正在加载图片...
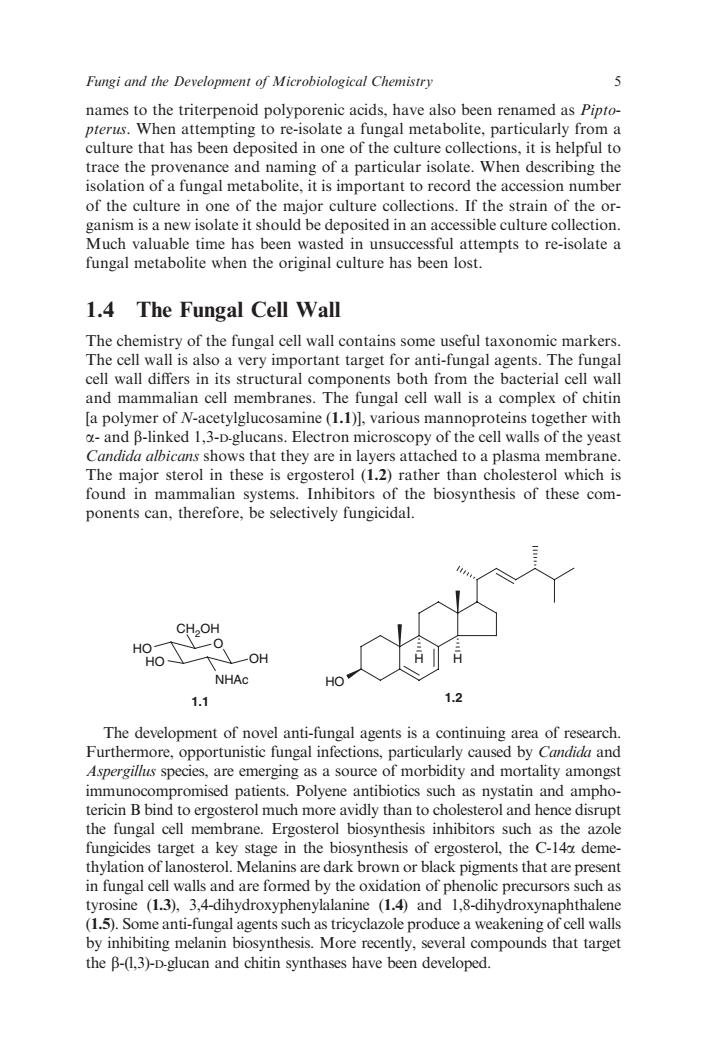
Fungi and the Development of Microbiological Chemistry names to the triterpenoid polyporenic acids,have also been renamed as Pipto- pterus.When attempting to re-isolate a fungal metabolite.particularly from a culture that has been deposited in one of the culture collections.it is helpful to ce and particular isolate When de tabolite,it is importantt ing the the accession of the culture in one of the major culture collections.If the strain of the or ganism is a new isolate it should be deposited in an accessible culture collection Much valuable time has been wasted in unsuccessful attempts to re-isolate a fungal metabolite when the original culture has been lost. 1.4 The Fungal Cell Wall The chemistry of the fungal cell wall contains some useful taxonomic markers The cell wall is also a very important target for anti-fungal agents.The fungal cell wall differs in its structural components both from the bacterial cell wall and mammalian cell membranes.The fungal cell wall is a complex of chitin la polymer of N-acetylglucosamine (11)1.various mannoproteins together with -and B-linked 13-D.glucans.electron microscony of the cell walls of the veas Candida albicans shows that they are in layers attached to a plasma m The erol (1.2) rather tha which ian systems. the biosynthesis of these com ponents can,therefore,be selectively fungicidal 一OH NHAC 1.1 1.2 The development of novel anti-fungal agents is a continuing area of research. Furthermore,opportunistic fungal infections,particularly caused by Candida and Aspergillus speci s,are emerging as a source of morbidity and mortality amongs ncin B bomp ised patients.Polyene antibiotics and to ergosterol much more ay aly th an to c erol and hence disrup the fungal cell membrane.Ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitors such as the azol fungicides target a key stage in the biosynthesis of ergosterol,the C-14a deme thylation of lanosterol.Melanins are dark brown or black pigments that are present in fungal cell walls and are formed by the oxidation of phenolic precursors such as tyrosine (1.3),3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (1.4)and 1,8-dihydroxynaphthalene (1.5).Some anti-fungal agents such as tricyclazole produce a weakening of cell walls by inhibiting melanin biosynthesis.,several compounds that target the B-(1,3)-D-glucan and chitin synthases have been developed. names to the triterpenoid polyporenic acids, have also been renamed as Piptopterus. When attempting to re-isolate a fungal metabolite, particularly from a culture that has been deposited in one of the culture collections, it is helpful to trace the provenance and naming of a particular isolate. When describing the isolation of a fungal metabolite, it is important to record the accession number of the culture in one of the major culture collections. If the strain of the organism is a new isolate it should be deposited in an accessible culture collection. Much valuable time has been wasted in unsuccessful attempts to re-isolate a fungal metabolite when the original culture has been lost. 1.4 The Fungal Cell Wall The chemistry of the fungal cell wall contains some useful taxonomic markers. The cell wall is also a very important target for anti-fungal agents. The fungal cell wall differs in its structural components both from the bacterial cell wall and mammalian cell membranes. The fungal cell wall is a complex of chitin [a polymer of N-acetylglucosamine (1.1)], various mannoproteins together with a- and b-linked 1,3-D-glucans. Electron microscopy of the cell walls of the yeast Candida albicans shows that they are in layers attached to a plasma membrane. The major sterol in these is ergosterol (1.2) rather than cholesterol which is found in mammalian systems. Inhibitors of the biosynthesis of these components can, therefore, be selectively fungicidal. O CH2OH HO HO OH NHAc 1.1 H H HO 1.2 The development of novel anti-fungal agents is a continuing area of research. Furthermore, opportunistic fungal infections, particularly caused by Candida and Aspergillus species, are emerging as a source of morbidity and mortality amongst immunocompromised patients. Polyene antibiotics such as nystatin and amphotericin B bind to ergosterol much more avidly than to cholesterol and hence disrupt the fungal cell membrane. Ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitors such as the azole fungicides target a key stage in the biosynthesis of ergosterol, the C-14a demethylation of lanosterol. Melanins are dark brown or black pigments that are present in fungal cell walls and are formed by the oxidation of phenolic precursors such as tyrosine (1.3), 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (1.4) and 1,8-dihydroxynaphthalene (1.5). Some anti-fungal agents such as tricyclazole produce a weakening of cell walls by inhibiting melanin biosynthesis. More recently, several compounds that target the b-(l,3)-D-glucan and chitin synthases have been developed. Fungi and the Development of Microbiological Chemistry 5