正在加载图片...
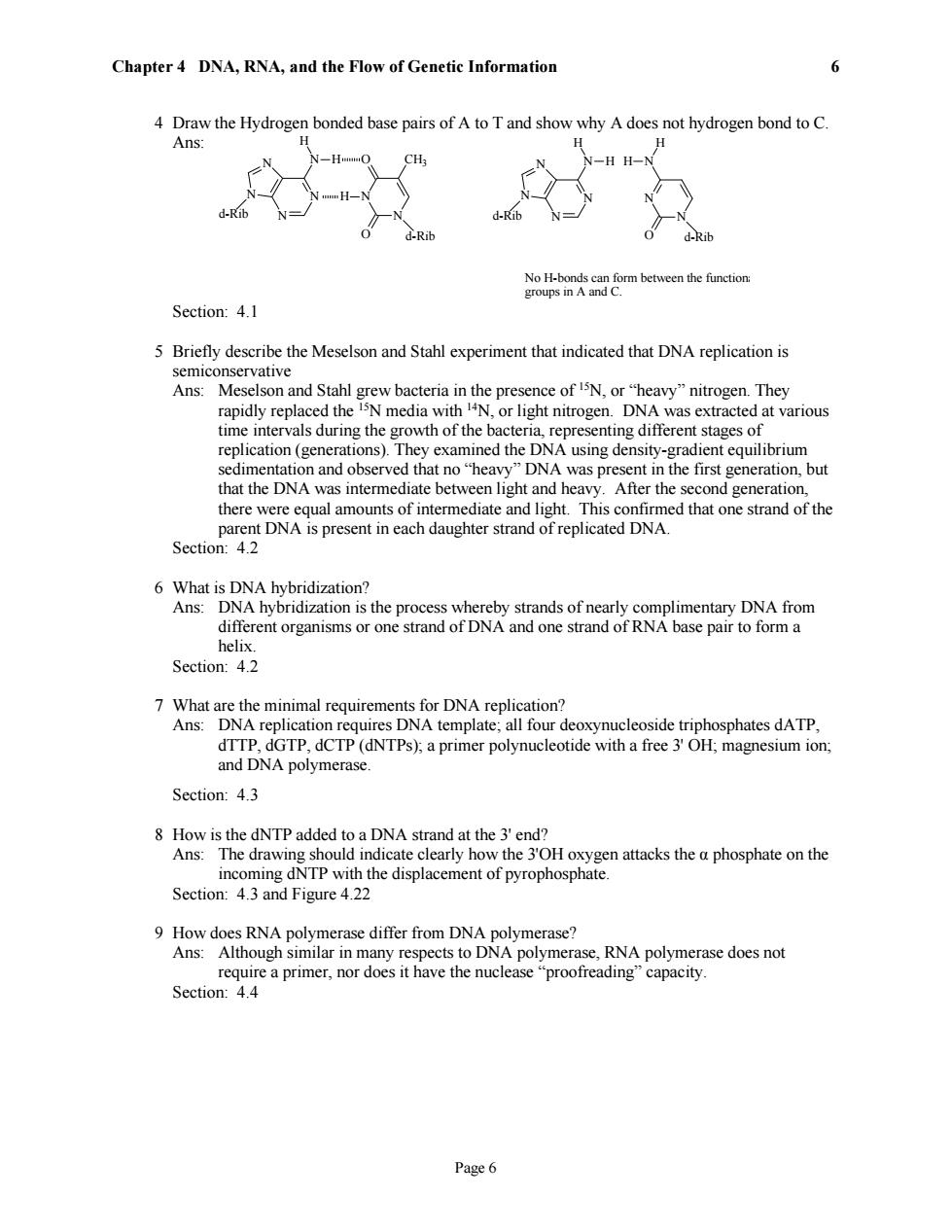
Chapter 4 DNA,RNA,and the Flow of Genetic Information 6 4 Draw the Hydrogen bonded base pairs of A to T and show why A does not hydrogen bond to C. Ans: H H H H-N d-Rib d-Rib d-Rib d-Rib No H-bonds can form between the function: groups in A and C. Section:4.1 5 Briefly describe the Meselson and Stahl experiment that indicated that DNA replication is semiconservative Ans:Meselson and Stahl grew bacteria in the presence of I5N,or"heavy"nitrogen.They rapidly replaced the I5N media with 4N,or light nitrogen.DNA was extracted at various time intervals during the growth of the bacteria,representing different stages of replication(generations).They examined the DNA using density-gradient equilibrium sedimentation and observed that no"heavy"DNA was present in the first generation,but that the DNA was intermediate between light and heavy.After the second generation, there were equal amounts of intermediate and light.This confirmed that one strand of the parent DNA is present in each daughter strand of replicated DNA. Section:4.2 6 What is DNA hybridization? Ans:DNA hybridization is the process whereby strands of nearly complimentary DNA from different organisms or one strand of DNA and one strand of RNA base pair to form a helix. Section:4.2 7 What are the minimal requirements for DNA replication? Ans:DNA replication requires DNA template;all four deoxynucleoside triphosphates dATP, dTTP,dGTP,dCTP(dNTPs);a primer polynucleotide with a free 3'OH;magnesium ion; and DNA polymerase. Section:4.3 8 How is the dNTP added to a DNA strand at the 3'end? Ans:The drawing should indicate clearly how the 3'OH oxygen attacks the a phosphate on the incoming dNTP with the displacement of pyrophosphate. Section:4.3 and Figure 4.22 9 How does RNA polymerase differ from DNA polymerase? Ans:Although similar in many respects to DNA polymerase,RNA polymerase does not require a primer,nor does it have the nuclease"proofreading"capacity. Section:4.4 Page 6Chapter 4 DNA, RNA, and the Flow of Genetic Information Page 6 6 4 Draw the Hydrogen bonded base pairs of A to T and show why A does not hydrogen bond to C. Ans: N N O O CH3 H N N N N N H H d-Rib d-Rib d-Rib d-Rib N N O N H H N N N N N H H No H-bonds can form between the functional groups in A and C. Section: 4.1 5 Briefly describe the Meselson and Stahl experiment that indicated that DNA replication is semiconservative Ans: Meselson and Stahl grew bacteria in the presence of 15N, or “heavy” nitrogen. They rapidly replaced the 15N media with 14N, or light nitrogen. DNA was extracted at various time intervals during the growth of the bacteria, representing different stages of replication (generations). They examined the DNA using density-gradient equilibrium sedimentation and observed that no “heavy” DNA was present in the first generation, but that the DNA was intermediate between light and heavy. After the second generation, there were equal amounts of intermediate and light. This confirmed that one strand of the parent DNA is present in each daughter strand of replicated DNA. Section: 4.2 6 What is DNA hybridization? Ans: DNA hybridization is the process whereby strands of nearly complimentary DNA from different organisms or one strand of DNA and one strand of RNA base pair to form a helix. Section: 4.2 7 What are the minimal requirements for DNA replication? Ans: DNA replication requires DNA template; all four deoxynucleoside triphosphates dATP, dTTP, dGTP, dCTP (dNTPs); a primer polynucleotide with a free 3' OH; magnesium ion; and DNA polymerase. Section: 4.3 8 How is the dNTP added to a DNA strand at the 3' end? Ans: The drawing should indicate clearly how the 3'OH oxygen attacks the α phosphate on the incoming dNTP with the displacement of pyrophosphate. Section: 4.3 and Figure 4.22 9 How does RNA polymerase differ from DNA polymerase? Ans: Although similar in many respects to DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase does not require a primer, nor does it have the nuclease “proofreading” capacity. Section: 4.4