正在加载图片...
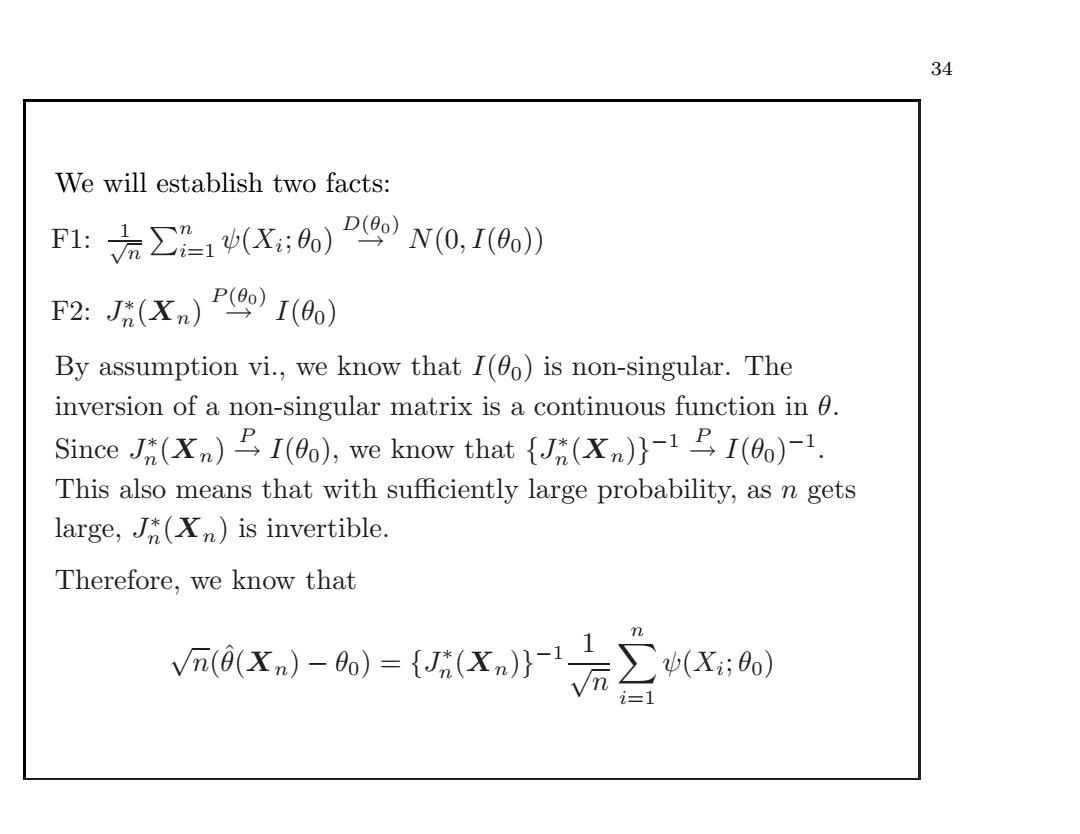
34 We will establish two facts: F1:(:0)N(0,I(0)) F2:J(Xn)P9oI(0)】 By assumption vi.,we know that I(0o)is non-singular.The inversion of a non-singular matrix is a continuous function in 0. Since (n)I(0o),we know that(n))I(00)-1. This also means that with sufficiently large probability,as n gets large,(Xn)is invertible. Therefore,we know that V0x-)=(Xa0X:则 TL i=134 We will establish two facts: F1: √1n ni=1 ψ(Xi; θ0) D(θ0) → N(0, I(θ0)) F2: J∗n(Xn) P (θ0) → I(θ0) By assumption vi., we know that I(θ0) is non-singular. The inversion of a non-singular matrix is a continuous function in θ. Since J∗n(Xn) P→ I(θ0), we know that {J∗n(Xn)}−1 P→ I(θ0)−1. This also means that with sufficiently large probability, as n gets large, J∗n(Xn) is invertible. Therefore, we know that √n(ˆθ(Xn) − θ0) = {J∗n(Xn)}−1 1√n ni=1 ψ(Xi; θ0)��