正在加载图片...
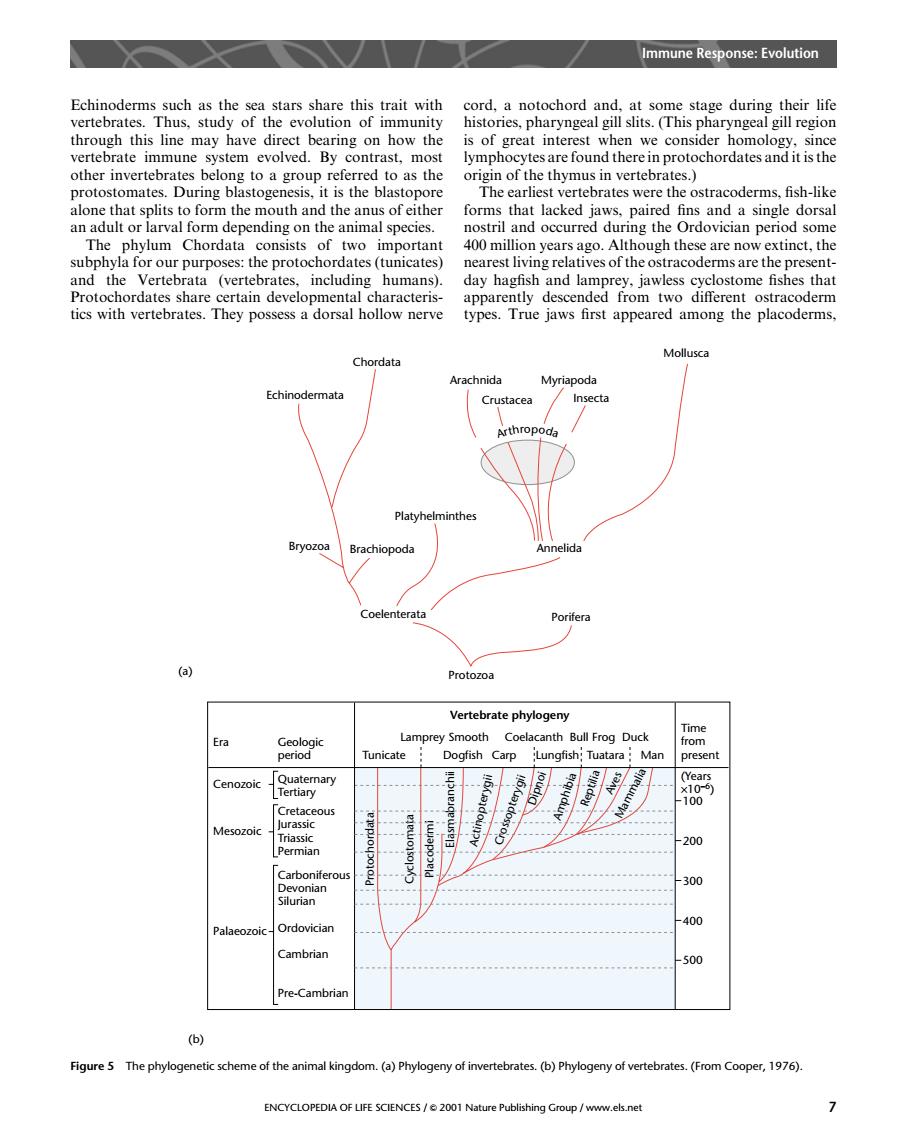
Immune Response:Evolution Echinode the sea stars share this trait with gh this lin how the of at in vertebrate immune system evolved.By contrast.most lymphocytes are found there in protochordates and it is the origin of the thymus in vertebrates.) mat stog the ebrates were tracoderms,fish-lik th an adult or larval form depending on the anim The phylum Chordata consists of two important 400 million years ago.Although these are now extinct,the subphyla for our purposes:the protochordates(tunicates) nearest living relatives of the ostracoderms are the present- including humans) Mollusca Chordata Arachnida Platyhelminthes Vertebrate phygeny Lamprey Smoo anth Bull Frog Duck 20 400 0z0 Cambrian -500 Pre-Cambrian (b) Figure5 The phylogenetic schemeof the animal kingdom.(a)Phylogeny of invertebrates (b)Phylogeny of vertebrates.(FromCooper,17) ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES/2001 Nature Publishing Group/www.els.net 7 Echinoderms such as the sea stars share this trait with vertebrates. Thus, study of the evolution of immunity through this line may have direct bearing on how the vertebrate immune system evolved. By contrast, most other invertebrates belong to a group referred to as the protostomates. During blastogenesis, it is the blastopore alone that splits to form the mouth and the anus of either an adult or larval form depending on the animal species. The phylum Chordata consists of two important subphyla for our purposes: the protochordates (tunicates) and the Vertebrata (vertebrates, including humans). Protochordates share certain developmental characteristics with vertebrates. They possess a dorsal hollow nerve cord, a notochord and, at some stage during their life histories, pharyngeal gill slits. (This pharyngeal gill region is of great interest when we consider homology, since lymphocytes are found there in protochordates and it is the origin of the thymus in vertebrates.) The earliest vertebrates were the ostracoderms, fish-like forms that lacked jaws, paired fins and a single dorsal nostril and occurred during the Ordovician period some 400 million years ago. Although these are now extinct, the nearest living relatives of the ostracoderms are the presentday hagfish and lamprey, jawless cyclostome fishes that apparently descended from two different ostracoderm types. True jaws first appeared among the placoderms, Arthropoda Arachnida Crustacea Myriapoda Insecta Mollusca Annelida Platyhelminthes Coelenterata Porifera Bryozoa Brachiopoda Echinodermata Chordata Protozoa Protochordata Cyclostomata Placodermi Elasmabranchii Actinopterygii Crossopterygii Dipnoi Amphibia Reptilia Aves Mammalia Cenozoic Quaternary Tertiary Mesozoic Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Palaeozoic Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Ordovician Cambrian Pre-Cambrian Era Geologic period Tunicate Dogfish Carp Lungfish Tuatara Man Lamprey Smooth Coelacanth Bull Frog Duck Time from present (Years ×10–6) 100 200 300 400 500 (a) (b) Vertebrate phylogeny Figure 5 The phylogenetic scheme of the animal kingdom. (a) Phylogeny of invertebrates. (b) Phylogeny of vertebrates. (From Cooper, 1976). Immune Response: Evolution ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www.els.net 7