正在加载图片...
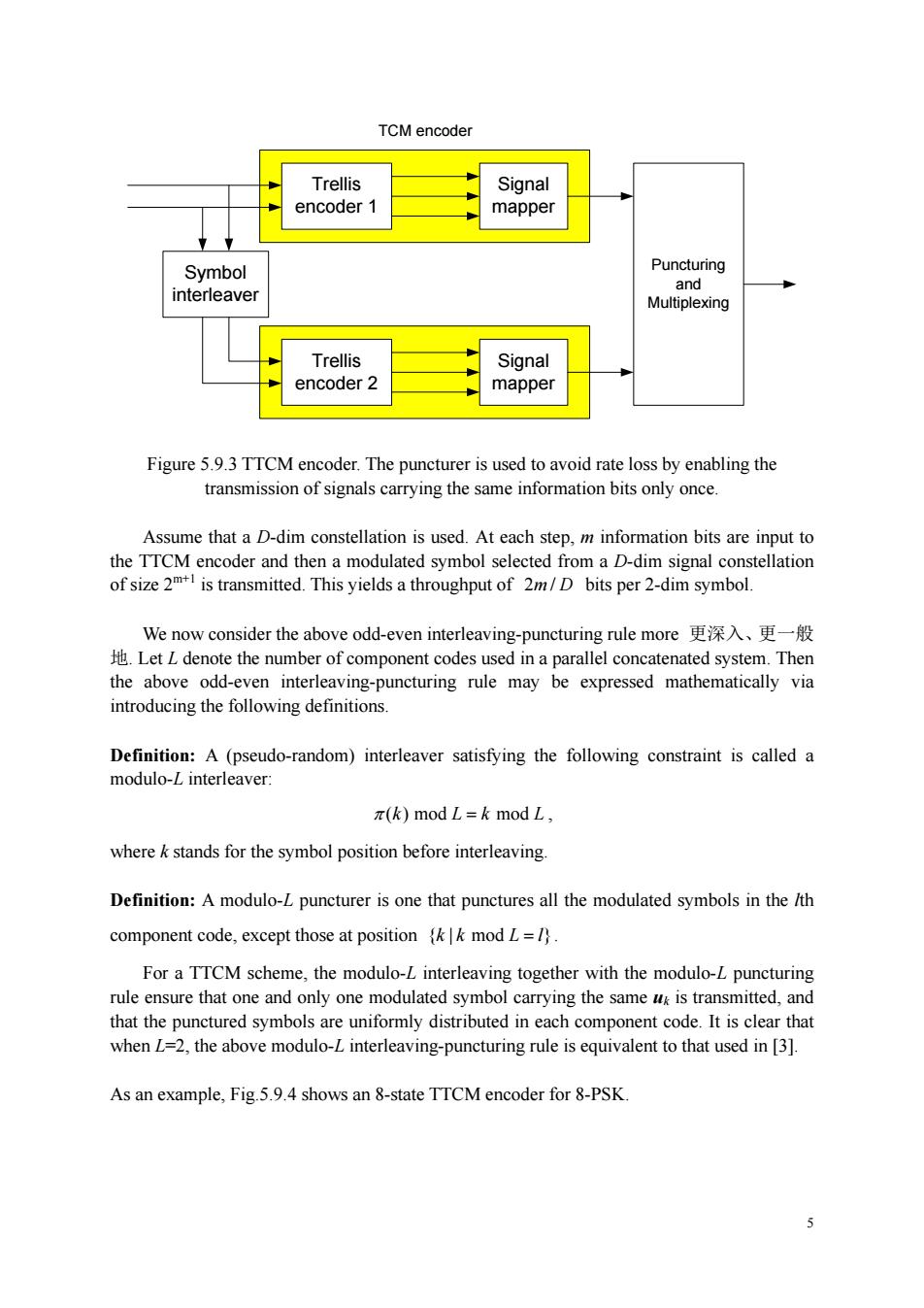
TCM encoder Trellis Signal encoder 1 mappe ymbol Puncturing ave Trellis encoder 2 Signal mappe Figure 5.9.3 TTCM encoder.The puncturer is used to avoid rate loss by enabling the transmission of signals carrying the same information bits only once. Assume that a D-dim constellation is used.At each step,m information bits are input to the TTCM ncode nodulated syn a D-dim s constellation of size2 1 We now consider the above odd-even interleaving-puncturing rule more更深入、更一般 LetL denote the number of component codes used in a parallel concatenated system.Then introducing the following definitions the above odd-even interleav rule may be expressed mathematically via Definition:A (pseudo-random)interleaver satisfying the following constraint is called a modulo-L interleaver: π(k)modL=k mod L, wherek stands for the symbol position before interleaving. Definition:A modulo-L puncturer is one that punctures all the modulated symbols in the /th component code,except those at positionk modL=1. For a TTCM scheme,the modulo-L interleaving together with the modulo-L puncturing rule ensure that one and only one modulated symbol carrying the same uk is transmitted,and that the punctured symbols are uniformly distributed in each component code.It is clear that when L=2,the above modulo-L interleaving-puncturing rule is equivalent to that used in [3]. As an example,Fig5.9.4 shows an 8-state TTCM encoder for 8-PSK 5 Trellis encoder 1 Trellis encoder 2 Signal mapper Signal mapper Symbol interleaver TCM encoder Puncturing and Multiplexing Figure 5.9.3 TTCM encoder. The puncturer is used to avoid rate loss by enabling the transmission of signals carrying the same information bits only once. Assume that a D-dim constellation is used. At each step, m information bits are input to the TTCM encoder and then a modulated symbol selected from a D-dim signal constellation of size 2m+1 is transmitted. This yields a throughput of 2 / m D bits per 2-dim symbol. We now consider the above odd-even interleaving-puncturing rule more 更深入、更一般 地. Let L denote the number of component codes used in a parallel concatenated system. Then the above odd-even interleaving-puncturing rule may be expressed mathematically via introducing the following definitions. Definition: A (pseudo-random) interleaver satisfying the following constraint is called a modulo-L interleaver: π ( ) mod mod k Lk L = , where k stands for the symbol position before interleaving. Definition: A modulo-L puncturer is one that punctures all the modulated symbols in the lth component code, except those at position { | mod } kk L l = . For a TTCM scheme, the modulo-L interleaving together with the modulo-L puncturing rule ensure that one and only one modulated symbol carrying the same uk is transmitted, and that the punctured symbols are uniformly distributed in each component code. It is clear that when L=2, the above modulo-L interleaving-puncturing rule is equivalent to that used in [3]. As an example, Fig.5.9.4 shows an 8-state TTCM encoder for 8-PSK