正在加载图片...
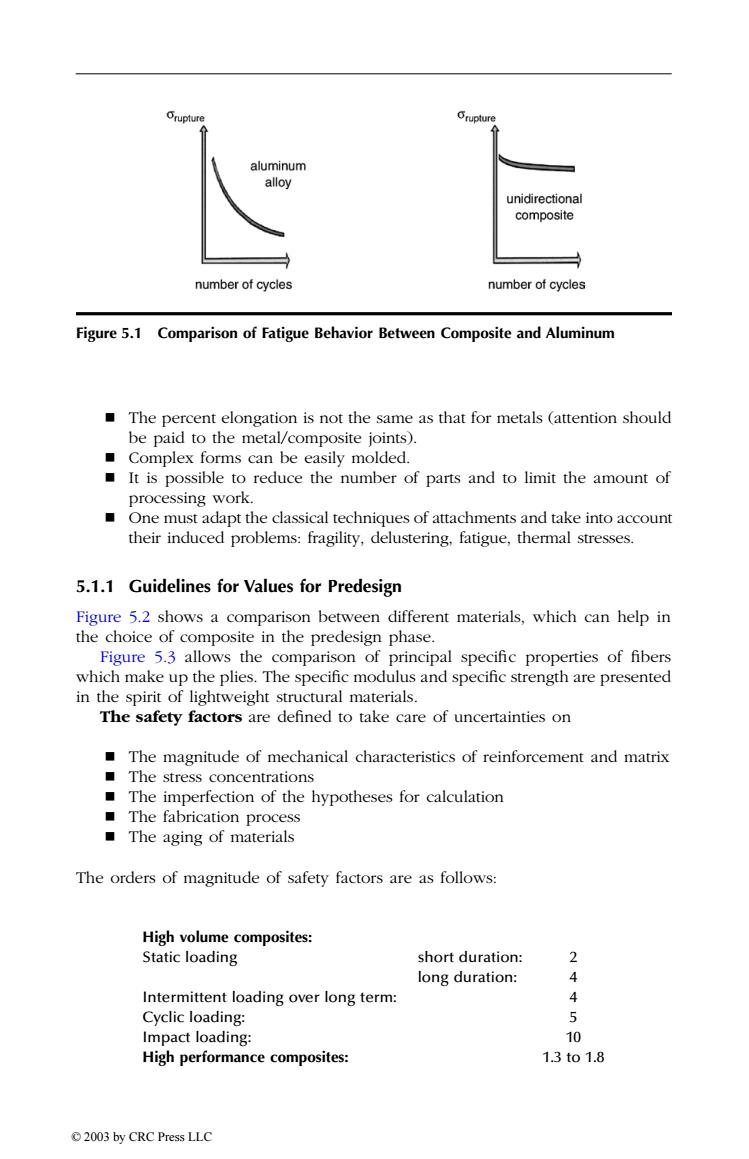
rupture aluminum alloy unidirectional composite number of cycles number of cycles Figure 5.1 Comparison of Fatigue Behavior Between Composite and Aluminum The percent elongation is not the same as that for metals (attention should be paid to the metal/composite joints). Complex forms can be easily molded. It is possible to reduce the number of parts and to limit the amount of processing work. One must adapt the classical techniques of attachments and take into account their induced problems:fragility,delustering,fatigue,thermal stresses. 5.1.1 Guidelines for Values for Predesign Figure 5.2 shows a comparison between different materials,which can help in the choice of composite in the predesign phase. Figure 5.3 allows the comparison of principal specific properties of fibers which make up the plies.The specific modulus and specific strength are presented in the spirit of lightweight structural materials. The safety factors are defined to take care of uncertainties on The magnitude of mechanical characteristics of reinforcement and matrix The stress concentrations The imperfection of the hypotheses for calculation The fabrication process The aging of materials The orders of magnitude of safety factors are as follows: High volume composites: Static loading short duration: 2 long duration: 4 Intermittent loading over long term: 4 Cyclic loading: 5 Impact loading: 10 High performance composites: 13to1.8 2003 by CRC Press LLC The percent elongation is not the same as that for metals (attention should be paid to the metal/composite joints). Complex forms can be easily molded. It is possible to reduce the number of parts and to limit the amount of processing work. One must adapt the classical techniques of attachments and take into account their induced problems: fragility, delustering, fatigue, thermal stresses. 5.1.1 Guidelines for Values for Predesign Figure 5.2 shows a comparison between different materials, which can help in the choice of composite in the predesign phase. Figure 5.3 allows the comparison of principal specific properties of fibers which make up the plies. The specific modulus and specific strength are presented in the spirit of lightweight structural materials. The safety factors are defined to take care of uncertainties on The magnitude of mechanical characteristics of reinforcement and matrix The stress concentrations The imperfection of the hypotheses for calculation The fabrication process The aging of materials The orders of magnitude of safety factors are as follows: Figure 5.1 Comparison of Fatigue Behavior Between Composite and Aluminum High volume composites: Static loading short duration: 2 long duration: 4 Intermittent loading over long term: 4 Cyclic loading: 5 Impact loading: 10 High performance composites: 1.3 to 1.8 TX846_Frame_C05 Page 70 Monday, November 18, 2002 12:09 PM © 2003 by CRC Press LLC