正在加载图片...
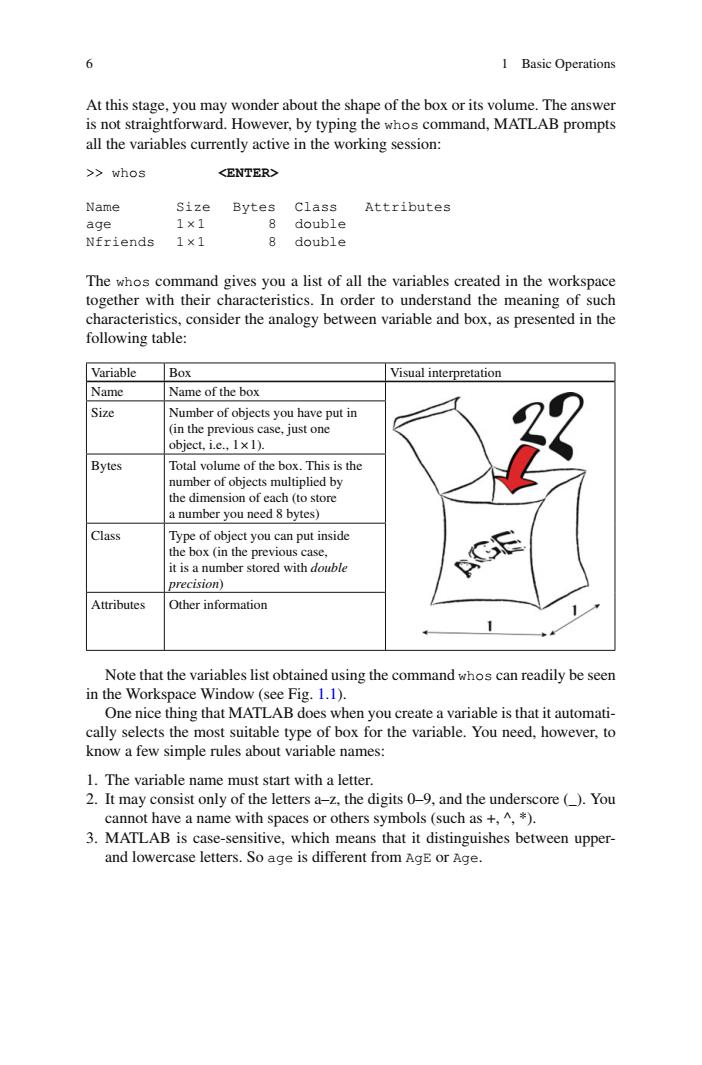
6 I BasicOperation At this stage,you may wonder about the shape of the box or its volume.The answer is not straightforward.However,by typing the whos command,MATLAB prompts all the variables currently active in the wo orking session >>whos Name cize Bytes Class Attributes age 1×1 8 double Nfriends1×1 8 double and ics.In order to understane the meaning of suck characteristics,consider the analogy between variable and box,as presented in the following table: Variable Box Visual interpretation Name Name of the box Size Number of objects you have put in ase,just one Bytes Total volume of the box.This is the a number you need 8 bytes) Class ct you can put inside it is a number stored with double precision) Attributes Other information Note that the variables list obtained using the command whos can readily be seen in the Workspace Window (see Fig.1.1). One nice thing that MATLAB does when you create a variable is that it automati- cally selects the most suitable type of box for the variable.You need,however.to know a few simple rules about variable names: 1.The variable name mu start with a letter 2.It may consist only of the lettersa.the digits9.and the underscore()You cannot have a name with spaces or others symbols(such as +,^ 3.MATLAB is case-sensitive,which means that it distinguishes between upper and lowercase letters.So age is different from AgE or Age.6 1 Basic Operations At this stage, you may wonder about the shape of the box or its volume. The answer is not straightforward. However, by typing the whos command, MATLAB prompts all the variables currently active in the working session: >> whos <ENTER> Name Size Bytes Class Attributes age 1× 1 8 double Nfriends 1× 1 8 double The whos command gives you a list of all the variables created in the workspace together with their characteristics. In order to understand the meaning of such characteristics, consider the analogy between variable and box, as presented in the following table: Variable Box Visual interpretation Name Name of the box Size Number of objects you have put in (in the previous case, just one object, i.e., 1 × 1). Bytes Total volume of the box. This is the number of objects multiplied by the dimension of each (to store a number you need 8 bytes) Class Type of object you can put inside the box (in the previous case, it is a number stored with double precision ) Attributes Other information Note that the variables list obtained using the command whos can readily be seen in the Workspace Window (see Fig. 1.1 ). One nice thing that MATLAB does when you create a variable is that it automatically selects the most suitable type of box for the variable. You need, however, to know a few simple rules about variable names: 1. The variable name must start with a letter. 2. It may consist only of the letters a–z, the digits 0–9, and the underscore (_). You cannot have a name with spaces or others symbols (such as +, ^, *). 3. MATLAB is case-sensitive, which means that it distinguishes between upperand lowercase letters. So age is different from AgE or Age