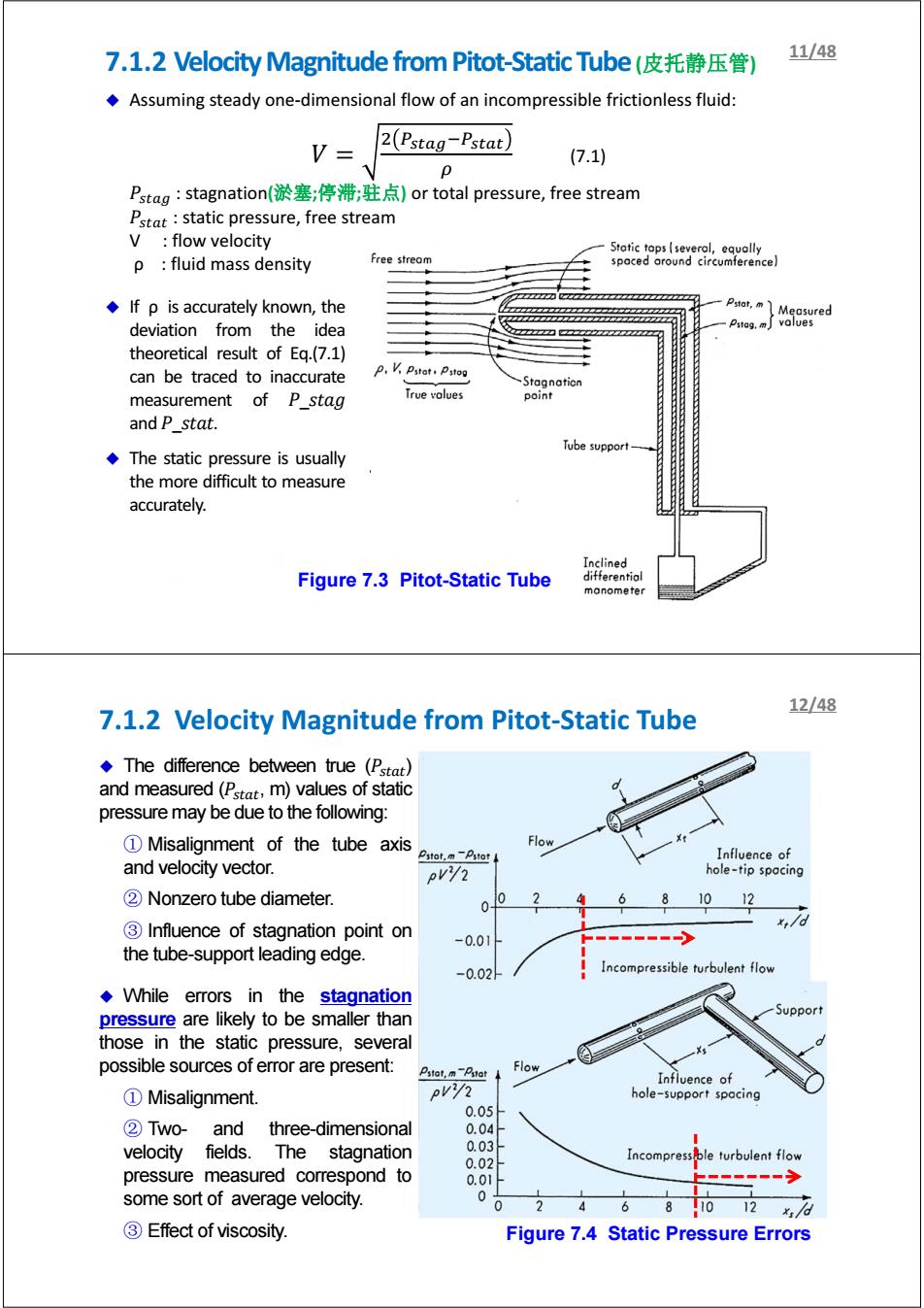
7.l.2 Velocity Magnitude from Pitot-Static Tube(皮托静压管) 11/48 Assuming steady one-dimensional flow of an incompressible frictionless fluid: V= Pstag-Pstat (7.1) P Pstag:stagnation(淤塞;停滞;驻点)or total pressure,free stream Pstat:static pressure,free stream V:flow velocity Static tops(several,equally p fluid mass density Free streom spaced around circumference) If p is accurately known,the Pstat,m Measured deviation from the idea Pstag.m values theoretical result of Eq.(7.1) can be traced to inaccurate p.V Pstot Psto Stagnaticn measurement of P_stag True values point and Pstat. Tube support-一 The static pressure is usually the more difficult to measure accurately. Inclined Figure 7.3 Pitot-Static Tube differential manometer 12/48 7.1.2 Velocity Magnitude from Pitot-Static Tube The difference between true (Pstat) and measured(Pstat,m)values of static pressure may be due to the following: 1 Misalignment of the tube axis Flow Pstot,mPstot Influence of and velocity vector. pVy2 hole-tip spacing 2 Nonzero tube diameter. 0 1012 3 Influence of stagnation point on -0.0 the tube-support leading edge. -0.02 Incompressible turbulent flow While errors in the stagnation pressure are likely to be smaller than Support those in the static pressure,several possible sources of error are present: Pstat,m Pstat Flow Influence of ①Misalignment. PVY hole-support spacing 0.05 2 Two-and three-dimensional 0.04 velocity fields.The stagnation 0.03 0.02 Incompress ble turbulent flow pressure measured correspond to 0.01 ■一=一。》 some sort of average velocity. 0 0 6 8 0 12名8 ③Effect of viscosity.. Figure 7.4 Static Pressure Errors Assuming steady one-dimensional flow of an incompressible frictionless fluid: ܸ ൌ ଶ ೞೌିೞೌ ఘ (7.1) ܲ௦௧ : stagnation(淤塞;停滞;驻点) or total pressure, free stream ܲ௦௧௧ : static pressure, free stream V : flow velocity ρ : fluid mass density Figure 7.3 Pitot-Static Tube If ρ is accurately known, the deviation from the idea theoretical result of Eq.(7.1) can be traced to inaccurate measurement of ܲ_ݐݏ݃ܽ .ݐܽݐݏ_ܲ and The static pressure is usually the more difficult to measure accurately. 7.1.2 Velocity Magnitude from Pitot-Static Tube(皮托静压管) Figure 7.3 Pitot-Static Tube 11/48 The difference between true (ܲ௦௧௧) and measured (ܲ௦௧௧, m) values of static pressure may be due to the following: ① Misalignment of the tube axis and velocity vector. ② Nonzero tube diameter. ③ Influence of stagnation point on the tube-support leading edge. While errors in the stagnation pressure are likely to be smaller than those in the static pressure, several possible sources of error are present: ① Misalignment. ② Two- and three-dimensional velocity fields. The stagnation pressure measured correspond to some sort of average velocity. ③ Effect of viscosity. 7.1.2 Velocity Magnitude from Pitot-Static Tube Figure 7.4 Static Pressure Errors 12/48