正在加载图片...
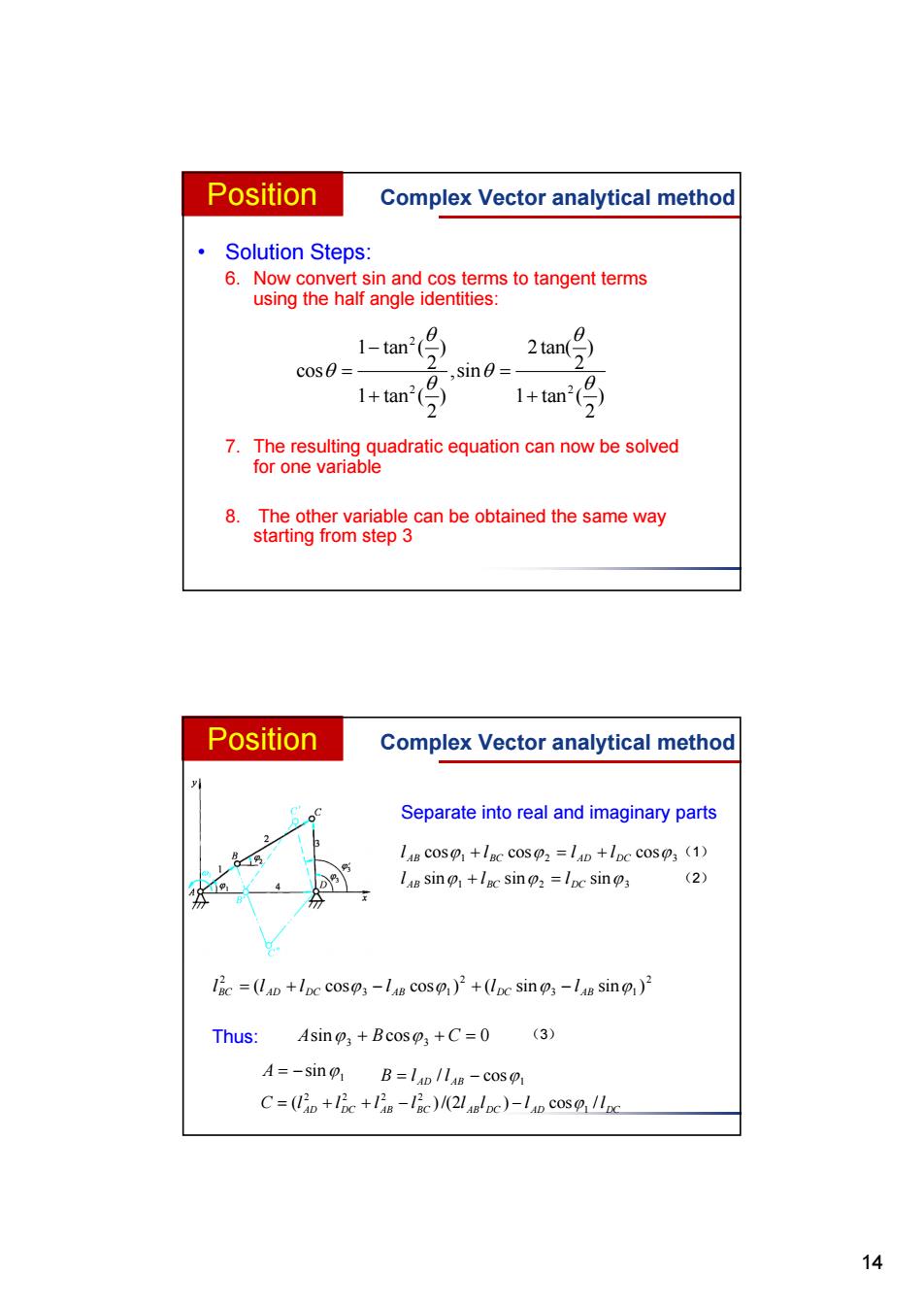
Position Complex Vector analytical method Solution Steps: 6.Now convert sin and cos terms to tangent terms using the half angle identities: 1-tan( cos0 sin0= 2tant 1+tan2( 1+tan2(号) 7.The resulting quadratic equation can now be solved for one variable 8.The other variable can be obtained the same way starting from step 3 Position Complex Vector analytical method Separate into real and imaginary parts LB cos+lac cos2 lD+lpc cos3 (1) La8 sin+lgc sin2 lpc sins (2) lic =(la+lpc coso;-ln cos)+(lpc sino;-laB sin) Thus:Asin;+Bcos +C=0 (3) A=-sin B=lAD/I8-cos C=(lip+lc+l-lic)/(2lglpc)-lap cos /Ipc 1414 • Solution Steps: 6. Now convert sin and cos terms to tangent terms using the half angle identities: 7. The resulting quadratic equation can now be solved for one variable 8. The other variable can be obtained the same way starting from step 3 2 2 2 1 tan ( ) 2 tan( ) 2 2 cos ,sin 1 tan ( ) 1 tan ( ) 2 2 Position Complex Vector analytical method (3) (1) (2) 1 2 3 l AB cos lBC cos l AD lDC cos 1 2 3 l AB sin lBC sin lDC sin 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 ( cos cos ) ( sin sin ) BC AD DC AB DC AB l l l l l l sin cos 0 A 3 B 3 C 1 A sin 1 B l AD / l AB cos AD DC AB BC AB DC AD DC C (l l l l )/(2l l ) l cos /l 1 2 2 2 2 Thus: Separate into real and imaginary parts Position Complex Vector analytical method