正在加载图片...
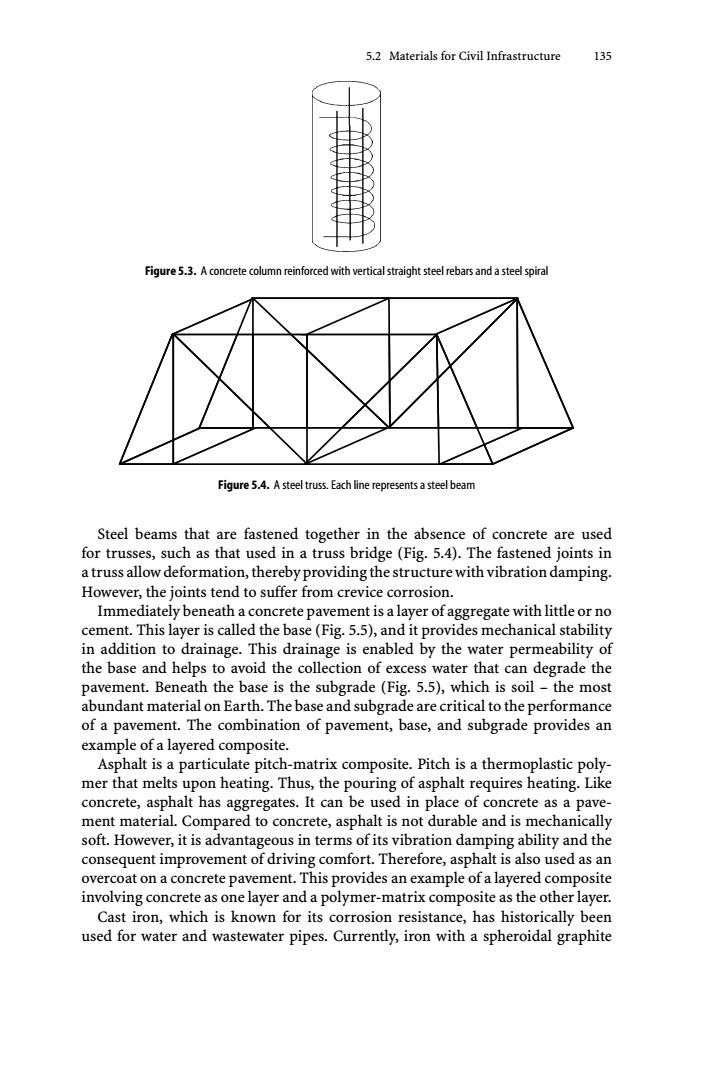
5.2 Materials for Civil Infrastructure 135 Figure 5.3.A concrete column reinforced with vertical straight steel rebars and a steel spiral Figure 5.4.A steel truss.Each line represents a steel beam Steel beams that are fastened together in the absence of concrete are used for trusses,such as that used in a truss bridge(Fig.5.4).The fastened joints in a truss allow deformation,thereby providing the structure with vibration damping. However,the joints tend to suffer from crevice corrosion. Immediately beneath a concrete pavement is a layer of aggregate with little or no cement.This layer is called the base(Fig.5.5),and it provides mechanical stability in addition to drainage.This drainage is enabled by the water permeability of the base and helps to avoid the collection of excess water that can degrade the pavement.Beneath the base is the subgrade (Fig.5.5),which is soil-the most abundant material on Earth.The base and subgrade are critical to the performance of a pavement.The combination of pavement,base,and subgrade provides an example of a layered composite. Asphalt is a particulate pitch-matrix composite.Pitch is a thermoplastic poly- mer that melts upon heating.Thus,the pouring of asphalt requires heating.Like concrete,asphalt has aggregates.It can be used in place of concrete as a pave- ment material.Compared to concrete,asphalt is not durable and is mechanically soft.However,it is advantageous in terms of its vibration damping ability and the consequent improvement of driving comfort.Therefore,asphalt is also used as an overcoat on a concrete pavement.This provides an example of a layered composite involving concrete as one layer and a polymer-matrix composite as the other layer. Cast iron,which is known for its corrosion resistance,has historically been used for water and wastewater pipes.Currently,iron with a spheroidal graphite5.2 Materials for Civil Infrastructure 135 Figure 5.3. A concrete column reinforced with vertical straight steel rebars and a steel spiral Figure 5.4. A steel truss. Each line represents a steel beam Steel beams that are fastened together in the absence of concrete are used for trusses, such as that used in a truss bridge (Fig. 5.4). The fastened joints in a truss allow deformation, thereby providing the structure with vibration damping. However, the joints tend to suffer from crevice corrosion. Immediately beneath a concrete pavement is a layer of aggregate with little or no cement. This layer is called the base (Fig. 5.5), and it provides mechanical stability in addition to drainage. This drainage is enabled by the water permeability of the base and helps to avoid the collection of excess water that can degrade the pavement. Beneath the base is the subgrade (Fig. 5.5), which is soil – the most abundant material on Earth. The base and subgrade are critical to the performance of a pavement. The combination of pavement, base, and subgrade provides an example of a layered composite. Asphalt is a particulate pitch-matrix composite. Pitch is a thermoplastic polymer that melts upon heating. Thus, the pouring of asphalt requires heating. Like concrete, asphalt has aggregates. It can be used in place of concrete as a pavement material. Compared to concrete, asphalt is not durable and is mechanically soft. However, it is advantageous in terms of its vibration damping ability and the consequent improvement of driving comfort. Therefore, asphalt is also used as an overcoat on a concrete pavement. This provides an example of a layered composite involving concrete as one layer and a polymer-matrix composite as the other layer. Cast iron, which is known for its corrosion resistance, has historically been used for water and wastewater pipes. Currently, iron with a spheroidal graphite