正在加载图片...
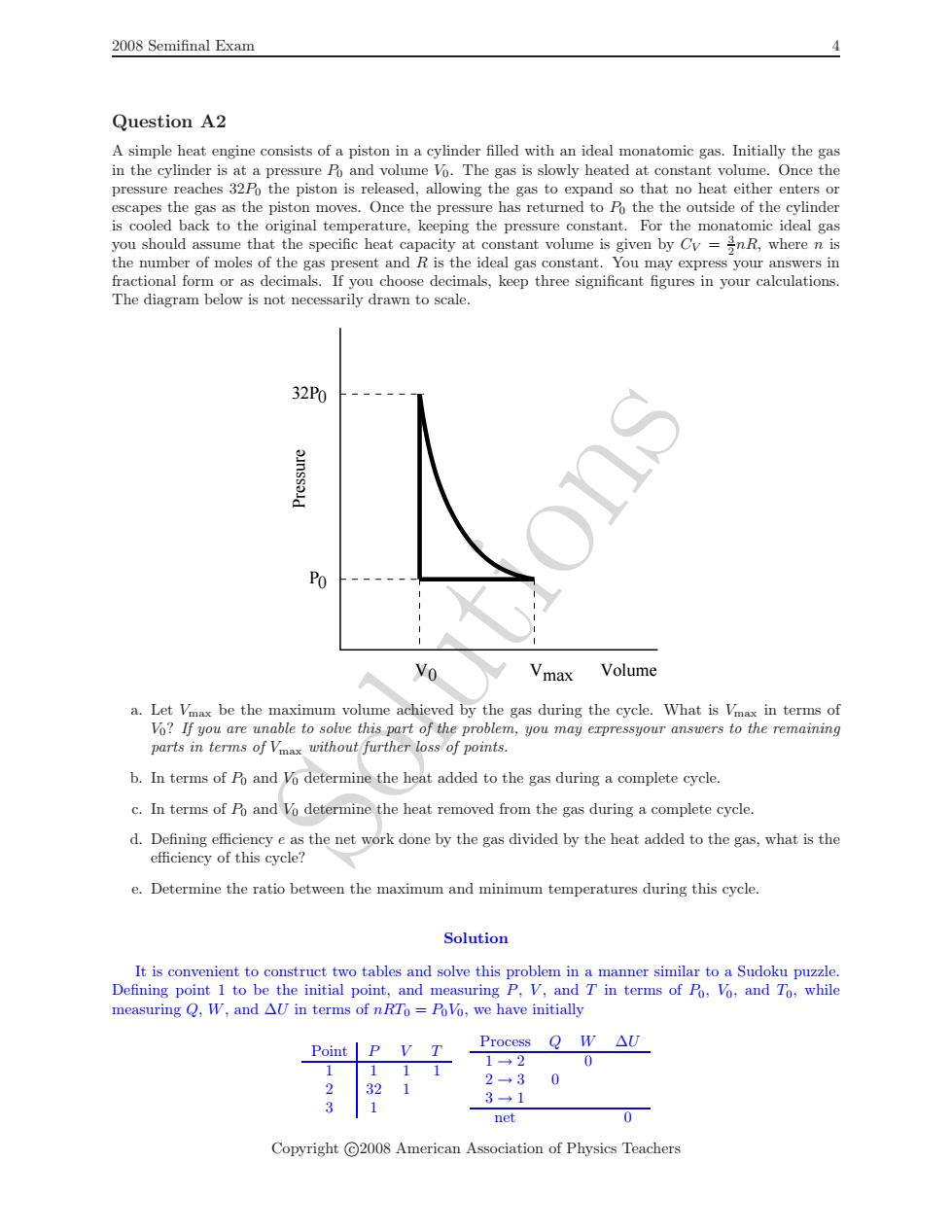
2008 Semifinal Exam Question A2 A simple heat engine consists of a piston in a cylinder filled with an ideal monatomic gas.Initially the gas in the cylinder is at a pressure Po and volume Vo.The gas is slowly heated at constant volume.Once the pressure reaches 32Po the piston is released,allowing the gas to expand so that no heat either enters or escapes the gas as the piston moves.Once the pressure has returned to Po thethe outside of the cylinder is cooled back to the original temperature,keeping the pressure constant.For the monatomic ideal gas you should assume that the specific heat capacity at constant volume is given by Cy =inR,where n is the number of moles of the gas present and R is the ideal gas constant.You may express your answers in fractional form or as decimals.If you choose decimals,keep three significant figures in your calculations. The diagram below is not necessarily drawn to scale. 32P0 ainssald Po Vmax Volume a.Let Vmax be the maximum volume achieved by the gas during the cycle.What is Vimax in terms of Vo?If you are unable to solve this part of the problem,you may erpressyour answers to the remaining parts in terms of Vmax without further loss of points. b.In terms of Po and Vo determine the heat added to the gas during a complete cycle. c.In terms of Po and Vo determine the heat removed from the gas during a complete cycle. d.Defining efficiency e as the net work done by the gas divided by the heat added to the gas,what is the efficiency of this cycle? e.Determine the ratio between the maximum and minimum temperatures during this cycle. Solution It is convenient to construct two tables and solve this problem in a manner similar to a Sudoku puzzle. Defining point 1 to be the initial point,and measuring P,V,and T in terms of Po,Vo,and To,while measuring Q,W,and AU in terms of nRTo PoVo,we have initially Process Q W△U Point P V T 1→2 0 111 321 2→30 3→1 3 net 0 Copyright C2008 American Association of Physics TeachersSolutions 2008 Semifinal Exam 4 Question A2 A simple heat engine consists of a piston in a cylinder filled with an ideal monatomic gas. Initially the gas in the cylinder is at a pressure P0 and volume V0. The gas is slowly heated at constant volume. Once the pressure reaches 32 P0 the piston is released, allowing the gas to expand so that no heat either enters or escapes the gas as the piston moves. Once the pressure has returned to P0 the the outside of the cylinder is cooled back to the original temperature, keeping the pressure constant. For the monatomic ideal gas you should assume that the specific heat capacity at constant volume is given by C V = 32 nR, where n is the number of moles of the gas present and R is the ideal gas constant. You may express your answers in fractional form or as decimals. If you choose decimals, keep three significant figures in your calculations. The diagram below is not necessarily drawn to scale. Pressure P00 V0 32P Vmax Volume a. Let Vmax be the maximum volume achieved by the gas during the cycle. What is Vmax in terms of V0 ? If you are unable to solve this part of the problem, you may expressyour answers to the remaining parts in terms of Vmax without further loss of points. b. In terms of P0 and V0 determine the heat added to the gas during a complete cycle. c. In terms of P0 and V0 determine the heat removed from the gas during a complete cycle. d. Defining efficiency e as the net work done by the gas divided by the heat added to the gas, what is the efficiency of this cycle? e. Determine the ratio between the maximum and minimum temperatures during this cycle. Solution It is convenient to construct two tables and solve this problem in a manner similar to a Sudoku puzzle. Defining point 1 to be the initial point, and measuring P , V , and T in terms of P0 , V0, and T0, while measuring Q , W, and ∆ U in terms of nRT0 = P0 V0, we have initially Point P V T 1 1 1 1 2 32 1 3 1 Process Q W ∆ U 1 → 2 0 2 → 3 0 3 → 1 net 0 Copyright c 2008 American Association of Physics Teachers