正在加载图片...
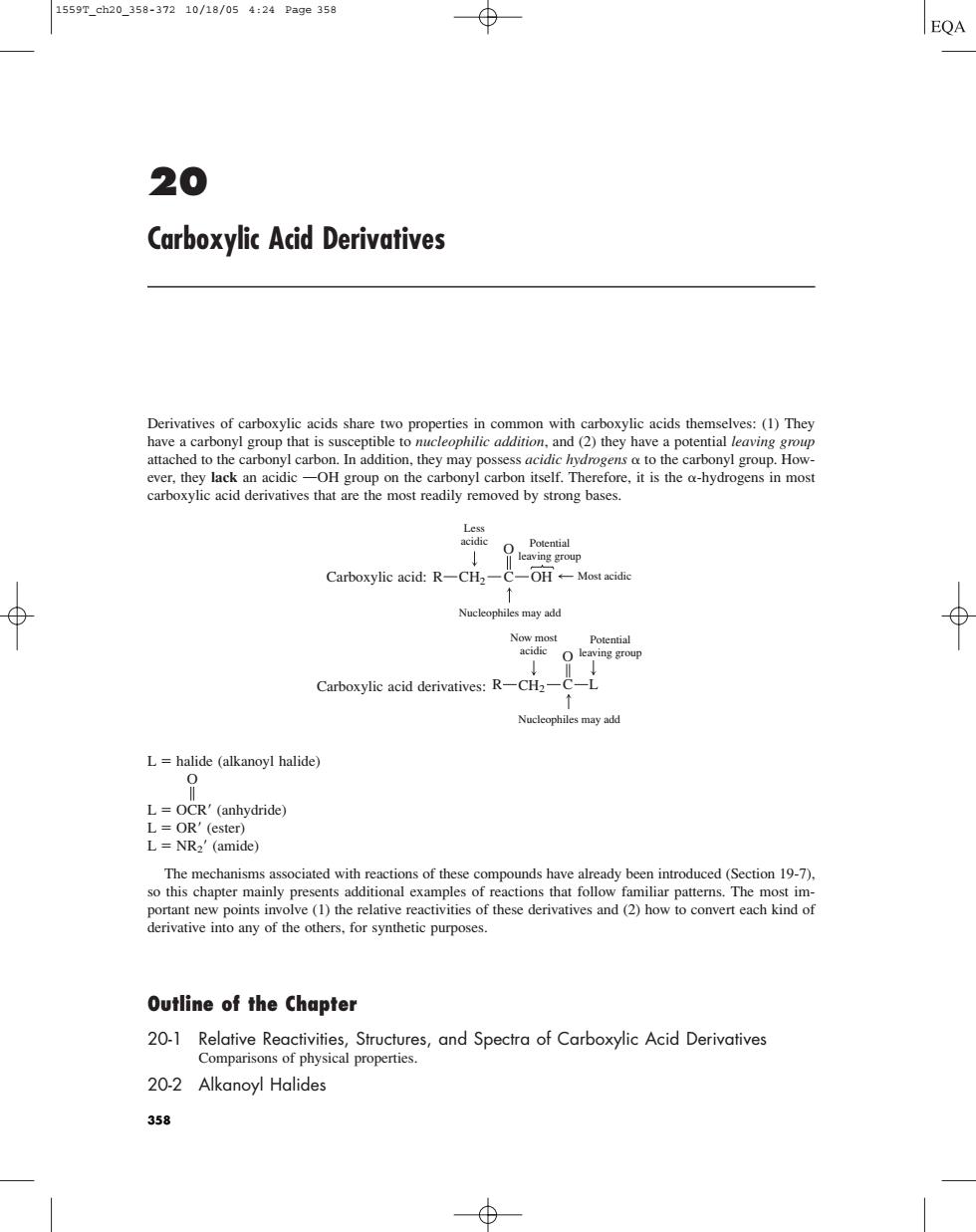
15597ch20.358-37210/18/054:24Page358 EQA 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives the carbonyl carbon itself.Therefore.it is the ahydrogens in most ed by strong bases Carboxylic acid:R-CH2-C-OH+-Most acidie Nucleophiles may add Carboxylic acid derivatives:R-CH2-( Nucleophiles may add L=halide (alkanoyl halide) L=OCR'(anhydride) =OR' L=NR2'(amide) bortant new pointsin derivative into any of the others.for synthetic purposes. Outline of the Chapter 20-2 Alkanoyl Halides 35820 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Derivatives of carboxylic acids share two properties in common with carboxylic acids themselves: (1) They have a carbonyl group that is susceptible to nucleophilic addition, and (2) they have a potential leaving group attached to the carbonyl carbon. In addition, they may possess acidic hydrogens to the carbonyl group. However, they lack an acidic OOH group on the carbonyl carbon itself. Therefore, it is the -hydrogens in most carboxylic acid derivatives that are the most readily removed by strong bases. Carboxylic acid: Carboxylic acid derivatives: L halide (alkanoyl halide) O B L OCR (anhydride) L OR (ester) L NR2 (amide) The mechanisms associated with reactions of these compounds have already been introduced (Section 19-7), so this chapter mainly presents additional examples of reactions that follow familiar patterns. The most important new points involve (1) the relative reactivities of these derivatives and (2) how to convert each kind of derivative into any of the others, for synthetic purposes. Outline of the Chapter 20-1 Relative Reactivities, Structures, and Spectra of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Comparisons of physical properties. 20-2 Alkanoyl Halides R C L O Now most acidic Potential leaving group Nucleophiles may add CH2 R C OH O Less acidic Potential leaving group Most acidic Nucleophiles may add CH2 358 1559T_ch20_358-372 10/18/05 4:24 Page 358�������