正在加载图片...
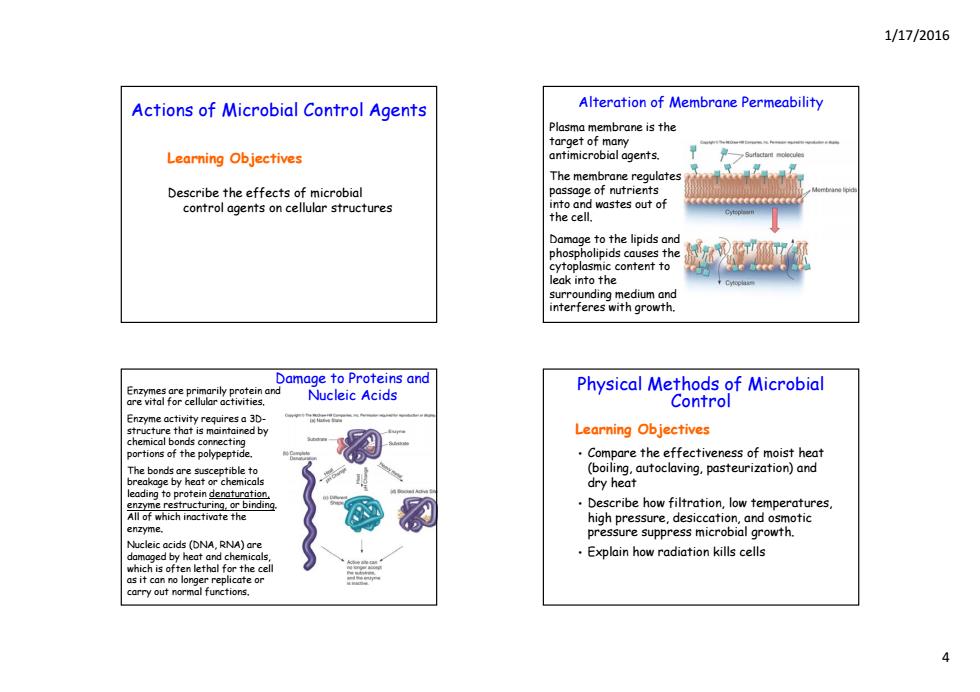
1/17/2016 Actions of Microbial Control Agents Alteration of Membrane Permeability Plasma membrane is the target of many Learning Objectives antimicrobial agents. The membrane regulates Describe the effects of microbial passage of nutrients control agents on cellular structures into and wastes out of the cell. Damage to the lipids and content to leak into the surroundina medium and interferes with growth. Damage to Proteins and rily Nucleic Acids Physical Methods of Microbial Control Enzyme activity requires a 3D- structure that is maintained by Learning Objectives chemical bonds connecting portions of the polypeptide. Compare the effectiveness of moist heat (boiling,autoclaving.pasteurization)and akage by h dry heat ing to prote denaturati Describe how filtration,low temperatures. high pressure,desiccation,and osmotic enzyme. pressure suppress microbial growth. Nucleic acids (DNA,RNA)are damoged by heat and chemicals Explain how radiation kills cells which is often lethal for the cell as it can no longer replicate or carry out normal functions.1/17/2016 4 Learning Objectives Actions of Microbial Control Agents g j Describe the effects of microbial control agents on cellular structures Alteration of Membrane Permeability Plasma membrane is the target of many antimicrobial agents. The membrane regulates passage of nutrients into and wastes out of the cell. Damag p e to the lipids and phospholipids causes the cytoplasmic content to leak into the surrounding medium and interferes with growth. Damage to Proteins and Nucleic Acids Enzymes are primarily protein and are vital for cellular activities. Enzyme activity requires a 3Dstructure that is maintained by chemical bonds connecting portions of the polypeptide. The bonds are susceptible to breakage by heat or chemicals leading to protein denaturation, enzyme restructuring, or binding. All of which inactivate the en mzy e. Nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) are damaged by heat and chemicals, which is often lethal for the cell as it can no longer replicate or carry out normal functions. Learning Objectives Physical Methods of Microbial Control • Compare the effectiveness of moist heat (boiling, autoclaving, pasteurization) and dry heat • Describe how filtration, low temperatures, high pressure, desiccation, and osmotic pressure suppress microbial growth. • Explain how radiation kills cells