正在加载图片...
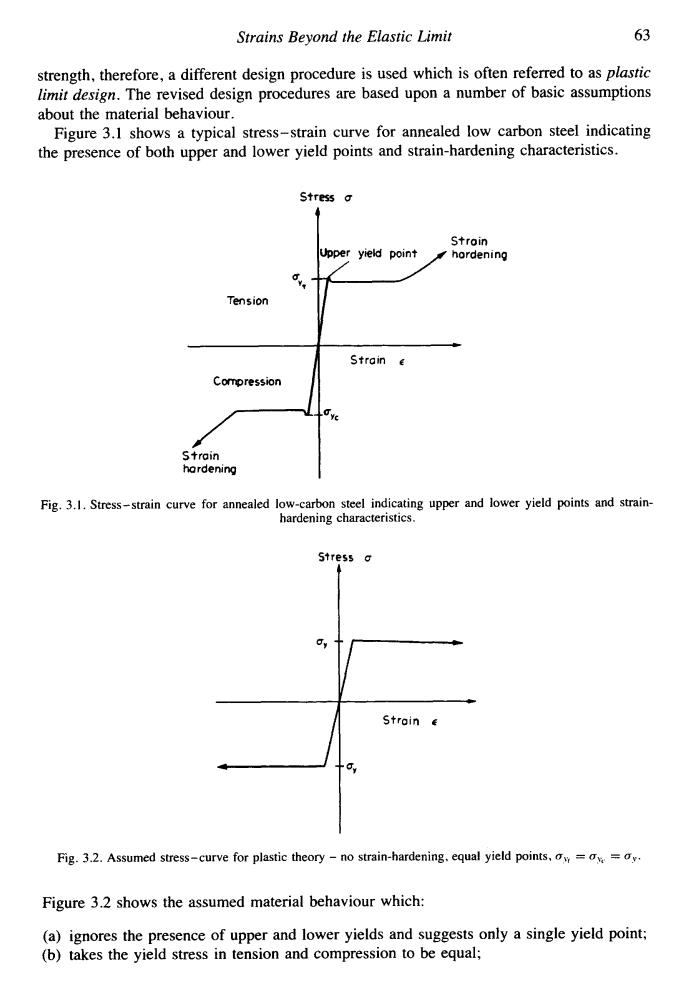
Strains Beyond the Elastic Limit 63 strength,therefore,a different design procedure is used which is often referred to as plastic limit design.The revised design procedures are based upon a number of basic assumptions about the material behaviour. Figure 3.1 shows a typical stress-strain curve for annealed low carbon steel indicating the presence of both upper and lower yield points and strain-hardening characteristics. Stress a Stroin Upper yield point hordening Tension Strain e Compression Strain hardening Fig.3.1.Stress-strain curve for annealed low-carbon steel indicating upper and lower yield points and strain- hardening characteristics. Stress o Stroin Fig.3.2.Assumed stress-curve for plastic theory -no strain-hardening.equal yield points,o=x=oy. Figure 3.2 shows the assumed material behaviour which: (a)ignores the presence of upper and lower yields and suggests only a single yield point; (b)takes the yield stress in tension and compression to be equal;Strains Beyond the Elastic Limit 63 strength, therefore, a different design procedure is used which is often referred to as plastic limit design. The revised design procedures are based upon a number of basic assumptions about the material behaviour. Figure 3.1 shows a typical stress-strain curve for annealed low carbon steel indicating the presence of both upper and lower yield points and strain-hardening characteristics. Stress u u. "I Tension Compression Strain hardening Stroin ~ Strain L =vc Fig. 3.1, Stress-strain curve for annealed low-carbon steel indicating upper and lower yield points and strainhardening characteristics. L - Strain c 4 Fig. 3.2. Assumed stress-curve for plastic theory - no strain-hardening, equal yield points, u,, = c,,~ = c". Figure 3.2 shows the assumed material behaviour which: (a) ignores the presence of upper and lower yields and suggests only a single yield point; (b) takes the yield stress in tension and compression to be equal;