正在加载图片...
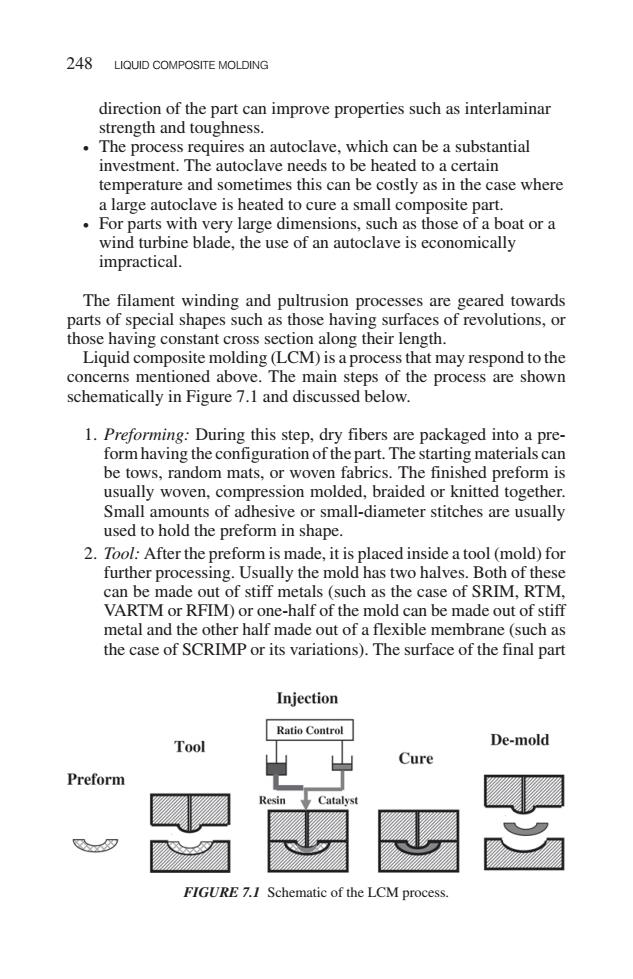
248 LIQUID COMPOSITE MOLDING direction of the part can improve properties such as interlaminar strength and toughness. The process requires an autoclave,which can be a substantial investment.The autoclave needs to be heated to a certain temperature and sometimes this can be costly as in the case where a large autoclave is heated to cure a small composite part. For parts with very large dimensions,such as those of a boat or a wind turbine blade,the use of an autoclave is economically impractical. The filament winding and pultrusion processes are geared towards parts of special shapes such as those having surfaces of revolutions,or those having constant cross section along their length. Liquid composite molding(LCM)is a process that may respond to the concerns mentioned above.The main steps of the process are shown schematically in Figure 7.1 and discussed below. 1.Preforming:During this step,dry fibers are packaged into a pre- form having the configuration of the part.The starting materials can be tows,random mats,or woven fabrics.The finished preform is usually woven,compression molded,braided or knitted together. Small amounts of adhesive or small-diameter stitches are usually used to hold the preform in shape. 2.Tool:After the preform is made,it is placed inside a tool(mold)for further processing.Usually the mold has two halves.Both of these can be made out of stiff metals (such as the case of SRIM,RTM. VARTM or RFIM)or one-half of the mold can be made out of stiff metal and the other half made out of a flexible membrane (such as the case of SCRIMP or its variations).The surface of the final part Injection Ratio Control Tool De-mold Cure Preform Resin Catalyst FIGURE 7.I Schematic of the LCM process.direction of the part can improve properties such as interlaminar strength and toughness. • The process requires an autoclave, which can be a substantial investment. The autoclave needs to be heated to a certain temperature and sometimes this can be costly as in the case where a large autoclave is heated to cure a small composite part. • For parts with very large dimensions, such as those of a boat or a wind turbine blade, the use of an autoclave is economically impractical. The filament winding and pultrusion processes are geared towards parts of special shapes such as those having surfaces of revolutions, or those having constant cross section along their length. Liquid composite molding (LCM) is a process that may respond to the concerns mentioned above. The main steps of the process are shown schematically in Figure 7.1 and discussed below. 1. Preforming: During this step, dry fibers are packaged into a preform having the configuration of the part. The starting materials can be tows, random mats, or woven fabrics. The finished preform is usually woven, compression molded, braided or knitted together. Small amounts of adhesive or small-diameter stitches are usually used to hold the preform in shape. 2. Tool: After the preform is made, it is placed inside a tool (mold) for further processing. Usually the mold has two halves. Both of these can be made out of stiff metals (such as the case of SRIM, RTM, VARTM or RFIM) or one-half of the mold can be made out of stiff metal and the other half made out of a flexible membrane (such as the case of SCRIMP or its variations). The surface of the final part 248 LIQUID COMPOSITE MOLDING FIGURE 7.1 Schematic of the LCM process