正在加载图片...
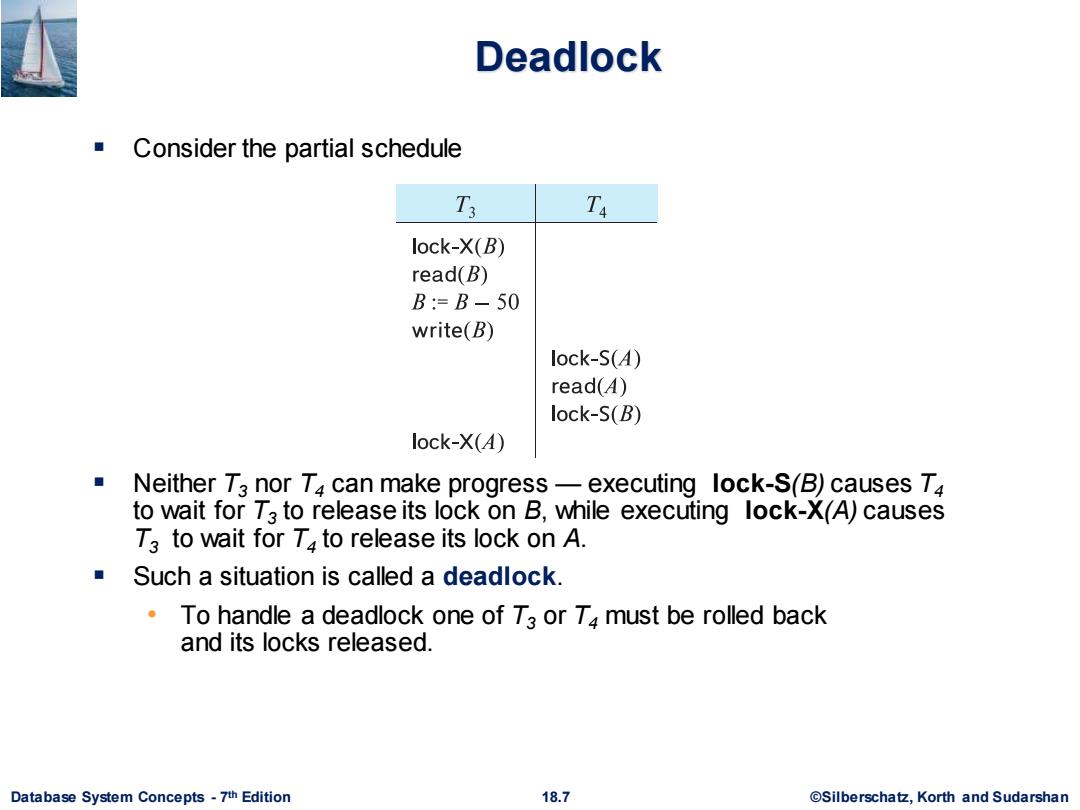
Deadlock Consider the partial schedule T3 Ta lock-X(B) read(B) B:=B-50 write(B) lock-S(A) read() lock-S(B) lock-X(4) ■ Neither T3 nor T4 can make progress-executing lock-S(B)causes T4 to wait for T3 to release its lock on B,while executing lock-X(A)causes T3 to wait for Ta to release its lock on A. Such a situation is called a deadlock. To handle a deadlock one of T3 or T4 must be rolled back and its locks released. Database System Concepts-7th Edition 18.7 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and SudarshanDatabase System Concepts - 7 18.7 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Deadlock ▪ Consider the partial schedule ▪ Neither T3 nor T4 can make progress — executing lock-S(B) causes T4 to wait for T3 to release its lock on B, while executing lock-X(A) causes T3 to wait for T4 to release its lock on A. ▪ Such a situation is called a deadlock. • To handle a deadlock one of T3 or T4 must be rolled back and its locks released