正在加载图片...
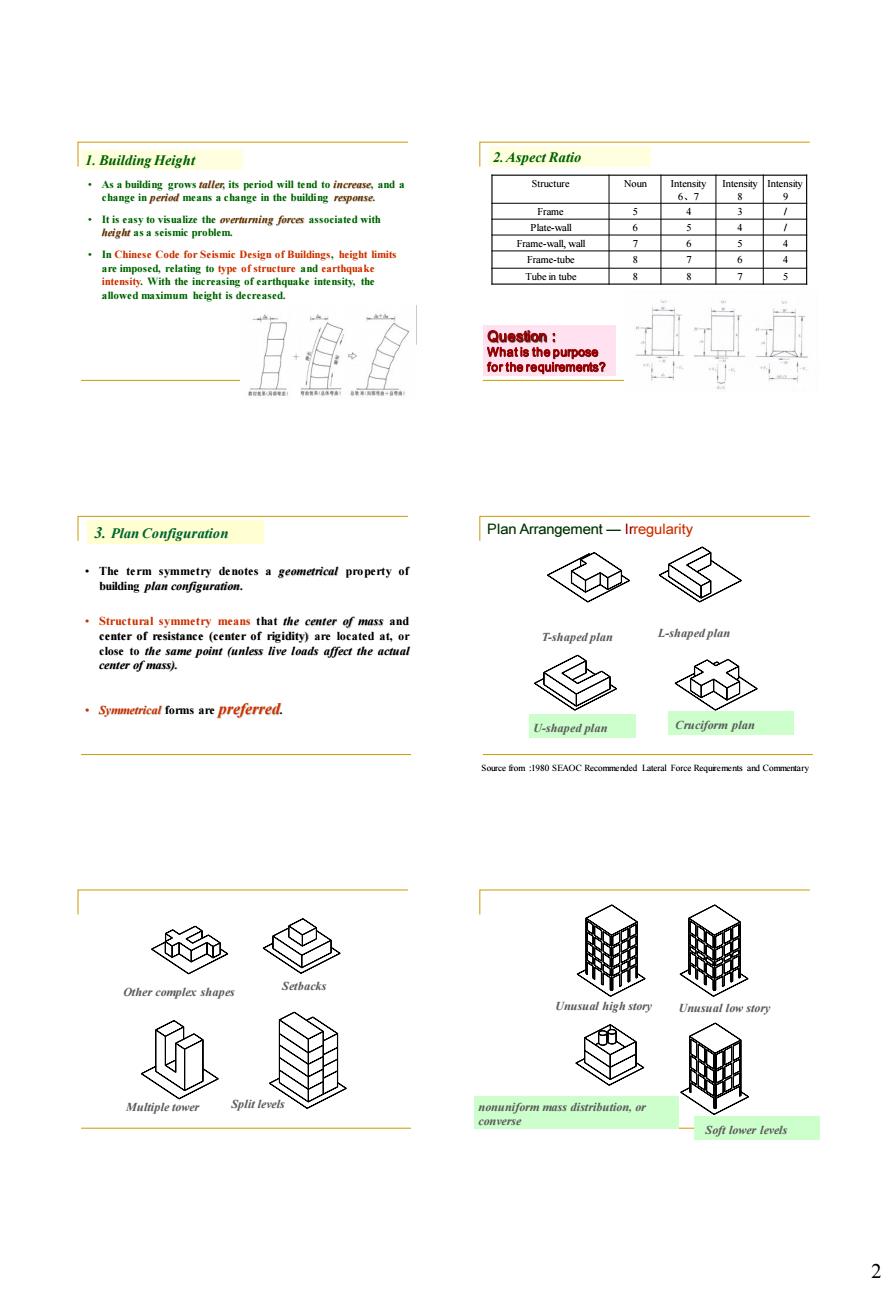
1.Building Height 2.Aspect Rati a beizht is e 3.Plan Configuration Plan Arrangement F-skapedplan L-shapedplan affect the Sywmetrical foms are preferred. U-shaped plan2 1. Building Height • As a building grows taller, its period will tend to increase, and a change in period means a change in the building response. • It is easy to visualize the overturning forces associated with height as a seismic problem. • In Chinese Code for Seismic Design of Buildings, height limits are imposed, relating to type of structure and earthquake intensity. With the increasing of earthquake intensity, the allowed maximum height is decreased. Structure Noun Intensity 6、7 Intensity 8 Intensity 9 Frame 5 4 3 / Plate-wall 6 5 4 / Frame-wall, wall 7 6 5 4 Frame-tube 8 7 6 4 Tube in tube 8 8 7 5 Question: What is the purpose for the requirements? 2. Aspect Ratio • The term symmetry denotes a geometrical property of building plan configuration. • Structural symmetry means that the center of mass and center of resistance (center of rigidity) are located at, or close to the same point (unless live loads affect the actual center of mass). • Symmetrical forms are preferred. 3. Plan Configuration T-shaped plan L-shaped plan U-shaped plan Cruciform plan Source from :1980 SEAOC Recommended Lateral Force Requirements and Commentary Plan Arrangement — Irregularity Split levels Other complex shapes Setbacks Multiple tower Unusual high story Unusual low story nonuniform mass distribution, or converse Soft lower levels