正在加载图片...
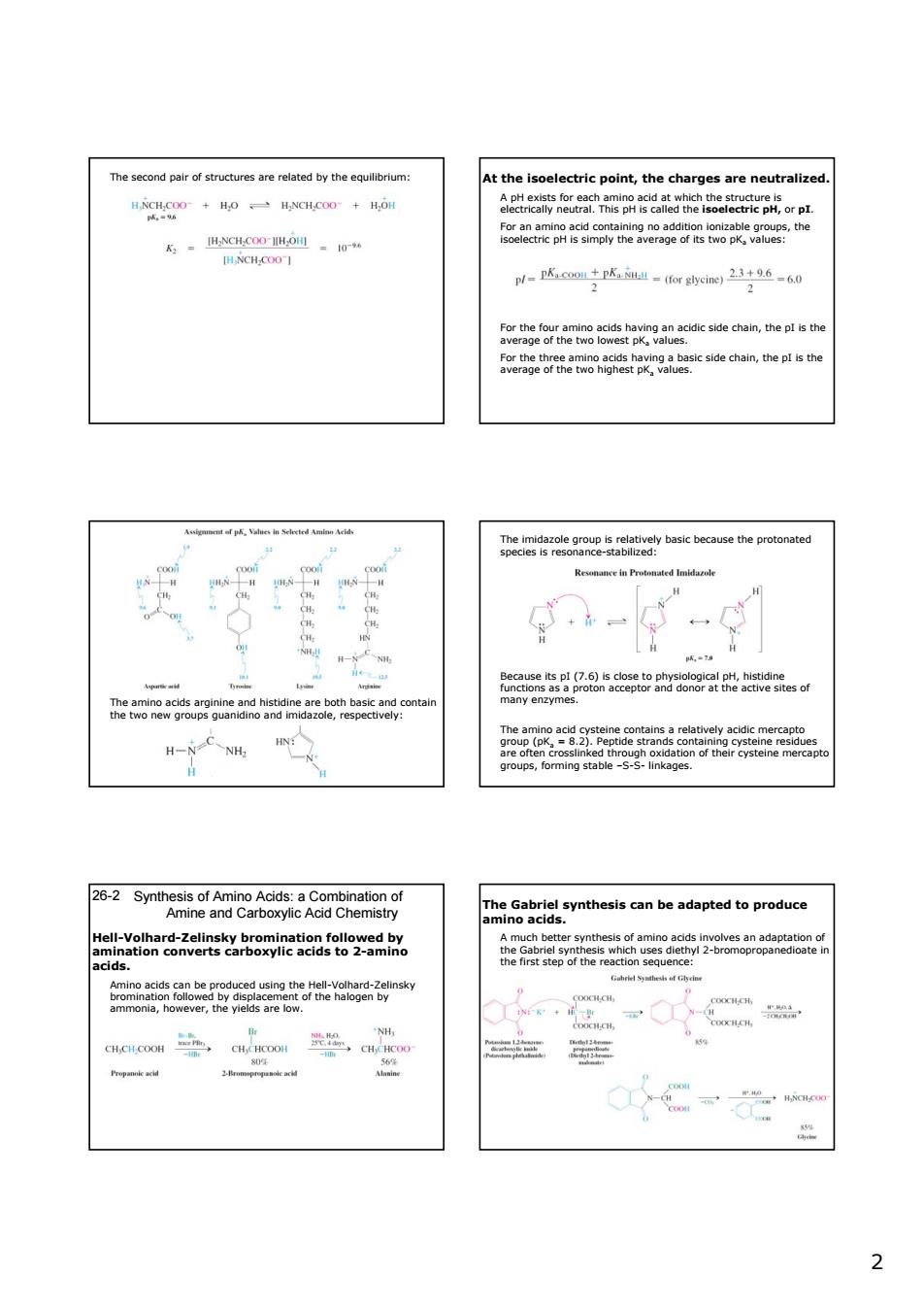
The second pair of structures are related by the equilibrium At the isoelectric point,the charges are neutralized. p-KP达-me2+96-60 sde hain,the ea他ane p basic because the pro -o 色 H-C-NH: roups,forming. 2-2 Hell-vohaeikywdby 22 The second pair of structures are related by the equilibrium: At the isoelectric point, the charges are neutralized. A pH exists for each amino acid at which the structure is electrically neutral. This pH is called the isoelectric pH, or pI. For an amino acid containing no addition ionizable groups, the isoelectric pH is simply the average of its two pKa values: For the four amino acids having an acidic side chain, the pI is the average of the two lowest pKa values. For the three amino acids having a basic side chain, the pI is the average of the two highest pKa values. The amino acids arginine and histidine are both basic and contain the two new groups guanidino and imidazole, respectively: The imidazole group is relatively basic because the protonated species is resonance-stabilized: Because its pI (7.6) is close to physiological pH, histidine functions as a proton acceptor and donor at the active sites of many enzymes. The amino acid cysteine contains a relatively acidic mercapto group (pKa = 8.2). Peptide strands containing cysteine residues are often crosslinked through oxidation of their cysteine mercapto groups, forming stable –S-S- linkages. Synthesis of Amino Acids: a Combination of Amine and Carboxylic Acid Chemistry 26-2 Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky bromination followed by amination converts carboxylic acids to 2-amino acids. Amino acids can be produced using the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky bromination followed by displacement of the halogen by ammonia, however, the yields are low. The Gabriel synthesis can be adapted to produce amino acids. A much better synthesis of amino acids involves an adaptation of the Gabriel synthesis which uses diethyl 2-bromopropanedioate in the first step of the reaction sequence: