正在加载图片...
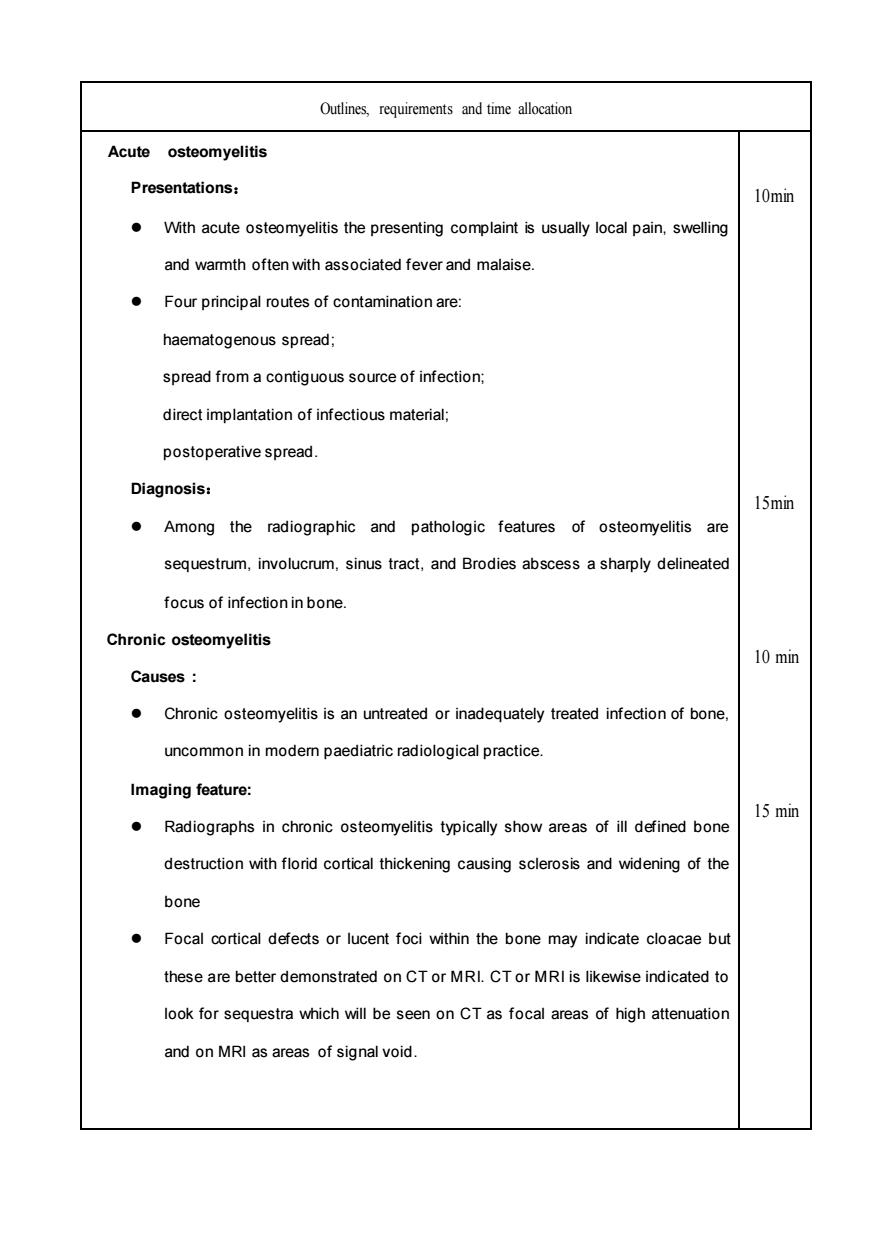
Outlines requirements and time allocation Acute osteomyelitis Presentations: 10min With acute osteomyelitis the presenting complaint is usually local pain,swelling and warmth often with associated fever and malaise. Four principal routes of contamination are: haematogenous spread; spread from a contiguous source of infection: direct implantation of infectious material: postoperative spread. Diagnosis: 15min Among the radiographic and pathologic features of osteomyelitis are sequestrum,involucrum,sinus tract,and Brodies abscess a sharply delineated focus of infection in bone Chronic osteomyelitis 10 min Causes: .Chronic osteomyelitis is an untreated or inadequately treated infection of bone. uncommon in modem paediatric radiological practice Imaging feature: Radiographs in chronic osteomyelitis typically show areas of ill defined bone 15 min destruction with florid cortical thickening causing sclerosis and widening of the bone Focal corical defects or lucent foci within the bone may indicate cloacae bu these are better demonstrated on CT or MRI.CTor MRI is likewise indicated to look for sequestra which will be seen on CT as focal areas of high attenuation and on MRI as areas of signal void.Outlines, requirements and time allocation Acute osteomyelitis Presentations: ⚫ With acute osteomyelitis the presenting complaint is usually local pain, swelling and warmth often with associated fever and malaise. ⚫ Four principal routes of contamination are: haematogenous spread; spread from a contiguous source of infection; direct implantation of infectious material; postoperative spread. Diagnosis: ⚫ Among the radiographic and pathologic features of osteomyelitis are sequestrum, involucrum, sinus tract, and Brodies abscess a sharply delineated focus of infection in bone. Chronic osteomyelitis Causes : ⚫ Chronic osteomyelitis is an untreated or inadequately treated infection of bone, uncommon in modern paediatric radiological practice. Imaging feature: ⚫ Radiographs in chronic osteomyelitis typically show areas of ill defined bone destruction with florid cortical thickening causing sclerosis and widening of the bone ⚫ Focal cortical defects or lucent foci within the bone may indicate cloacae but these are better demonstrated on CT or MRI. CT or MRI is likewise indicated to look for sequestra which will be seen on CT as focal areas of high attenuation and on MRI as areas of signal void. 10min 15min 10 min 15 min