正在加载图片...
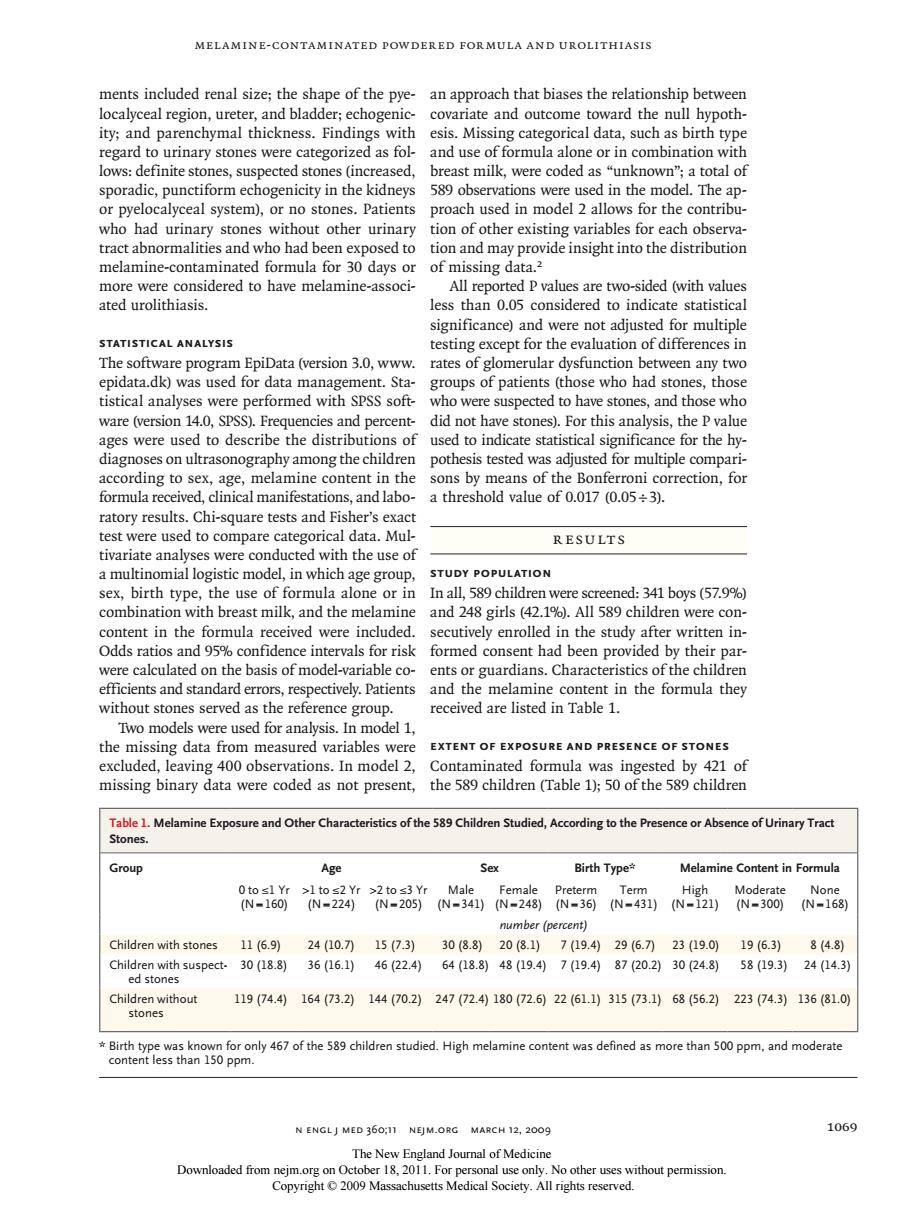
MELAMINE-CONTAMINATED POWDERED FORMULA AND UROLITHIASIS ments included renal size;the shape of the pye-an approach that biases the relationship between localyceal region,ureter,and bladder;echogenic covariate and outcome toward the null hypoth- ity;and parenchymal thickness.Findings with hnifoneswereCaegorizaisfol esis.Missing categorical data,such as birth type nd use ormula nilk used inthe del Th who had urinary stones without other urinary tion of other existing variables for each observa- tract abnormalities and who had been exposed to tion and may provide insight into the distribution melamine-contaminated formula for 30 days or of missing data. uoihstrodoharemchmincasoc A less tha reported Pv sided (with ated an0.0 signific adj multipl STATISTICAL ANALYSIS The software program epiData (version 3.0.www. rates of omerular dysfunction between any two epidata.dk)was used for data management.Sta- groups of patients (those who had stones,those tistical analyses were performed with SPSS soft- who were suspected to have stones,and those who ware (,).and percen did not have stones).For this analysis,the P value ages were use the distri used to indicate statis efor the hy diagnoses on u the for formula received clinical manifestations.and labo- a threshold value of 0.017 (0.05+3). ratory results chi-square tests and fisher's exac test were used to compare categorical data.Mul RESULTS tivariate analyses we ere conducted with the use of model,in which age group, use c alone or 3irs42.19. A589 7 en Odds ratios and o5 confidence int vals for risk formed consent had heen t ovided by thei were calculated on the basis of model-variable co- ents or guardians.Characteristics of the children efficients and standard errors,respectively.Patients and the melamine content in the formula they without stones served as the reference group. received are listed in Table 1. were used for analysis. measur el? EXTENT OF EXPOSURE AND PRESENCE OF STONES d by 421 of missing binary data were coded as not present. the 589 children CTable 1):50 of the 589 children Table 1.Melamine Exposure and Other Characteristics of the 58 Children Studied,According to the Presence or Absence of Urinary Tract Group Birth Type Melamine Content in formula 断22海66 number (percent) Children with stones 11(6.9)24(10.刀1573)3088)20(81)79.4296.刀239.019(6.3) 8(4.8) Ch003割36n6)4622到6408周48a9利79到87o习3024周58093)2443到 119(74.4)164(73.2144(70.2)247(72.180(72.6)22(61.1)315(73.1)6856.2)223(74.3)136(81.0 N ENGLJ MED 360,11 NEJM.ORG MARCH 12,2009 06g The New England Joual of Medicine Melamine-Contaminated Powdered Formula and Urolithiasis n engl j med 360;11 nejm.org march 12, 2009 1069 ments included renal size; the shape of the pyelocalyceal region, ureter, and bladder; echogenicity; and parenchymal thickness. Findings with regard to urinary stones were categorized as follows: definite stones, suspected stones (increased, sporadic, punctiform echogenicity in the kidneys or pyelocalyceal system), or no stones. Patients who had urinary stones without other urinary tract abnormalities and who had been exposed to melamine-contaminated formula for 30 days or more were considered to have melamine-associated urolithiasis. Statistical Analysis The software program EpiData (version 3.0, www. epidata.dk) was used for data management. Statistical analyses were performed with SPSS software (version 14.0, SPSS). Frequencies and percentages were used to describe the distributions of diagnoses on ultrasonography among the children according to sex, age, melamine content in the formula received, clinical manifestations, and laboratory results. Chi-square tests and Fisher’s exact test were used to compare categorical data. Multivariate analyses were conducted with the use of a multinomial logistic model, in which age group, sex, birth type, the use of formula alone or in combination with breast milk, and the melamine content in the formula received were included. Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals for risk were calculated on the basis of model-variable coefficients and standard errors, respectively. Patients without stones served as the reference group. Two models were used for analysis. In model 1, the missing data from measured variables were excluded, leaving 400 observations. In model 2, missing binary data were coded as not present, an approach that biases the relationship between covariate and outcome toward the null hypothesis. Missing categorical data, such as birth type and use of formula alone or in combination with breast milk, were coded as “unknown”; a total of 589 observations were used in the model. The approach used in model 2 allows for the contribution of other existing variables for each observation and may provide insight into the distribution of missing data.2 All reported P values are two-sided (with values less than 0.05 considered to indicate statistical significance) and were not adjusted for multiple testing except for the evaluation of differences in rates of glomerular dysfunction between any two groups of patients (those who had stones, those who were suspected to have stones, and those who did not have stones). For this analysis, the P value used to indicate statistical significance for the hypothesis tested was adjusted for multiple comparisons by means of the Bonferroni correction, for a threshold value of 0.017 (0.05÷3). Results Study Population In all, 589 children were screened: 341 boys (57.9%) and 248 girls (42.1%). All 589 children were consecutively enrolled in the study after written informed consent had been provided by their parents or guardians. Characteristics of the children and the melamine content in the formula they received are listed in Table 1. Extent of Exposure and Presence of Stones Contaminated formula was ingested by 421 of the 589 children (Table 1); 50 of the 589 children Table 1. Melamine Exposure and Other Characteristics of the 589 Children Studied, According to the Presence or Absence of Urinary Tract Stones. Group Age Sex Birth Type* Melamine Content in Formula 0 to ≤1 Yr (N=160) >1 to ≤2 Yr (N=224) >2 to ≤3 Yr (N=205) Male (N=341) Female (N=248) Preterm (N=36) Term (N=431) High (N=121) Moderate (N=300) None (N=168) number (percent) Children with stones 11 (6.9) 24 (10.7) 15 (7.3) 30 (8.8) 20 (8.1) 7 (19.4) 29 (6.7) 23 (19.0) 19 (6.3) 8 (4.8) Children with suspected stones 30 (18.8) 36 (16.1) 46 (22.4) 64 (18.8) 48 (19.4) 7 (19.4) 87 (20.2) 30 (24.8) 58 (19.3) 24 (14.3) Children without stones 119 (74.4) 164 (73.2) 144 (70.2) 247 (72.4) 180 (72.6) 22 (61.1) 315 (73.1) 68 (56.2) 223 (74.3) 136 (81.0) * Birth type was known for only 467 of the 589 children studied. High melamine content was defined as more than 500 ppm, and moderate content less than 150 ppm. The New England Journal of Medicine Downloaded from nejm.org on October 18, 2011. For personal use only. No other uses without permission. Copyright © 2009 Massachusetts Medical Society. All rights reserved