正在加载图片...
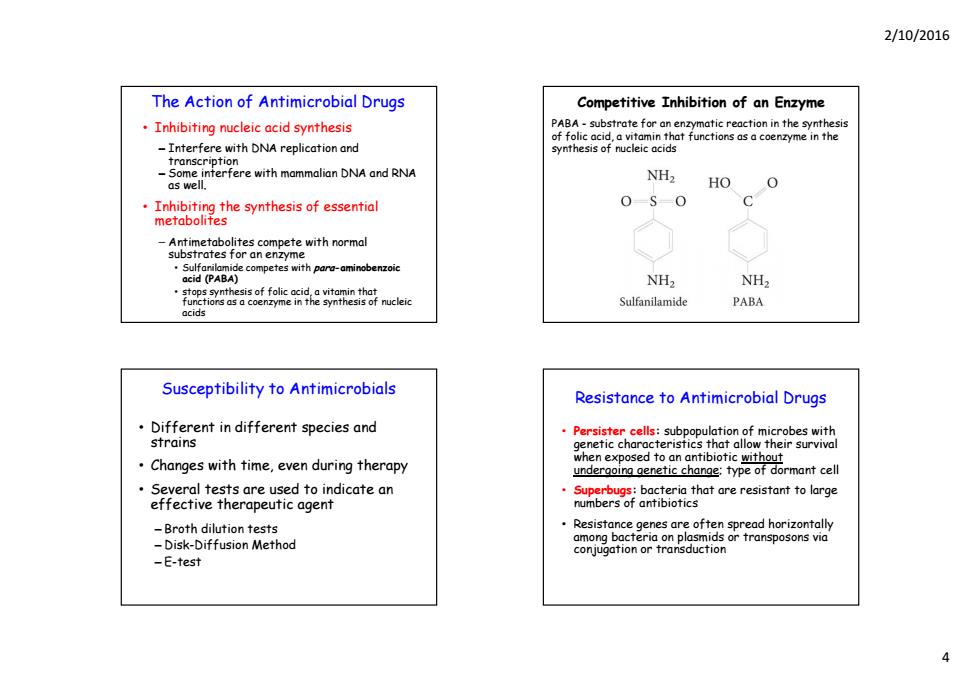
2/10/2016 The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs Competitive Inhibition of an Enzyme Inhibiting nucleic acid synthesis PABA-substrate for an enzymatic reaction in the synthesis of folic acid,a vitamin that functions as a coenzyme in the -Interfere with DNA replication and synthesis of nucleic acids transcription -Some interfere with mammalian DNA and RNA NH2 as well. HO Inhibiting the synthesis of essential 0S0 metabolites -Antimetabolites compete with normal rates for an enzyme cpparg-minobenoie NH2 NH2 hemef nucleic Sulfanilamide PABA Susceptibility to Antimicrobials Resistance to Antimicrobial Drugs Different in different species and Persister cells:subpopulation of microbes with strains C characteristics that allow their s Changes with time,even during therapy en exposed to antibiotic witho undergoing genetic change:type of dormant cell Several tests are used to indicate an Superbugs:bacteria that are resistant to large effective therapeutic agent numbers of antibiofics -Broth dilution tests Resistance genes are often spread horizontally -Disk-Diffusion Method among bacteria on plasmids or transposons via conjugation or transduction -E-test 2/10/2016 4 The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs • Inhibiting nucleic acid synthesis – Interfere with DNA replication and transcr transcr pt on i i – Some interfere with mammalian DNA and RNA as well. • Inhibiting the synthesis of essential metabolites – Antimetabolites compete with normal substrates for an enzyme • Sulfanilamide competes with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) • stops synthesis of folic acid, a vitamin that functions as a coenzyme in the synthesis of nucleic acids Competitive Inhibition of an Enzyme PABA - substrate for an enzymatic reaction in the synthesis of folic acid, a vitamin that functions as a coenzyme in the synthesis of nucleic acids Susceptibility to Antimicrobials • Different in different species and stra ns i • Changes with time, even during therapy • Several tests are used to indicate an effective therapeutic agent – B th dil ti t sts Broth dilution tests – Disk-Diffusion Method – E-test Resistance to Antimicrobial Drugs • Persister cells: subpopulation of microbes with genetic characteristics that allow their survival when exposed to an antibiotic without undergoing genetic change; type of dormant cell • Superbugs: bacteria that are resistant to large numbers of antibiotics • Resistance genes are often spread horizontally among bacteria on plasmids or transposons via conjugation or transduction