正在加载图片...
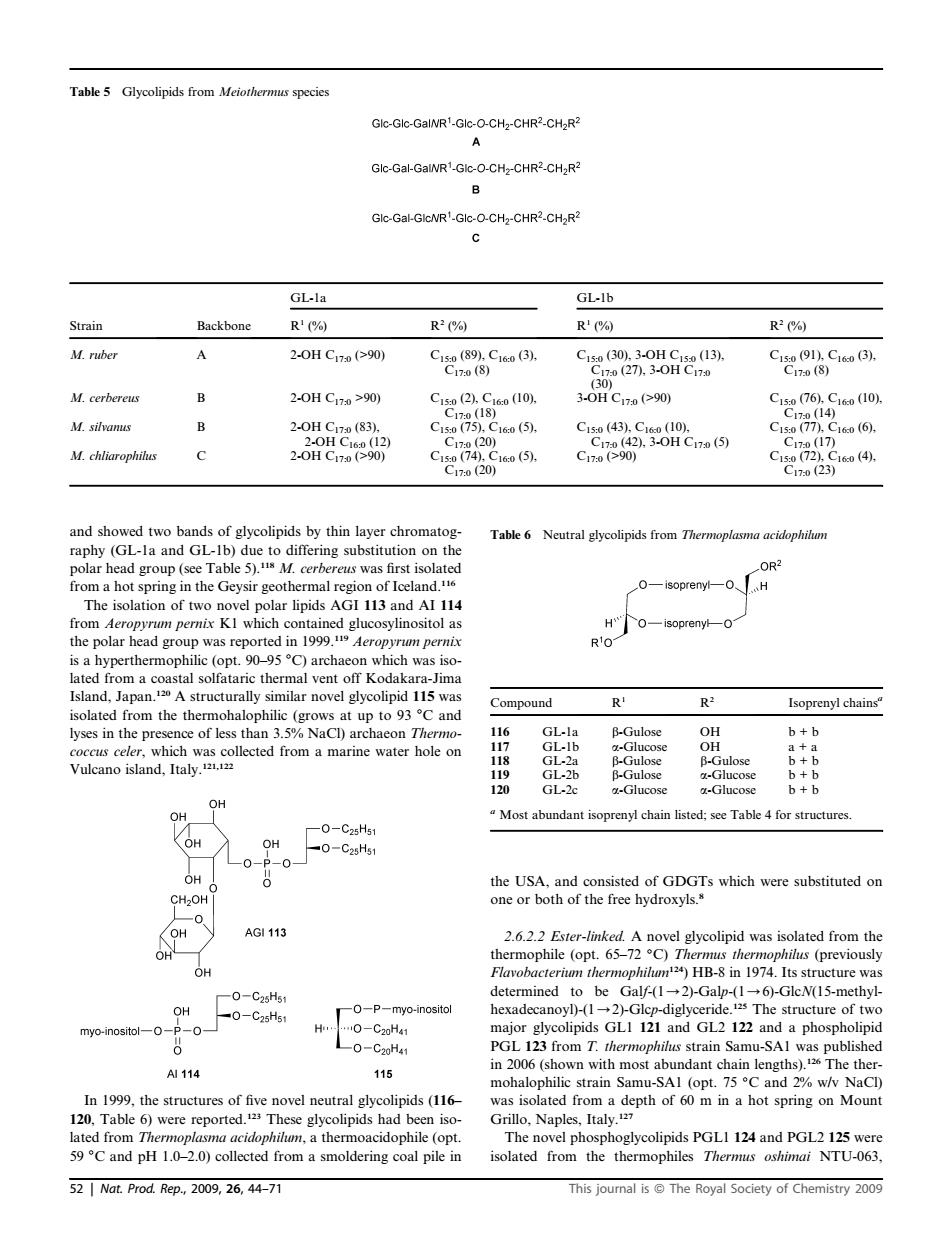
Gkc-GIc-GaINR'.Glc-O-CHzCHRCH,R 9 Gkc-Gal-GaIWRGkc-O-CH-CHR>CH.R 9 Gkc-Gal-GIcNR'-Glc-O-CH.-CHR-CHaR GLla GL-lb Strain Backbone R'% R2(% R) R2% M ruber A 2.0HCm90 B 2.0HCm≥90 CeSol M.silvanus 2-0HC2n(83) C1s077 C10(6. M.chliarophils 2.0HC,m90 60(5. Cra (5) Ci (4. and showed two bands of glycolipids by thin layer chromatog Table 6 from a hot s which cont cosylin R he R3 Isoprenyl chains lyses in the pres GL-I B-Gulose + 120 群 Most abundant isoprenyl chain listed;see Table 4 for structures OH OH OH AG1113 2.6.2.2 Ester-linked.A novel glycolipid was isolated from the OH cture 一0-Ca4 OH hexadecanoyl)-(12)-Glcp digl ceride The structure of two myo-inositol- 0-C2H4 major glycolipids GLI 121 and GL2 122 and a phospholipid o-C20H41 o with most ab amu-S The th A114 115 mohalophilic strain Samu-SAl (opt.75C and%w NaCl) a5 m a depth of0m in a hot spring on Mount ated thermoacidophile (opt. ThePGLl 124d PGL212re 59C and pH 1.0-2.0)collected from a smoldering coal pile in isolated from the thermophiles Thermus oshimai NTU-063. 521 Nat.Prod.Rep2009,26,44-77 This journal isThe Royal Society of Chemistry009 and showed two bands of glycolipids by thin layer chromatography (GL-1a and GL-1b) due to differing substitution on the polar head group (see Table 5).118 M. cerbereus was first isolated from a hot spring in the Geysir geothermal region of Iceland.116 The isolation of two novel polar lipids AGI 113 and AI 114 from Aeropyrum pernix K1 which contained glucosylinositol as the polar head group was reported in 1999.119 Aeropyrum pernix is a hyperthermophilic (opt. 90–95 C) archaeon which was isolated from a coastal solfataric thermal vent off Kodakara-Jima Island, Japan.120 A structurally similar novel glycolipid 115 was isolated from the thermohalophilic (grows at up to 93 C and lyses in the presence of less than 3.5% NaCl) archaeon Thermococcus celer, which was collected from a marine water hole on Vulcano island, Italy.121,122 In 1999, the structures of five novel neutral glycolipids (116– 120, Table 6) were reported.123 These glycolipids had been isolated from Thermoplasma acidophilum, a thermoacidophile (opt. 59 C and pH 1.0–2.0) collected from a smoldering coal pile in the USA, and consisted of GDGTs which were substituted on one or both of the free hydroxyls.8 2.6.2.2 Ester-linked. A novel glycolipid was isolated from the thermophile (opt. 65–72 C) Thermus thermophilus (previously Flavobacterium thermophilum124) HB-8 in 1974. Its structure was determined to be Galf-(1/2)-Galp-(1/6)-GlcN(15-methylhexadecanoyl)-(1/2)-Glcp-diglyceride.125 The structure of two major glycolipids GL1 121 and GL2 122 and a phospholipid PGL 123 from T. thermophilus strain Samu-SA1 was published in 2006 (shown with most abundant chain lengths).126 The thermohalophilic strain Samu-SA1 (opt. 75 C and 2% w/v NaCl) was isolated from a depth of 60 m in a hot spring on Mount Grillo, Naples, Italy.127 The novel phosphoglycolipids PGL1 124 and PGL2 125 were isolated from the thermophiles Thermus oshimai NTU-063, Table 5 Glycolipids from Meiothermus species Strain Backbone GL-1a GL-1b R1 (%) R2 (%) R1 (%) R2 (%) M. ruber A 2-OH C17:0 (>90) C15:0 (89), C16:0 (3), C17:0 (8) C15:0 (30), 3-OH C15:0 (13), C17:0 (27), 3-OH C17:0 (30) C15:0 (91), C16:0 (3), C17:0 (8) M. cerbereus B 2-OH C17:0 >90) C15:0 (2), C16:0 (10), C17:0 (18) 3-OH C17:0 (>90) C15:0 (76), C16:0 (10), C17:0 (14) M. silvanus B 2-OH C17:0 (83), 2-OH C16:0 (12) C15:0 (75), C16:0 (5), C17:0 (20) C15:0 (43), C16:0 (10), C17:0 (42), 3-OH C17:0 (5) C15:0 (77), C16:0 (6), C17:0 (17) M. chliarophilus C 2-OH C17:0 (>90) C15:0 (74), C16:0 (5), C17:0 (20) C17:0 (>90) C15:0 (72), C16:0 (4), C17:0 (23) Table 6 Neutral glycolipids from Thermoplasma acidophilum Compound R1 R2 Isoprenyl chainsa 116 GL-1a b-Gulose OH b + b 117 GL-1b a-Glucose OH a + a 118 GL-2a b-Gulose b-Gulose b + b 119 GL-2b b-Gulose a-Glucose b + b 120 GL-2c a-Glucose a-Glucose b + b a Most abundant isoprenyl chain listed; see Table 4 for structures. 52 | Nat. Prod. Rep., 2009, 26, 44–71 This journal is ª The Royal Society of Chemistry 2009