正在加载图片...
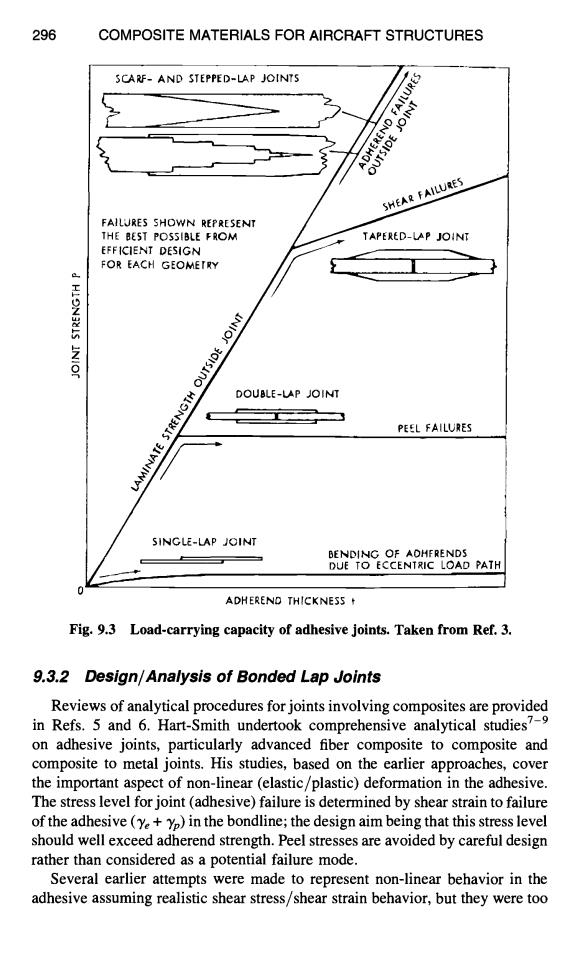
296 COMPOSITE MATERIALS FOR AIRCRAFT STRUCTURES SCARF-AND STEPPED-LAP JOINTS FAILURES OUTSIDE SHEAR FAILURES FAILURES SHOWN REPRESENT THE BEST POSSIBLE FROM TAPERED-LAP JOINT EFFICIENT DESIGN FOR EACH GEOMETRY LAMINATE STRENGTH OUTSIDE JOINT DOUBLE-LAP JOINT PEEL FAILURES SINGLE-LAP JOINT BENDING OF AOHFRENDS DUE TO ECCENTRIC LOAD PATH ADHEREND THICKNESS Fig.9.3 Load-carrying capacity of adhesive joints.Taken from Ref.3. 9.3.2 Design/Analysis of Bonded Lap Joints Reviews of analytical procedures for joints involving composites are provided in Refs.5 and 6.Hart-Smith undertook comprehensive analytical studies7-9 on adhesive joints,particularly advanced fiber composite to composite and composite to metal joints.His studies,based on the earlier approaches,cover the important aspect of non-linear (elastic/plastic)deformation in the adhesive. The stress level for joint (adhesive)failure is determined by shear strain to failure of the adhesive(y+yp)in the bondline;the design aim being that this stress level should well exceed adherend strength.Peel stresses are avoided by careful design rather than considered as a potential failure mode. Several earlier attempts were made to represent non-linear behavior in the adhesive assuming realistic shear stress/shear strain behavior,but they were too296 COMPOSITE MATERIALS FOR AIRCRAFT STRUCTURES O Z o SCAPJ:- AND STEPPED-LAP JOINTS i , , J" FAILURES SHOWN REPRESENT THE BEST POSSIBLE FROM EFFICIENT DI~SION FOR EACH GEOMETRY TAPERED-!~P JOINT ' DOUBLE-LAP JOINT II . , '! PEEL FAILURES SINGLE-LAP JOINT i BENDING OF AOHFRENDS DUE TO ECCENTRIC LOAD PATH ADHEREND THICKNESS t Fig. 9.3 Load-carrying capacity of adhesive joints. Taken from Ref. 3. 9.3.2 Design~Analysis of Bonded Lap Joints Reviews of analytical procedures for joints involving composites are provided in Refs. 5 and 6. Hart-Smith undertook comprehensive analytical studies 7-9 on adhesive joints, particularly advanced fiber composite to composite and composite to metal joints. His studies, based on the earlier approaches, cover the important aspect of non-linear (elastic/plastic) deformation in the adhesive. The stress level for joint (adhesive) failure is determined by shear strain to failure of the adhesive (% + "yp) in the bondline; the design aim being that this stress level should well exceed adherend strength. Peel stresses are avoided by careful design rather than considered as a potential failure mode. Several earlier attempts were made to represent non-linear behavior in the adhesive assuming realistic shear stress/shear strain behavior, but they were too