正在加载图片...
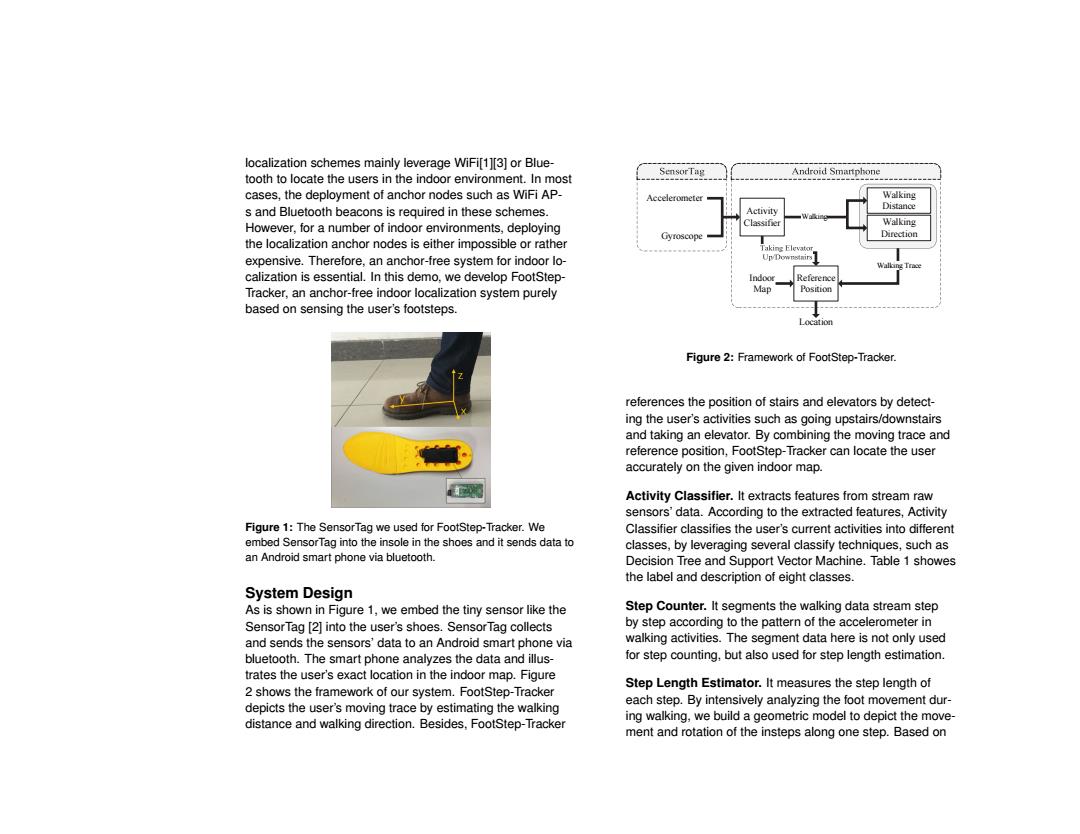
localization schemes mainly leverage WiFi[1][3]or Blue- SensorTag tooth to locate the users in the indoor environment.In most Android Smartphone cases,the deployment of anchor nodes such as WiFi AP- Accelerometer Walking s and Bluetooth beacons is required in these schemes. Activity Distance However,for a number of indoor environments,deploying Classifier Walking Gyroscope Direction the localization anchor nodes is either impossible or rather Taking Elevato可 expensive.Therefore,an anchor-free system for indoor lo- Up/Downestairs】 calization is essential.In this demo,we develop FootStep- Indoor Relereno Tracker,an anchor-free indoor localization system purely Map Position based on sensing the user's footsteps. Location Figure 2:Framework of FootStep-Tracker. references the position of stairs and elevators by detect- ing the user's activities such as going upstairs/downstairs and taking an elevator.By combining the moving trace and reference position,FootStep-Tracker can locate the user accurately on the given indoor map. Activity Classifier.It extracts features from stream raw sensors'data.According to the extracted features,Activity Figure 1:The SensorTag we used for FootStep-Tracker.We Classifier classifies the user's current activities into different embed SensorTag into the insole in the shoes and it sends data to classes,by leveraging several classify techniques,such as an Android smart phone via bluetooth. Decision Tree and Support Vector Machine.Table 1 showes the label and description of eight classes. System Design As is shown in Figure 1,we embed the tiny sensor like the Step Counter.It segments the walking data stream step SensorTag [2]into the user's shoes.SensorTag collects by step according to the pattern of the accelerometer in and sends the sensors'data to an Android smart phone via walking activities.The segment data here is not only used bluetooth.The smart phone analyzes the data and illus- for step counting,but also used for step length estimation. trates the user's exact location in the indoor map.Figure Step Length Estimator.It measures the step length of 2 shows the framework of our system.FootStep-Tracker each step.By intensively analyzing the foot movement dur- depicts the user's moving trace by estimating the walking ing walking,we build a geometric model to depict the move- distance and walking direction.Besides,FootStep-Tracker ment and rotation of the insteps along one step.Based onlocalization schemes mainly leverage WiFi[1][3] or Bluetooth to locate the users in the indoor environment. In most cases, the deployment of anchor nodes such as WiFi APs and Bluetooth beacons is required in these schemes. However, for a number of indoor environments, deploying the localization anchor nodes is either impossible or rather expensive. Therefore, an anchor-free system for indoor localization is essential. In this demo, we develop FootStepTracker, an anchor-free indoor localization system purely based on sensing the user’s footsteps. Figure 1: The SensorTag we used for FootStep-Tracker. We embed SensorTag into the insole in the shoes and it sends data to an Android smart phone via bluetooth. System Design As is shown in Figure 1, we embed the tiny sensor like the SensorTag [2] into the user’s shoes. SensorTag collects and sends the sensors’ data to an Android smart phone via bluetooth. The smart phone analyzes the data and illustrates the user’s exact location in the indoor map. Figure 2 shows the framework of our system. FootStep-Tracker depicts the user’s moving trace by estimating the walking distance and walking direction. Besides, FootStep-Tracker Accelerometer Gyroscope Activity Classifier Walking Distance Walking Direction Reference Position Walking Walking Trace Indoor Map Location Figure 2: Framework of FootStep-Tracker. references the position of stairs and elevators by detecting the user’s activities such as going upstairs/downstairs and taking an elevator. By combining the moving trace and reference position, FootStep-Tracker can locate the user accurately on the given indoor map. Activity Classifier. It extracts features from stream raw sensors’ data. According to the extracted features, Activity Classifier classifies the user’s current activities into different classes, by leveraging several classify techniques, such as Decision Tree and Support Vector Machine. Table 1 showes the label and description of eight classes. Step Counter. It segments the walking data stream step by step according to the pattern of the accelerometer in walking activities. The segment data here is not only used for step counting, but also used for step length estimation. Step Length Estimator. It measures the step length of each step. By intensively analyzing the foot movement during walking, we build a geometric model to depict the movement and rotation of the insteps along one step. Based on