正在加载图片...
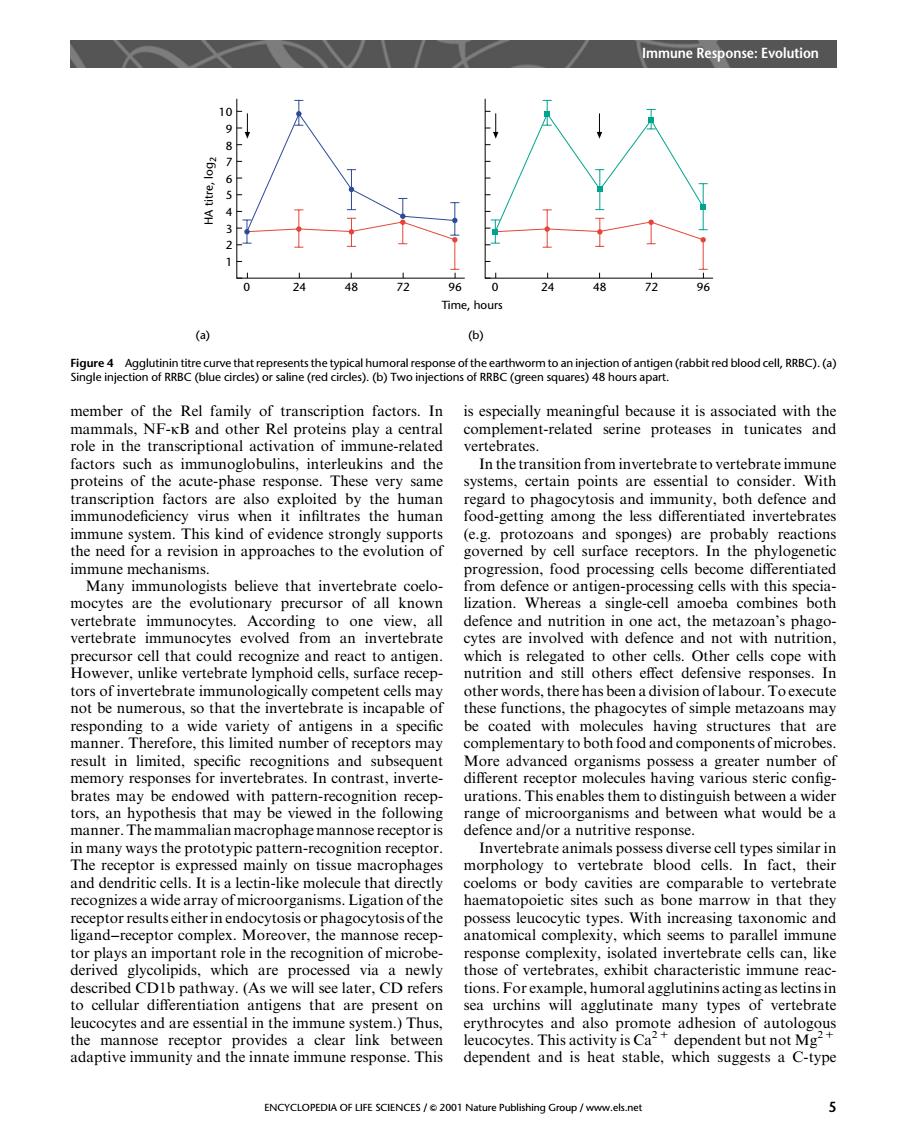
Immune Response:Evolution 4 ts the of of a abbit red blood cell.RRBC).(a) s).(b)Two injectic of RRB (green squa member of the Rel family of transcription factors.In is especially meaningful because it is associated with the mammals,NF-KB and other Rel proteins play a central complement-related serine proteases in tunicates and role in the transcriptional activation of mmun-relate vertebrates. ors such as mmunoglo Th ins and the ard to phage ocvtosis and immunity.both defence and immunodeficiency virus when it infiltrates the human food-getting among the less differentiated invertebrates immune system. reactions the nee surface recept :e Many immunologists believe that invertebrate coelo- from defence or antige n-proe c mocytes are the evolutionary precursor of all known o Whersaseot vertebrate immunocytes vertebrate from an siesnendoioagCnaca metazoan's phago that h However.unlike vertebrate lymphoid cells-surface recep tors of invertebrate immunologically competent cells may other words,there has been a division oflabour.Toexecute not be numerous,so that the invertebrate i incapable these fun the phagocytes of simple metazoans may TaPoe'nce&rwidesmc 01 of in a specmne coated that ar result in limited.specific recognitions and sub More advanced organisms possess a greater number of memory responses for invertebrates.In contrast,inverte- different receptor molecules having various steric config rations. at may dnge of be a term-recognitionrecp tor Invertebrate animals p iverse cell t mainly on tissue macrophages morphology to vertebrate blood cells. and der oorganisn .Liga SaConobodycavi ligand rceptor comple Moreover.the mannose recep tor plays an important role in the recognition of microb response complexity,isolated invertebrate cells can,like derive lipic which nev hose of vertebrate exhibit chara we w CD refers ns act leucocytes and are essential in the immune s em.)Thus ervthrocvtes and also pro adhesion of autolo the mannose receptor the mnae link betwe cucocytes.This activity is Ca adaptive immunity and response.This dependent and is heat stable ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES/2001 Nature Publishing Group /www.els.net member of the Rel family of transcription factors. In mammals, NF-kB and other Rel proteins play a central role in the transcriptional activation of immune-related factors such as immunoglobulins, interleukins and the proteins of the acute-phase response. These very same transcription factors are also exploited by the human immunodeficiency virus when it infiltrates the human immune system. This kind of evidence strongly supports the need for a revision in approaches to the evolution of immune mechanisms. Many immunologists believe that invertebrate coelomocytes are the evolutionary precursor of all known vertebrate immunocytes. According to one view, all vertebrate immunocytes evolved from an invertebrate precursor cell that could recognize and react to antigen. However, unlike vertebrate lymphoid cells, surface receptors of invertebrate immunologically competent cells may not be numerous, so that the invertebrate is incapable of responding to a wide variety of antigens in a specific manner. Therefore, this limited number of receptors may result in limited, specific recognitions and subsequent memory responses for invertebrates. In contrast, invertebrates may be endowed with pattern-recognition receptors, an hypothesis that may be viewed in the following manner. The mammalian macrophage mannose receptor is in many ways the prototypic pattern-recognition receptor. The receptor is expressed mainly on tissue macrophages and dendritic cells. It is a lectin-like molecule that directly recognizes a wide array of microorganisms. Ligation of the receptor results either in endocytosis or phagocytosis of the ligand–receptor complex. Moreover, the mannose receptor plays an important role in the recognition of microbederived glycolipids, which are processed via a newly described CD1b pathway. (As we will see later, CD refers to cellular differentiation antigens that are present on leucocytes and are essential in the immune system.) Thus, the mannose receptor provides a clear link between adaptive immunity and the innate immune response. This is especially meaningful because it is associated with the complement-related serine proteases in tunicates and vertebrates. In the transition from invertebrate to vertebrate immune systems, certain points are essential to consider. With regard to phagocytosis and immunity, both defence and food-getting among the less differentiated invertebrates (e.g. protozoans and sponges) are probably reactions governed by cell surface receptors. In the phylogenetic progression, food processing cells become differentiated from defence or antigen-processing cells with this specialization. Whereas a single-cell amoeba combines both defence and nutrition in one act, the metazoan’s phagocytes are involved with defence and not with nutrition, which is relegated to other cells. Other cells cope with nutrition and still others effect defensive responses. In other words, there has been a division of labour. To execute these functions, the phagocytes of simple metazoans may be coated with molecules having structures that are complementary to both food and components of microbes. More advanced organisms possess a greater number of different receptor molecules having various steric configurations. This enables them to distinguish between a wider range of microorganisms and between what would be a defence and/or a nutritive response. Invertebrate animals possess diverse cell types similar in morphology to vertebrate blood cells. In fact, their coeloms or body cavities are comparable to vertebrate haematopoietic sites such as bone marrow in that they possess leucocytic types. With increasing taxonomic and anatomical complexity, which seems to parallel immune response complexity, isolated invertebrate cells can, like those of vertebrates, exhibit characteristic immune reactions. For example, humoral agglutinins acting as lectins in sea urchins will agglutinate many types of vertebrate erythrocytes and also promote adhesion of autologous leucocytes. This activity is Ca2 1 dependent but not Mg2 1 dependent and is heat stable, which suggests a C-type 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 HA titre, log2 (a) Time, hours 0 24 48 72 96 0 24 48 72 96 (b) Figure 4 Agglutinin titre curve that represents the typical humoral response of the earthworm to an injection of antigen (rabbit red blood cell, RRBC). (a) Single injection of RRBC (blue circles) or saline (red circles). (b) Two injections of RRBC (green squares) 48 hours apart. Immune Response: Evolution ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www.els.net 5