正在加载图片...
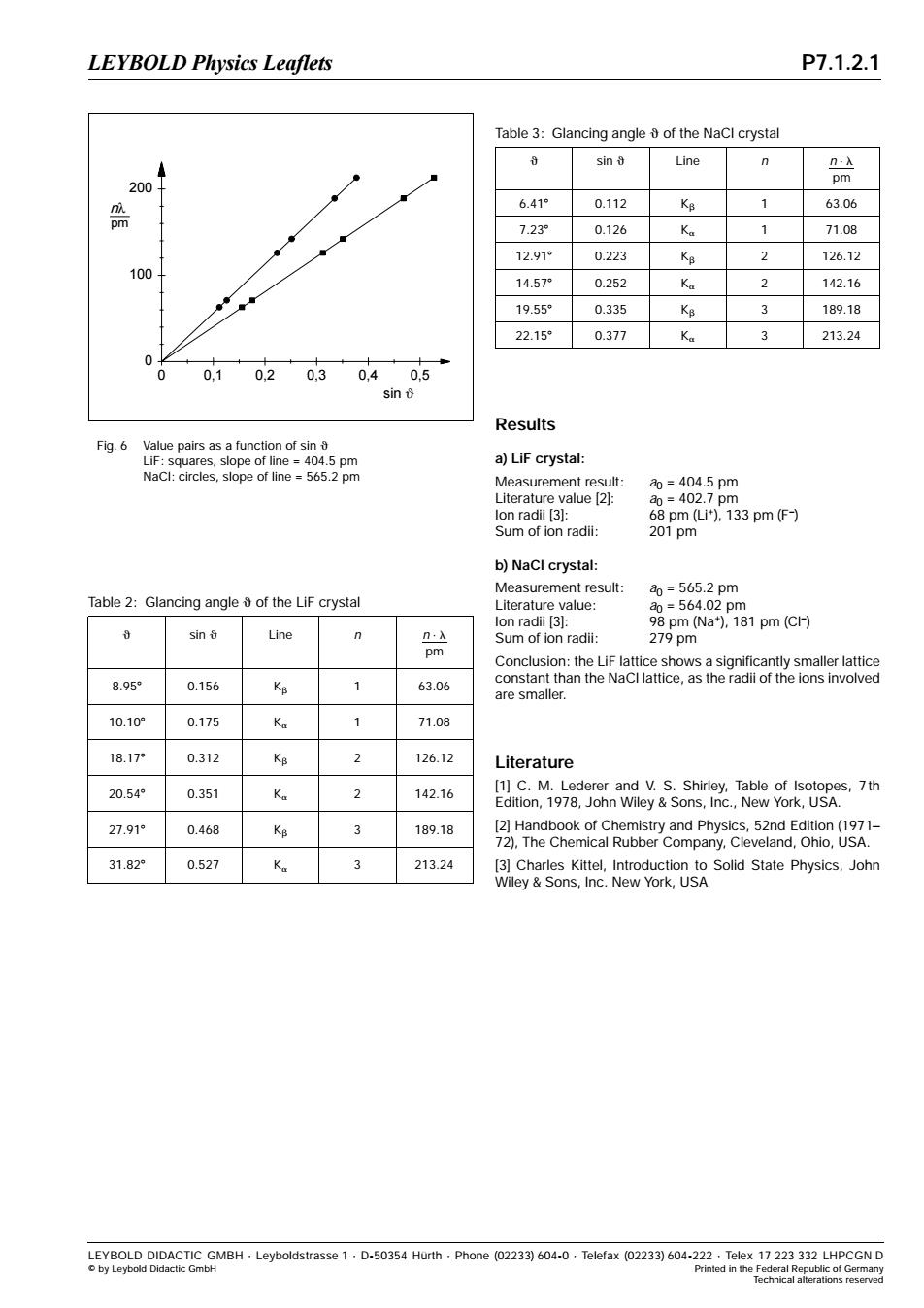
LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets P7.1.2.1 Table 3:Glancing angle of the NaCl crystal sin Line n .x pm 200 6.41° 0.112 KB 1 63.06 pm 7.23 0.126 Ka 1 71.08 12.91 0.223 K8 2 126.12 100 14.57 0.252 Ka 2 142.16 19.55 0.335 Ke 3 189.18 22.15 0.377 Ka 3 213.24 0 0 0,1 0.2 0.3 0.40.5 sin Results Fig.6 Value pairs as a function of sin LiF:squares,slope of line =404.5 pm a)LiF crystal: NaCl:circles,slope of line =565.2 pm Measurement result: ao=404.5pm Literature value [2]: a0=402.7pm lon radii [3]: 68pm(i).133pm(F) Sum of ion radii: 201pm b)NaCl crystal: Measurement result: a0=565.2pm Table 2:Glancing angle of the LiF crystal Literature value: a0=564.02pm lon radii [3]: 98 pm (Na),181 pm(Cl-) sin Line n.x Sum of ion radii: 279pm pm Conclusion:the LiF lattice shows a significantly smaller lattice 8.95 0.156 4 constant than the NaCl lattice,as the radii of the ions involved 63.06 are smaller. 10.10 0.175 Ka 71.08 18.17 0.312 2 126.12 Literature 20.54 0.351 2 142.16 [1]C.M.Lederer and V.S.Shirley,Table of Isotopes,7th Edition,1978,John Wiley Sons,Inc.,New York,USA. 27.91 0.468 KB 189.18 [2]Handbook of Chemistry and Physics,52nd Edition(1971- 72),The Chemical Rubber Company,Cleveland,Ohio,USA. 31.82 0.527 Ka 3 213.24 [3]Charles Kittel,Introduction to Solid State Physics,John Wiley Sons,Inc.New York,USA LEYBOLD DIDACTIC GMBH.Leyboldstrasse 1.D-50354 Hurth.Phone(02233)604-0.Telefax (02233)604-222.Telex 17 223 332 LHPCGN D o by Leybold Didactic GmbH Printed in the Federal Republic of Germany lechnical alterations reservedResults a) LiF crystal: Measurement result: a0 = 404.5 pm Literature value [2]: a0 = 402.7 pm Ion radii [3]: 68 pm (Li+), 133 pm (F–) Sum of ion radii: 201 pm b) NaCl crystal: Measurement result: a0 = 565.2 pm Literature value: a0 = 564.02 pm Ion radii [3]: 98 pm (Na+), 181 pm (Cl–) Sum of ion radii: 279 pm Conclusion: the LiF lattice shows a significantly smaller lattice constant than the NaCl lattice, as the radii of the ions involved are smaller. Literature [1] C. M. Lederer and V. S. Shirley, Table of Isotopes, 7th Edition, 1978, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, USA. [2] Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 52nd Edition (1971− 72), The Chemical Rubber Company, Cleveland, Ohio, USA. [3] Charles Kittel, Introduction to Solid State Physics, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York, USA Table 2: Glancing angle q of the LiF crystal q sin q Line n n ⋅ l pm 8.958 0.156 Kb 1 63.06 10.108 0.175 Ka 1 71.08 18.178 0.312 Kb 2 126.12 20.548 0.351 Ka 2 142.16 27.918 0.468 Kb 3 189.18 31.828 0.527 Ka 3 213.24 Table 3: Glancing angle q of the NaCl crystal q sin q Line n n ⋅ l pm 6.418 0.112 Kb 1 63.06 7.238 0.126 Ka 1 71.08 12.918 0.223 Kb 2 126.12 14.578 0.252 Ka 2 142.16 19.558 0.335 Kb 3 189.18 22.158 0.377 Ka 3 213.24 0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 sin ϑ 0 100 200 nλ pm Fig. 6 Value pairs as a function of sin q LiF: squares, slope of line = 404.5 pm NaCl: circles, slope of line = 565.2 pm LEYBOLD DIDACTIC GMBH ⋅ Leyboldstrasse 1 ⋅ D-50354 Hürth ⋅ Phone (02233) 604-0 ⋅ Telefax (02233) 604-222 ⋅ Telex 17 223 332 LHPCGN D © by Leybold Didactic GmbH Printed in the Federal Republic of Germany Technical alterations reserved LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets P7.1.2.1