正在加载图片...
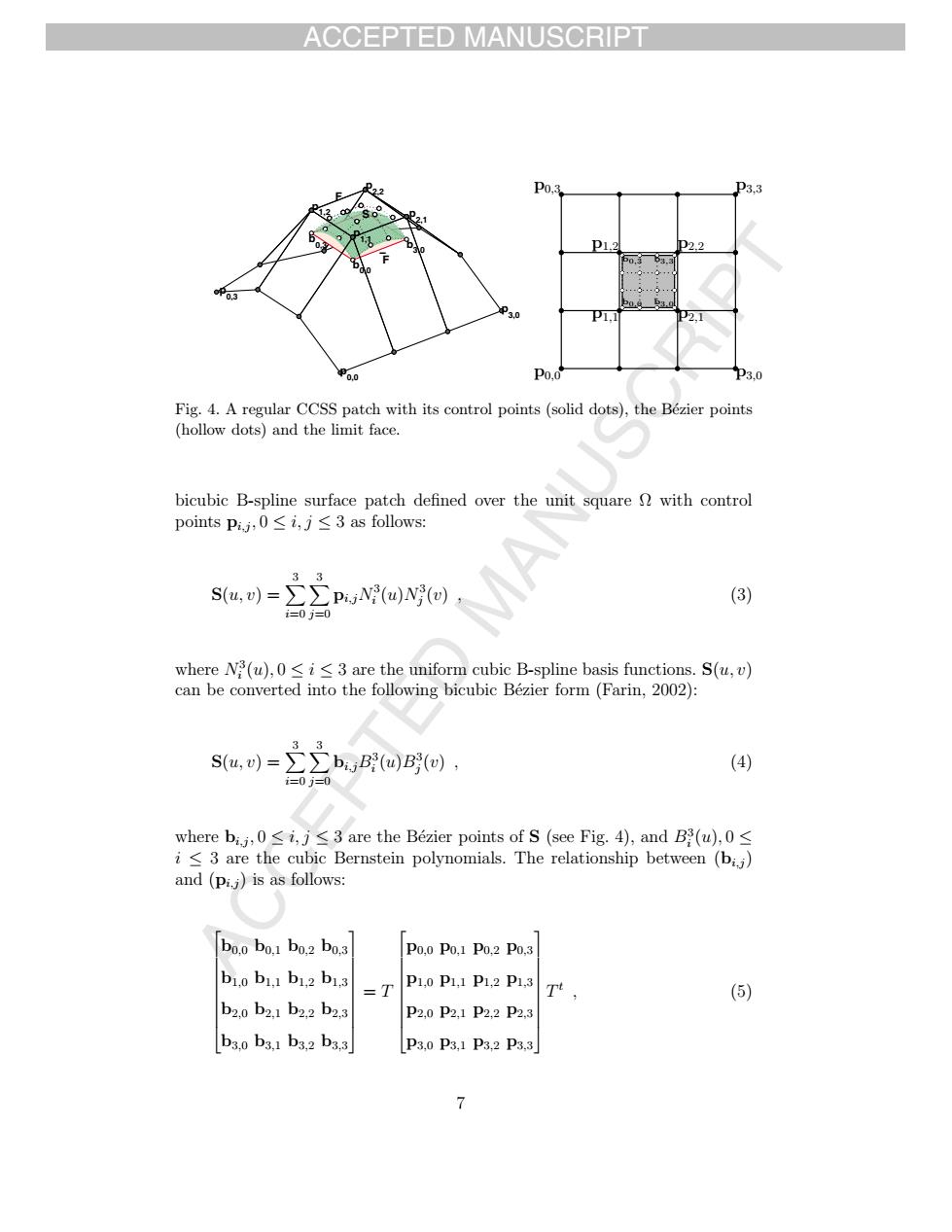
ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT deglrCsprhnihtscoatralpoiatsaddot,theBaicrpo pounts P.follo s.)=广b,o回 (4 Po.Po,1 P0.2 P0. P20P2,P2,2P2 bio bi.:bi.z bi.s Pao Pi Pa2 Pa3 7 ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT p3,0 F _ b3,0 p2,1 b0,0 p2,2 S p b 1,1 0,3 p0,0 F p1,2 p0,3 p0,0 p0,3 p3,0 p3,3 p1,1 p1,2 p2,1 p2,2 b0,0 b3,0 b0,3 b3,3 Fig. 4. A regular CCSS patch with its control points (solid dots), the B´ezier points (hollow dots) and the limit face. bicubic B-spline surface patch defined over the unit square Ω with control points pi,j , 0 ≤ i, j ≤ 3 as follows: S(u, v) = 3 i=0 3 j=0 pi,jN3 i (u)N3 j (v) , (3) where N3 i (u), 0 ≤ i ≤ 3 are the uniform cubic B-spline basis functions. S(u, v) can be converted into the following bicubic B´ezier form (Farin, 2002): S(u, v) = 3 i=0 3 j=0 bi,jB3 i (u)B3 j (v) , (4) where bi,j , 0 ≤ i, j ≤ 3 are the B´ezier points of S (see Fig. 4), and B3 i (u), 0 ≤ i ≤ 3 are the cubic Bernstein polynomials. The relationship between (bi,j ) and (pi,j ) is as follows: ⎡ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ b0,0 b0,1 b0,2 b0,3 b1,0 b1,1 b1,2 b1,3 b2,0 b2,1 b2,2 b2,3 b3,0 b3,1 b3,2 b3,3 ⎤ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ = T ⎡ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ p0,0 p0,1 p0,2 p0,3 p1,0 p1,1 p1,2 p1,3 p2,0 p2,1 p2,2 p2,3 p3,0 p3,1 p3,2 p3,3 ⎤ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ Tt , (5) 7����