正在加载图片...
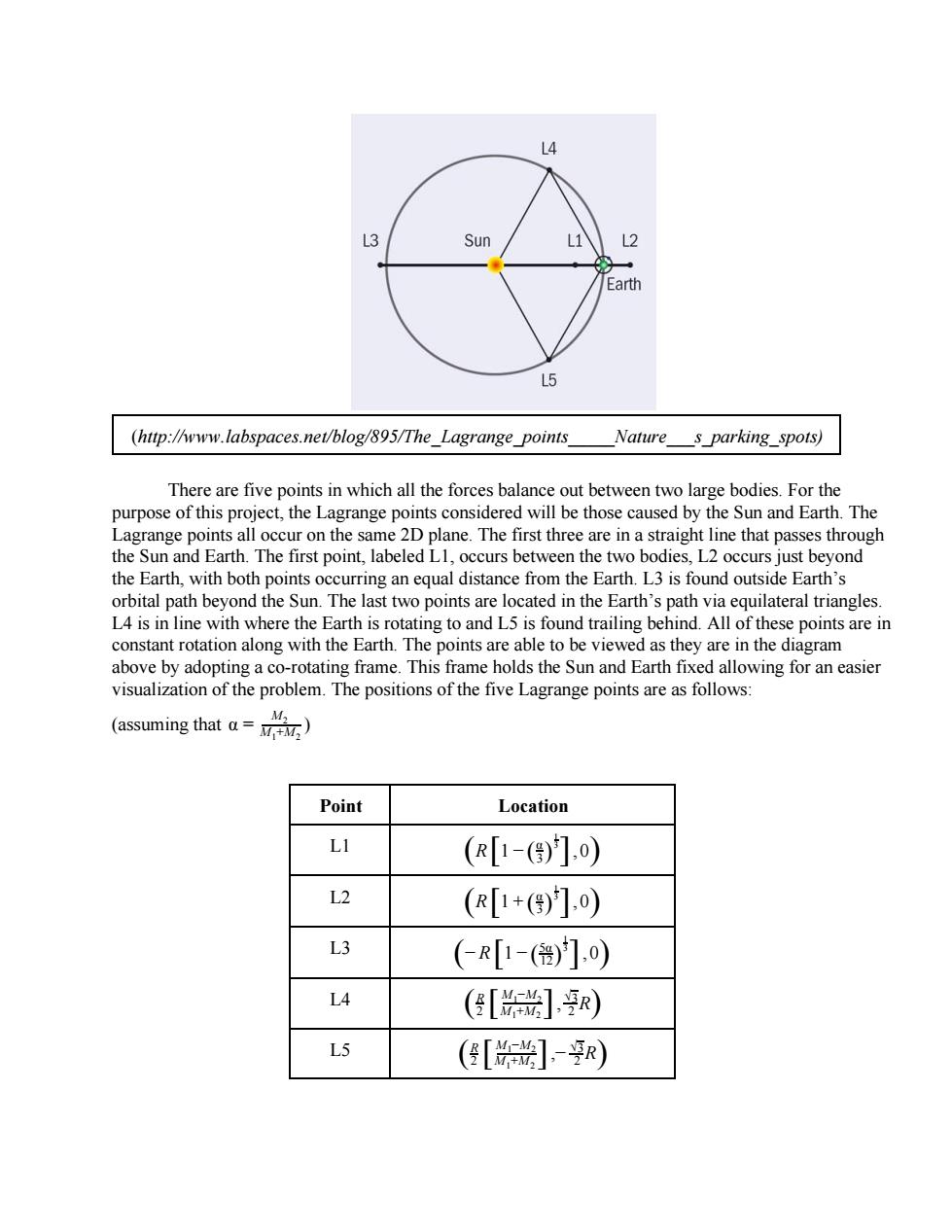
14 L3 Sun L1 L2 Earth L5 (http://www.labspaces.net/blog/895/The_Lagrange_points Nature s parking_spots) There are five points in which all the forces balance out between two large bodies.For the purpose of this project,the Lagrange points considered will be those caused by the Sun and Earth.The Lagrange points all occur on the same 2D plane.The first three are in a straight line that passes through the Sun and Earth.The first point,labeled L1,occurs between the two bodies,L2 occurs just beyond the Earth,with both points occurring an equal distance from the Earth.L3 is found outside Earth's orbital path beyond the Sun.The last two points are located in the Earth's path via equilateral triangles. L4 is in line with where the Earth is rotating to and L5 is found trailing behind.All of these points are in constant rotation along with the Earth.The points are able to be viewed as they are in the diagram above by adopting a co-rotating frame.This frame holds the Sun and Earth fixed allowing for an easier visualization of the problem.The positions of the five Lagrange points are as follows: ((uming that=0) Point Location LI (R1-()],) L2 (R[1+()门,0) L3 (R[1-(ě)],) L4 ([*]r) L5 ([*]-r)(http://www.labspaces.net/blog/895/The_Lagrange_points_____Nature___s_parking_spots) There are five points in which all the forces balance out between two large bodies. For the purpose of this project, the Lagrange points considered will be those caused by the Sun and Earth. The Lagrange points all occur on the same 2D plane. The first three are in a straight line that passes through the Sun and Earth. The first point, labeled L1, occurs between the two bodies, L2 occurs just beyond the Earth, with both points occurring an equal distance from the Earth. L3 is found outside Earth’s orbital path beyond the Sun. The last two points are located in the Earth’s path via equilateral triangles. L4 is in line with where the Earth is rotating to and L5 is found trailing behind. All of these points are in constant rotation along with the Earth. The points are able to be viewed as they are in the diagram above by adopting a corotating frame. This frame holds the Sun and Earth fixed allowing for an easier visualization of the problem. The positions of the five Lagrange points are as follows: (assuming that α = ) M2 M1+M2 Point Location L1 (R[1 − (3 α ) 3 1 ],0) L2 (R[1 + (3 α ) 3 1 ],0) L3 (− R[1 − (12 5α ) 3 1 ], 0) L4 ( R 2 R [M1+M2 M1−M2 ], 2 √3 ) L5 ( − R 2 R [M1+M2 M1−M2 ], 2 √3 )