正在加载图片...
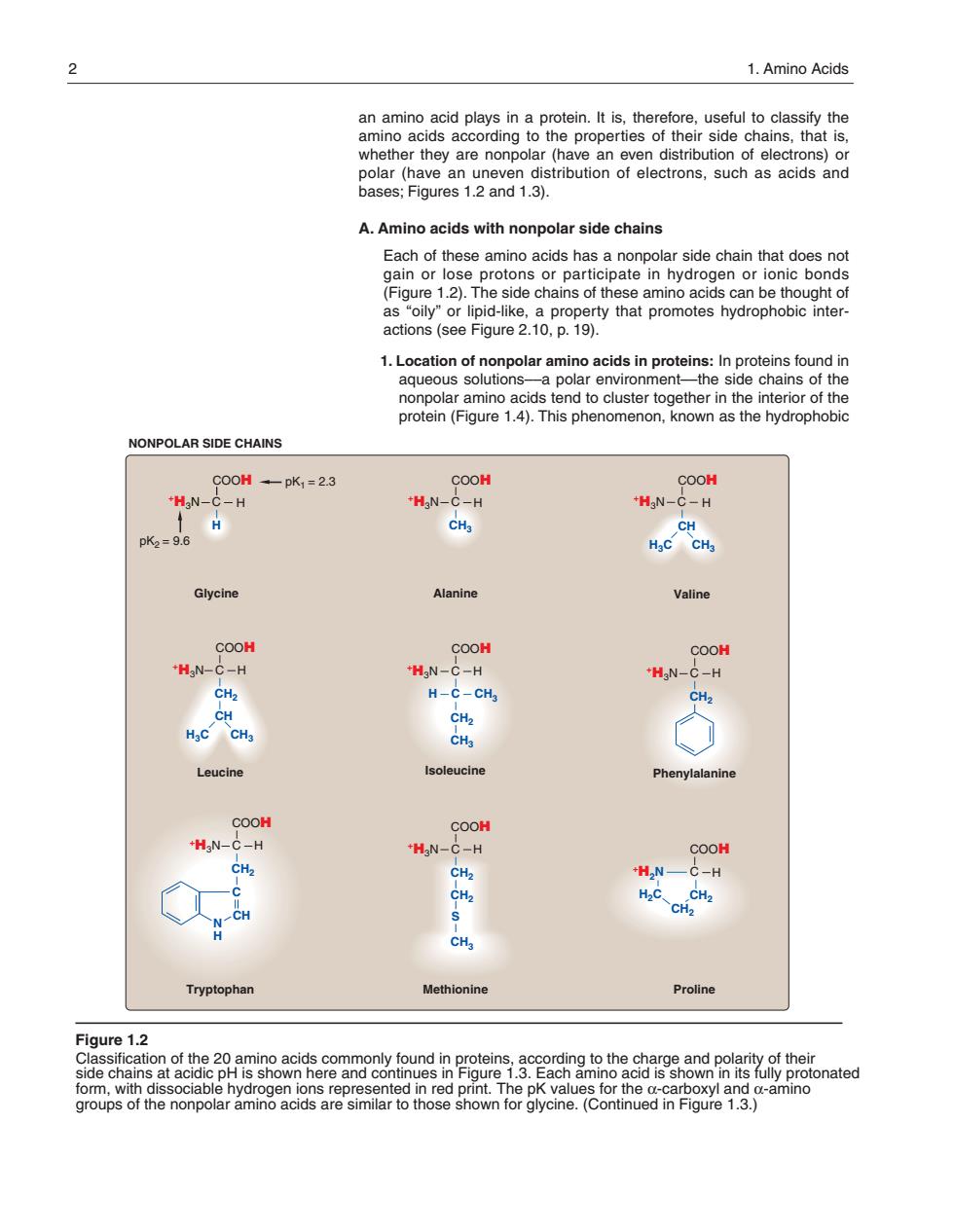
2 1.Amino Acids an amino acid plays in a protein.It is,therefore,useful to classify the amino acids according to the properties of their side chains,that is, whe etner they are nonpol A.Amino acids with nonpolar side chains Each of these amino acids has a nonpolar side chain that does not gain or lose protons or participate in hydrogen or ionic bonds (Figure 1.2).The side chains of these amino acids can be thought of NONPOLAR SIDE CHAINS 00H-pK,=23 COOH COOH 'HgN-C -H "HgN- -H 'HgN-C-H CH pk=9.6 HaC CHa Glycine Alanine Valine COOH COOH COOH H N-C-H 'HgN C-H +HaN-C-H CH> H-C-CHg CH HaC CHa Leucine COOH COOH -HgN- C-H CH2 Tryptophan Methionine Proline Figure 1.2 ciab for the x-amino onated groups onpo an amino acid plays in a protein. It is, therefore, useful to classify the amino acids according to the properties of their side chains, that is, whether they are nonpolar (have an even distribution of electrons) or polar (have an uneven distribution of electrons, such as acids and bases; Figures 1.2 and 1.3). A. Amino acids with nonpolar side chains Each of these amino acids has a nonpolar side chain that does not gain or lose protons or participate in hydrogen or ionic bonds (Figure 1.2). The side chains of these amino acids can be thought of as “oily” or lipid-like, a property that promotes hydro phobicinter - actions (see Figure 2.10, p. 19). 1. Location of nonpolar amino acids in proteins: In proteins found in aqueous solutions––a polar environment––the side chains of the nonpolar amino acids tend to cluster together in the interior of the protein (Figure 1.4). This phenomenon, known as the hydrophobic C +H3N COOH H H pK2 = 9.6 pK1 = 2.3 Glycine C +H3N COOH H CH3 Alanine Valine C +H3N COOH H CH2 Methionine CH2 C +H3N COOH H CH2 Phenylalanine C +H3N COOH H CH2 Tryptophan C CH N H S CH3 COOH H Proline C CH2 +H2N CH2 H2C NONPOLAR SIDE CHAINS Figure 1.2 Classification of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins, according to the charge and polarity of their side chains at acidic pH is shown here and continues in Figure 1.3. Each amino acid is shown in its fully protonated form, with dissociable hydrogen ions represented in red print. The pK values for the α-carboxyl and α-amino groups of the nonpolar amino acids are similar to those shown for glycine. (Continued in Figure 1.3.) C +H3N COOH H CH H3C CH3 C +H3N COOH H CH2 Leucine CH H3C CH3 C +H3N COOH H CH3 H CH C 3 CH2 Isoleucine 2 1. Amino Acids 168397_P001-012.qxd7.0:02 Protein structure 5-20-04 2010.4.4 9:45 AM Page 2