正在加载图片...
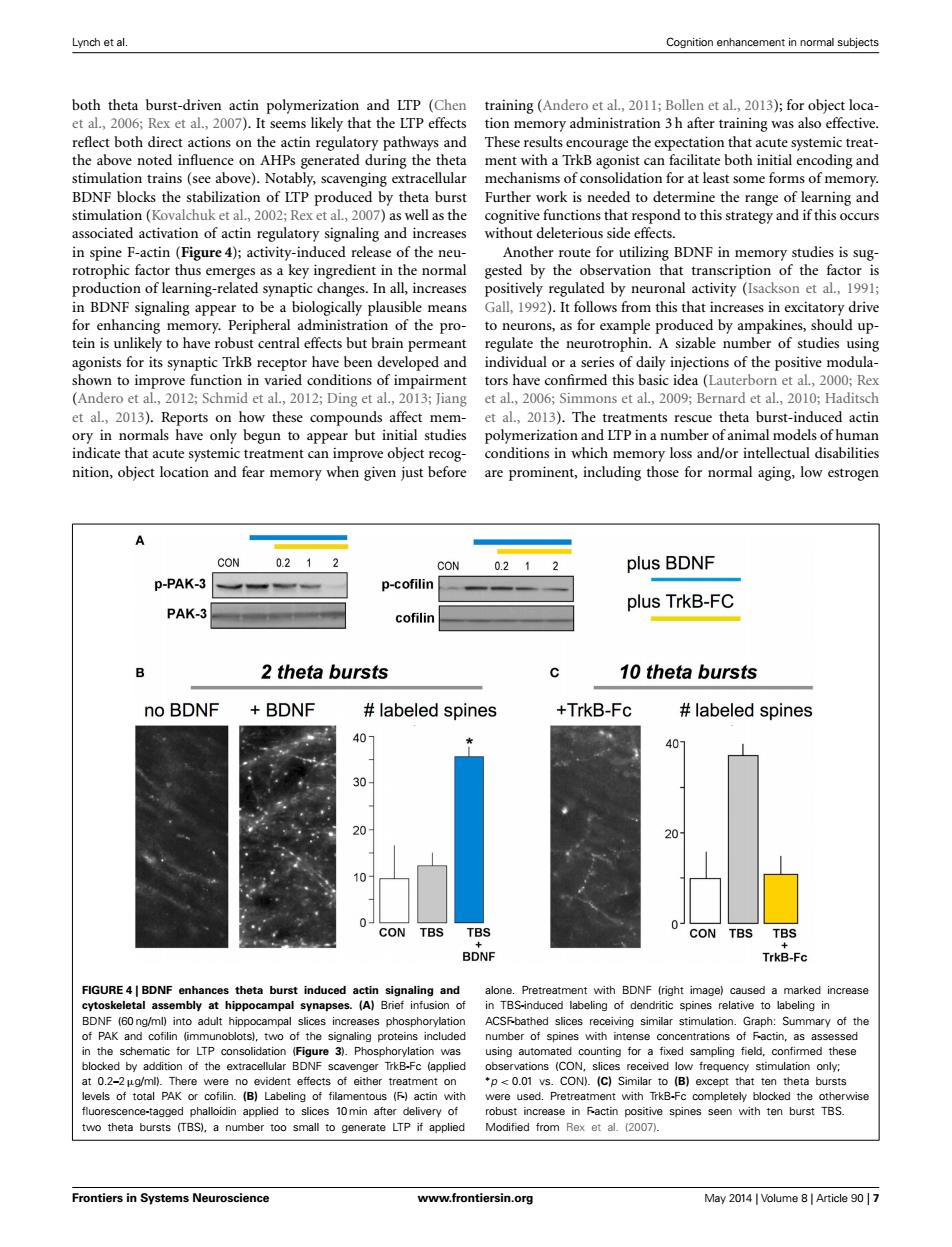
Lynch et al. Cognition enhancement in normal subjects both theta burst-driven actin polymerization and LTP (Chen training(Andero et al.,2011;Bollen et al,2013);for object loca- et al.,2006;Rex et al.,2007).It seems likely that the LTP effects tion memory administration 3 h after training was also effective. reflect both direct actions on the actin regulatory pathways and These results encourage the expectation that acute systemic treat- the above noted influence on AHPs generated during the theta ment with a TrkB agonist can facilitate both initial encoding and stimulation trains(see above).Notably,scavenging extracellular mechanisms of consolidation for at least some forms of memory BDNF blocks the stabilization of LTP produced by theta burst Further work is needed to determine the range of learning and stimulation(Kovalchuk et al.,2002;Rex et al.,2007)as well as the cognitive functions that respond to this strategy and if this occurs associated activation of actin regulatory signaling and increases without deleterious side effects. in spine F-actin(Figure 4);activity-induced release of the neu- Another route for utilizing BDNF in memory studies is sug- rotrophic factor thus emerges as a key ingredient in the normal gested by the observation that transcription of the factor is production of learning-related synaptic changes.In all,increases positively regulated by neuronal activity (Isackson et al.,1991; in BDNF signaling appear to be a biologically plausible means Gall,1992).It follows from this that increases in excitatory drive for enhancing memory.Peripheral administration of the pro- to neurons,as for example produced by ampakines,should up- tein is unlikely to have robust central effects but brain permeant regulate the neurotrophin.A sizable number of studies using agonists for its synaptic TrkB receptor have been developed and individual or a series of daily injections of the positive modula- shown to improve function in varied conditions of impairment tors have confirmed this basic idea(Lauterborn et al,2000;Rex (Andero et al,2012;Schmid et al.,2012;Ding et al.,2013;Jiang et al,2006;Simmons et al.,2009;Bernard et al,2010;Haditsch et al.,2013).Reports on how these compounds affect mem- et al.,2013).The treatments rescue theta burst-induced actin ory in normals have only begun to appear but initial studies polymerization and LTP in a number of animal models of human indicate that acute systemic treatment can improve object recog- conditions in which memory loss and/or intellectual disabilities nition,object location and fear memory when given just before are prominent,including those for normal aging,low estrogen CON 0.21 CON 0.212 plus BDNF p-PAK-3 p-cofilin plus TrkB-FC PAK-3 cofilin B 2 theta bursts 10 theta bursts no BDNF BDNF labeled spines +TrkB-Fc labeled spines 40- 40 30 20 20- 10 0 0 CON TBS TBS CON TBS TBS BDNF TrkB-Fc FIGURE4 BDNF enhances theta burst induced actin signaling and alone.Pretreatment with BDNF (right image)caused a marked increase cytoskeletal assembly at hippocampal synapses.(A)Brief infusion of in TBS-induced labeling of dendritic spines relative to labeling in BDNF (60 ng/ml)into adult hippocampal slices increases phosphorylation ACSFbathed slices receiving similar stimulation.Graph:Summary of the of PAK and cofilin (immunoblots),two of the signaling proteins included number of spines with intense concentrations of Factin,as assessed in the schematic for LTP consolidation (Figure 3).Phosphorylation was using automated counting for a fixed sampling field,confirmed these blocked by addition of the extracellular BDNF scavenger TrkB-Fc (applied observations (CON,slices received low frequency stimulation only; at 0.2-2ug/ml).There were no evident effects of either treatment on *p<0.01 vs.CON).(C)Similar to (B)except that ten theta bursts levels of total PAK or cofilin.(B)Labeling of filamentous (F)actin with were used.Pretreatment with TrkB-Fc completely blocked the otherwise fluorescence-tagged phalloidin applied to slices 10min after delivery of robust increase in Factin positive spines seen with ten burst TBS. two theta bursts (TBS),a number too small to generate LTP if applied Modified from Rex et al.(2007). Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience www.frontiersin.org May 2014 Volume 8 Article 907Lynch et al. Cognition enhancement in normal subjects both theta burst-driven actin polymerization and LTP (Chen et al., 2006; Rex et al., 2007). It seems likely that the LTP effects reflect both direct actions on the actin regulatory pathways and the above noted influence on AHPs generated during the theta stimulation trains (see above). Notably, scavenging extracellular BDNF blocks the stabilization of LTP produced by theta burst stimulation (Kovalchuk et al., 2002; Rex et al., 2007) as well as the associated activation of actin regulatory signaling and increases in spine F-actin (Figure 4); activity-induced release of the neurotrophic factor thus emerges as a key ingredient in the normal production of learning-related synaptic changes. In all, increases in BDNF signaling appear to be a biologically plausible means for enhancing memory. Peripheral administration of the protein is unlikely to have robust central effects but brain permeant agonists for its synaptic TrkB receptor have been developed and shown to improve function in varied conditions of impairment (Andero et al., 2012; Schmid et al., 2012; Ding et al., 2013; Jiang et al., 2013). Reports on how these compounds affect memory in normals have only begun to appear but initial studies indicate that acute systemic treatment can improve object recognition, object location and fear memory when given just before training (Andero et al., 2011; Bollen et al., 2013); for object location memory administration 3 h after training was also effective. These results encourage the expectation that acute systemic treatment with a TrkB agonist can facilitate both initial encoding and mechanisms of consolidation for at least some forms of memory. Further work is needed to determine the range of learning and cognitive functions that respond to this strategy and if this occurs without deleterious side effects. Another route for utilizing BDNF in memory studies is suggested by the observation that transcription of the factor is positively regulated by neuronal activity (Isackson et al., 1991; Gall, 1992). It follows from this that increases in excitatory drive to neurons, as for example produced by ampakines, should upregulate the neurotrophin. A sizable number of studies using individual or a series of daily injections of the positive modulators have confirmed this basic idea (Lauterborn et al., 2000; Rex et al., 2006; Simmons et al., 2009; Bernard et al., 2010; Haditsch et al., 2013). The treatments rescue theta burst-induced actin polymerization and LTP in a number of animal models of human conditions in which memory loss and/or intellectual disabilities are prominent, including those for normal aging, low estrogen FIGURE 4 | BDNF enhances theta burst induced actin signaling and cytoskeletal assembly at hippocampal synapses. (A) Brief infusion of BDNF (60 ng/ml) into adult hippocampal slices increases phosphorylation of PAK and cofilin (immunoblots), two of the signaling proteins included in the schematic for LTP consolidation (Figure 3). Phosphorylation was blocked by addition of the extracellular BDNF scavenger TrkB-Fc (applied at 0.2–2µg/ml). There were no evident effects of either treatment on levels of total PAK or cofilin. (B) Labeling of filamentous (F-) actin with fluorescence-tagged phalloidin applied to slices 10 min after delivery of two theta bursts (TBS), a number too small to generate LTP if applied alone. Pretreatment with BDNF (right image) caused a marked increase in TBS-induced labeling of dendritic spines relative to labeling in ACSF-bathed slices receiving similar stimulation. Graph: Summary of the number of spines with intense concentrations of F-actin, as assessed using automated counting for a fixed sampling field, confirmed these observations (CON, slices received low frequency stimulation only; ∗p < 0.01 vs. CON). (C) Similar to (B) except that ten theta bursts were used. Pretreatment with TrkB-Fc completely blocked the otherwise robust increase in F-actin positive spines seen with ten burst TBS. Modified from Rex et al. (2007). Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience www.frontiersin.org May 2014 | Volume 8 | Article 90 | 7