正在加载图片...
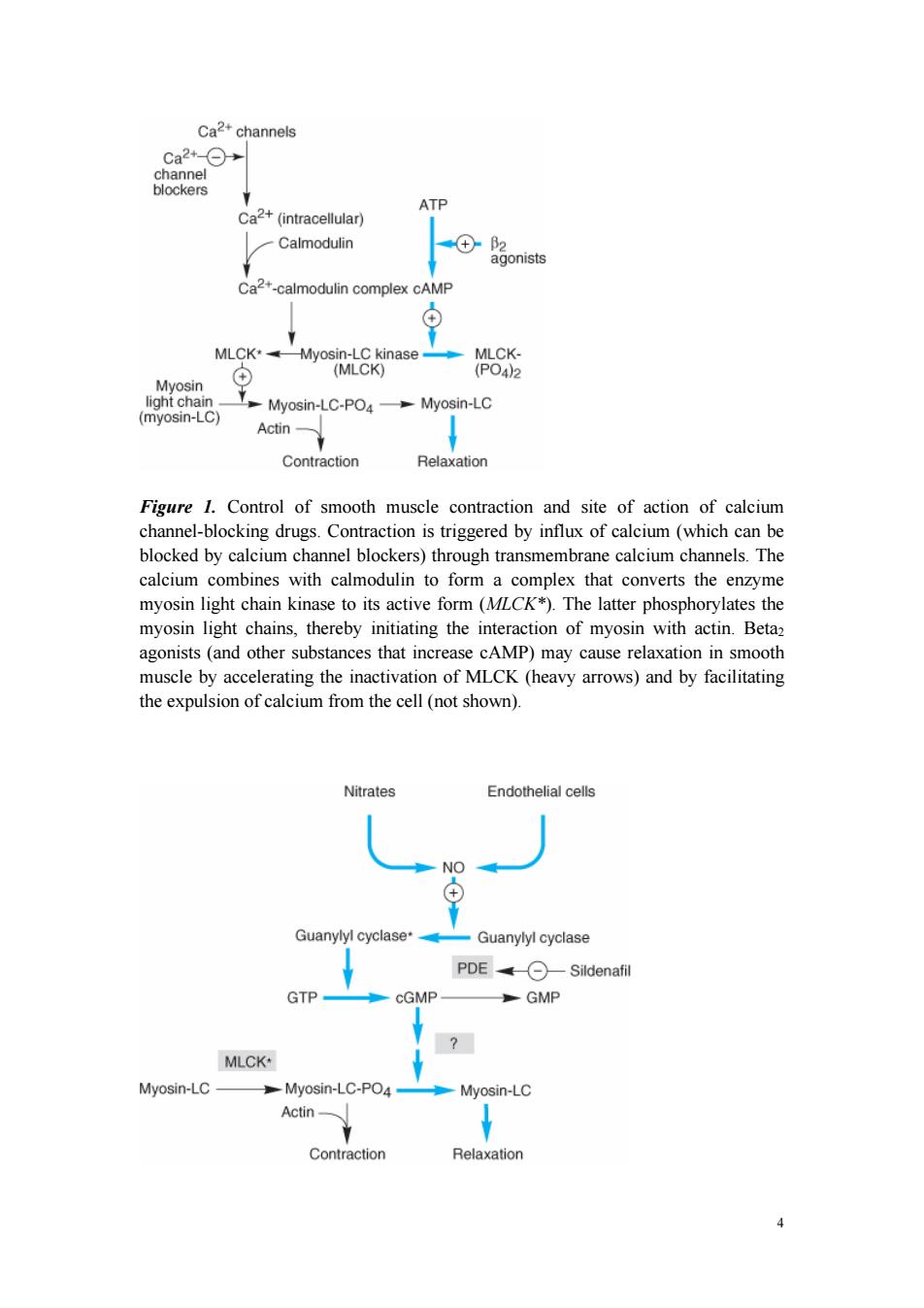
Ca2+channels ca2+-O→ channel blockers ATP Ca2+(intracellular) Calmodulin +-2 agonists Ca2+-calmodulin complex cAMP MLCK*Myosin-LC kinase MLCK- (+ (MLCK) (PO42 Myosin light chain- (myosin-LC) Myosin-LC-PO4Myosin-LC Actin- Contraction Relaxation Figure 1.Control of smooth muscle contraction and site of action of calcium channel-blocking drugs.Contraction is triggered by influx of calcium (which can be blocked by calcium channel blockers)through transmembrane calcium channels.The calcium combines with calmodulin to form a complex that converts the enzyme myosin light chain kinase to its active form (MLCK*).The latter phosphorylates the myosin light chains,thereby initiating the interaction of myosin with actin.Betaz agonists (and other substances that increase cAMP)may cause relaxation in smooth muscle by accelerating the inactivation of MLCK (heavy arrows)and by facilitating the expulsion of calcium from the cell(not shown). Nitrates Endothelial cells NO Guanylyl cyclase* Guanylyl cyclase PDE Sildenafil GTP cGMP GMP MLCK* Myosin-LC Myosin-LC-PO4- Myosin-LC Actin- Contraction Relaxation4 Figure 1. Control of smooth muscle contraction and site of action of calcium channel-blocking drugs. Contraction is triggered by influx of calcium (which can be blocked by calcium channel blockers) through transmembrane calcium channels. The calcium combines with calmodulin to form a complex that converts the enzyme myosin light chain kinase to its active form (MLCK*). The latter phosphorylates the myosin light chains, thereby initiating the interaction of myosin with actin. Beta2 agonists (and other substances that increase cAMP) may cause relaxation in smooth muscle by accelerating the inactivation of MLCK (heavy arrows) and by facilitating the expulsion of calcium from the cell (not shown)