正在加载图片...
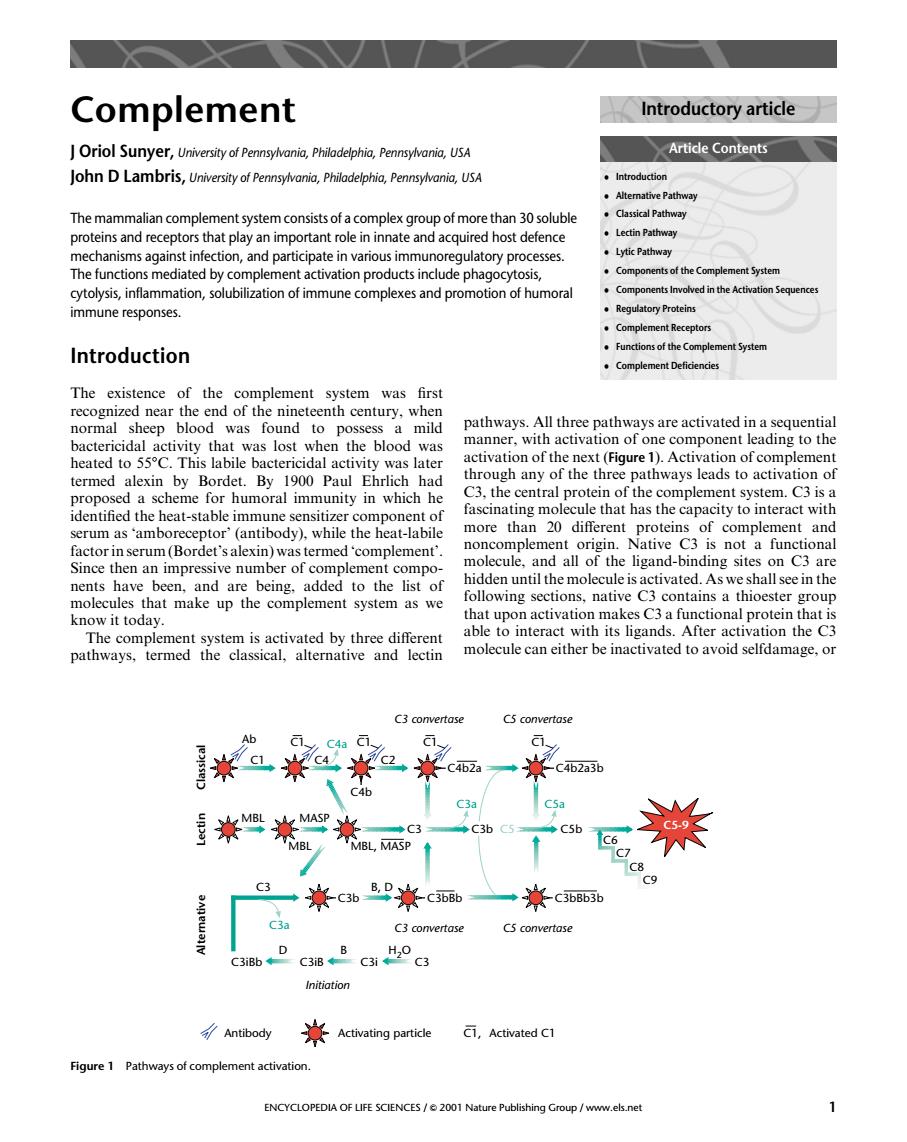
Complement Introductory article Oriol Sunyer,University of Pennsylvania,Philadelphia,Pennsylvania,USA Artice Contents The mammalian complement system consists of a complex group of more than 30 soluble proteins and receptors that play an important role in innate and acquired host defence 。Lytic Paway ents of the Complement Syste cytolysis,inf mmune responses Reaulatory Proteins Complement Receptors .Functions of the Complement Systen Introduction The existence of the complement system was first recognized nea pathways.All three pathways are activated in a sequential bactericidal activ thawas heated to 55C.This labile bactericidal activity was later re 1).Activa through any of the three pathways leads to activation of sedceme for humoral immunity i which he C3.the central protein of the complement system.C3 is a while the heatlabile fascinating molecu le that has the capacity to interact with more than 2 factorinserum(Bordet'salexin)was termed 'complement'. Since then an impressive number of complement compo molecule.and all of the ligand-binding sites on C3 are to the list of hidden until the molecule is activated.As we shall sce in the up t systen ollowing sections,native C3 contain know it today. the C? The complement system is activated by three different pathways,termed the classical,alternative and lectin molecule can either be inactivated to avoid selfdamage,or CS convertase A **米2*一米 c4b ◆C3北 c51c6 C3 ◆米c3b8P米c助 ◆☆c3bB66 C3 convertase Cs convertase Antibody Activating particle Ci,Activated C1 Figure 1 Pathwaysof complement activation. ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES/001 Nature Publishing Group/www.els.netComplement J Oriol Sunyer, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA John D Lambris, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA The mammalian complement system consists of a complex group of more than 30 soluble proteins and receptors that play an important role in innate and acquired host defence mechanisms against infection, and participate in various immunoregulatory processes. The functions mediated by complement activation products include phagocytosis, cytolysis, inflammation, solubilization of immune complexes and promotion of humoral immune responses. Introduction The existence of the complement system was first recognized near the end of the nineteenth century, when normal sheep blood was found to possess a mild bactericidal activity that was lost when the blood was heated to 558C. This labile bactericidal activity was later termed alexin by Bordet. By 1900 Paul Ehrlich had proposed a scheme for humoral immunity in which he identified the heat-stable immune sensitizer component of serum as ‘amboreceptor’ (antibody), while the heat-labile factor in serum (Bordet’s alexin) was termed ‘complement’. Since then an impressive number of complement components have been, and are being, added to the list of molecules that make up the complement system as we know it today. The complement system is activated by three different pathways, termed the classical, alternative and lectin pathways. All three pathways are activated in a sequential manner, with activation of one component leading to the activation of the next (Figure 1). Activation of complement through any of the three pathways leads to activation of C3, the central protein of the complement system. C3 is a fascinating molecule that has the capacity to interact with more than 20 different proteins of complement and noncomplement origin. Native C3 is not a functional molecule, and all of the ligand-binding sites on C3 are hidden until the molecule is activated. As we shall see in the following sections, native C3 contains a thioester group that upon activation makes C3 a functional protein that is able to interact with its ligands. After activation the C3 molecule can either be inactivated to avoid selfdamage, or Article Contents Introductory article . Introduction . Alternative Pathway . Classical Pathway . Lectin Pathway . Lytic Pathway . Components of the Complement System . Components Involved in the Activation Sequences . Regulatory Proteins . Complement Receptors . Functions of the Complement System . Complement Deficiencies C6 Classical Ab C1 C4 C1 C4a C2 C1 C4b C1 Lectin MBL MASP MBL MBL, MASP C3 C3b B, D Alternative C3a C3 C3iBb C3bBb D C3iB B C3i H2O C3 Initiation C4b2a C3b C3a C1 C4b2a3b C5b C5a C5 C7 C8 C9 C5-9 C3 convertase C5 convertase C3bBb3b C3 convertase C5 convertase Antibody Activating particle C1, Activated C1 Figure 1 Pathways of complement activation. ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www.els.net 1