正在加载图片...
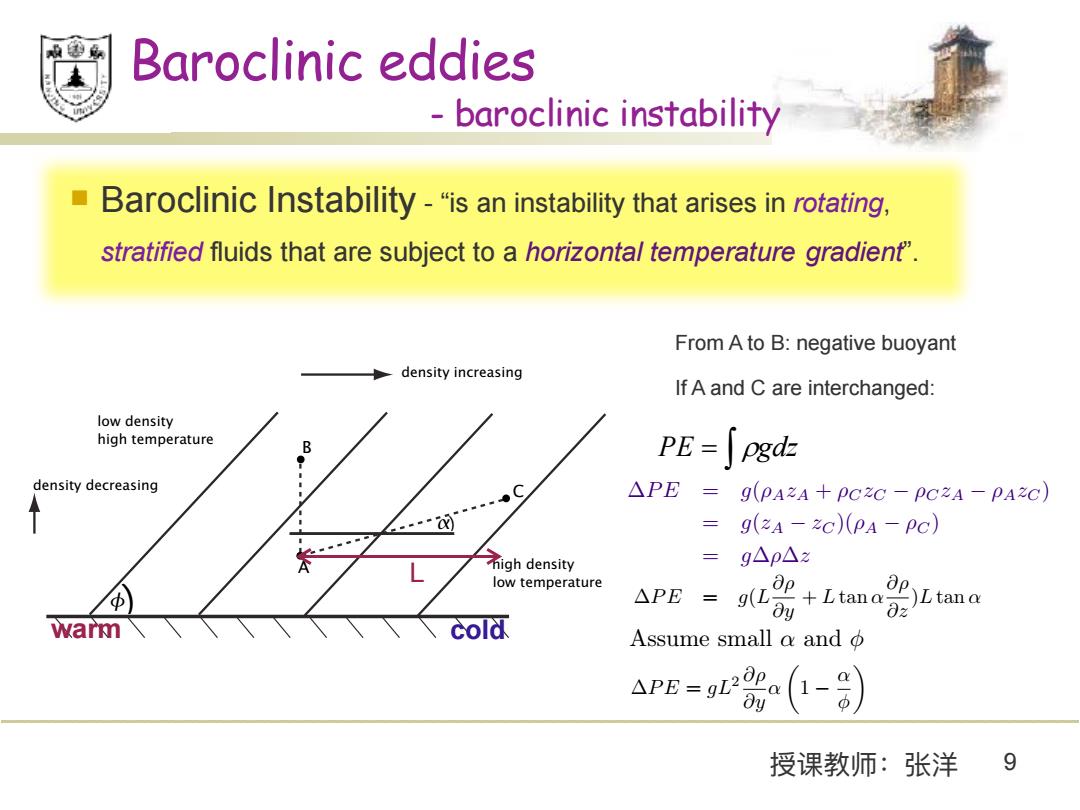
Baroclinic eddies baroclinic instability Baroclinic Instability-"is an instability that arises in rotating, stratified fluids that are subject to a horizontal temperature gradient". From A to B:negative buoyant density increasing If A and C are interchanged: low density high temperature PE=∫pgdE density decreasing △PE g(PAZA+PCZC-PCZA-PAZC) = g(zA-ZC)(PA-PC) igh density =g△p△z low temperature △PE = +Ltan g(Lau Ltana 8z warm cold Assume small a andφ APE-9a (1-9 授课教师:张洋 9P E = g(L@⇢ @y + Ltan ↵ @⇢ @z )Ltan ↵ Assume small ↵ and P E = gL2 @⇢ @y ↵ ✓ 1 ↵ ◆ 授课教师:张洋 9 Baroclinic eddies - baroclinic instability n Baroclinic Instability - “is an instability that arises in rotating, stratified fluids that are subject to a horizontal temperature gradient”. i i i i i i i i ) ) ⇥ A B C high density low density low temperature high temperature density increasing density decreasing Fig. 6.9 A steady basic state giving rise to baroclinic instability. Potential density decreases upwards and equatorwards, and the associated horizontal pressure gradient is balanced by the Coriolis force. Parcel ‘A’ is heavier than ‘C’, and so statically stable, but it is lighter than ‘B’. Hence, if ‘A’ and ‘B’ are interchanged there is a release of potential energy. From Vallis (2006) From Vallis (2006) warm cold From A to B: negative buoyant If A and C are interchanged: y fu
b z
0 b g y b z u
v w 0 S N X X X X X PE gdz PE g z z z z gz z g z A A B B A B B A A B A B
1 2 y L gL z L y PE g z g L P E = g(⇢AzA + ⇢C zC ⇢C zA ⇢AzC ) = g(zA zC )(⇢A ⇢C ) = g⇢z L�����