正在加载图片...
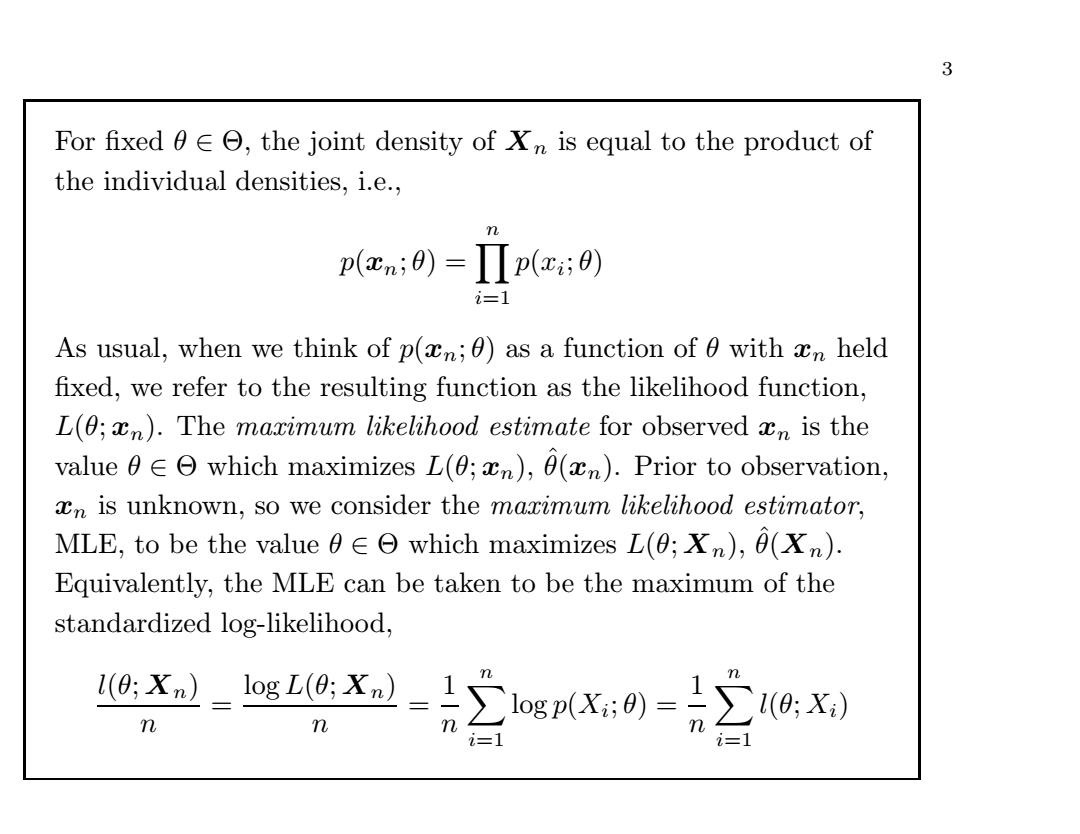
3 For fixed aee,the joint density of Xn is equal to the product of the individual densities,i.e., p(cn;0)=Πp(c;8) i=1 As usual,when we think of p(n;0)as a function of 0 with n held fixed,we refer to the resulting function as the likelihood function, L(0;n).The maximum likelihood estimate for observed xn is the value 0 which maximizes L(;),0(n).Prior to observation, xn is unknown,so we consider the marimum likelihood estimator, MLE,to be the value 0e which maximizes L(;Xn),0(Xn). Equivalently,the MLE can be taken to be the maximum of the standardized log-likelihood, 1(0;Xn)log L(0;Xn) 2 -2∑1ogp(x:0)=∑ (0:X) n n m m i=1 i=13 For fixed θ ∈ Θ, the joint density of Xn is equal to the product of the individual densities, i.e., p(xn; θ) = n i=1 p(xi; θ) As usual, when we think of p(xn; θ) as a function of θ with xn held fixed, we refer to the resulting function as the likelihood function, L(θ; xn). The maximum likelihood estimate for observed xn is the value θ ∈ Θ which maximizes L(θ; xn), ˆ θ(xn). Prior to observation, xn is unknown, so we consider the maximum likelihood estimator, MLE, to be the value θ ∈ Θ which maximizes L(θ; Xn), ˆ θ(Xn). Equivalently, the MLE can be taken to be the maximum of the standardized log-likelihood, l(θ; Xn) n = log L(θ; Xn) n = 1 n n i=1 log p(Xi; θ) = 1n n i=1 l(θ; Xi)��