正在加载图片...
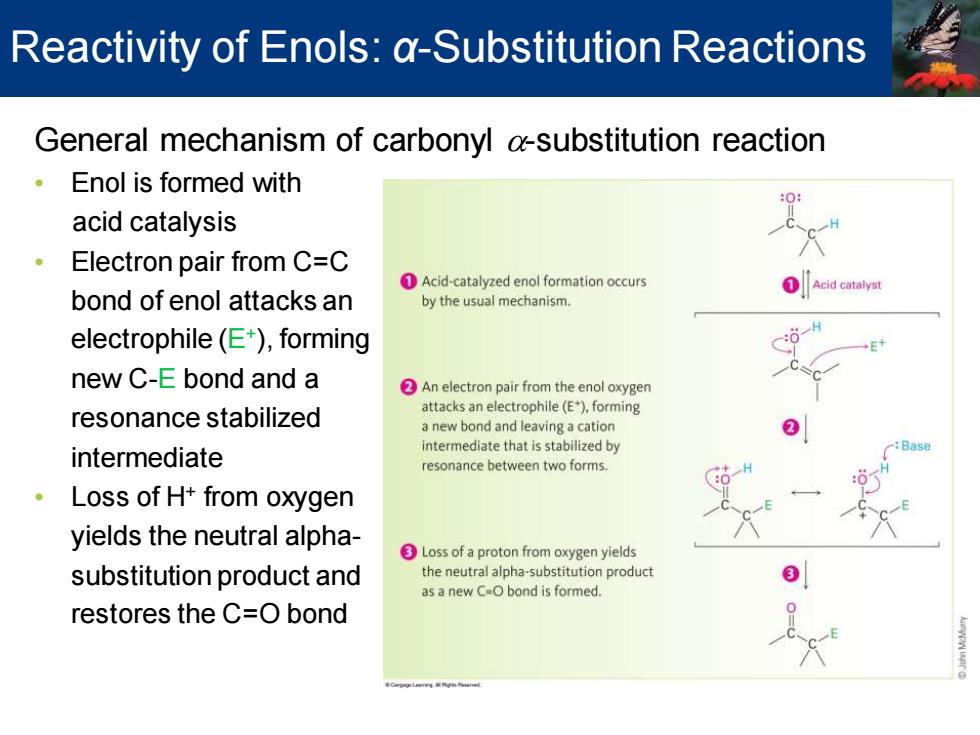
Reactivity of Enols:a-Substitution Reactions General mechanism of carbonyl a-substitution reaction 。 Enol is formed with acid catalysis Electron pair from C=C Acid-catalyzed enol formation occurs Acid catalyst bond of enol attacks an by the usual mechanism. electrophile(E),forming new C-E bond and a An electron pair from the enol oxygen resonance stabilized attacks an electrophile(E),forming a new bond and leaving a cation intermediate intermediate that is stabilized by resonance between two forms. ·Loss of H+from oxygen yields the neutral alpha- Loss of a proton from oxygen yields substitution product and the neutral alpha-substitution product as a new C-O bond is formed. restores the C=O bondGeneral mechanism of carbonyl a-substitution reaction • Enol is formed with acid catalysis • Electron pair from C=C bond of enol attacks an electrophile (E+ ), forming new C-E bond and a resonance stabilized intermediate • Loss of H+ from oxygen yields the neutral alphasubstitution product and restores the C=O bond Reactivity of Enols: α-Substitution Reactions