正在加载图片...
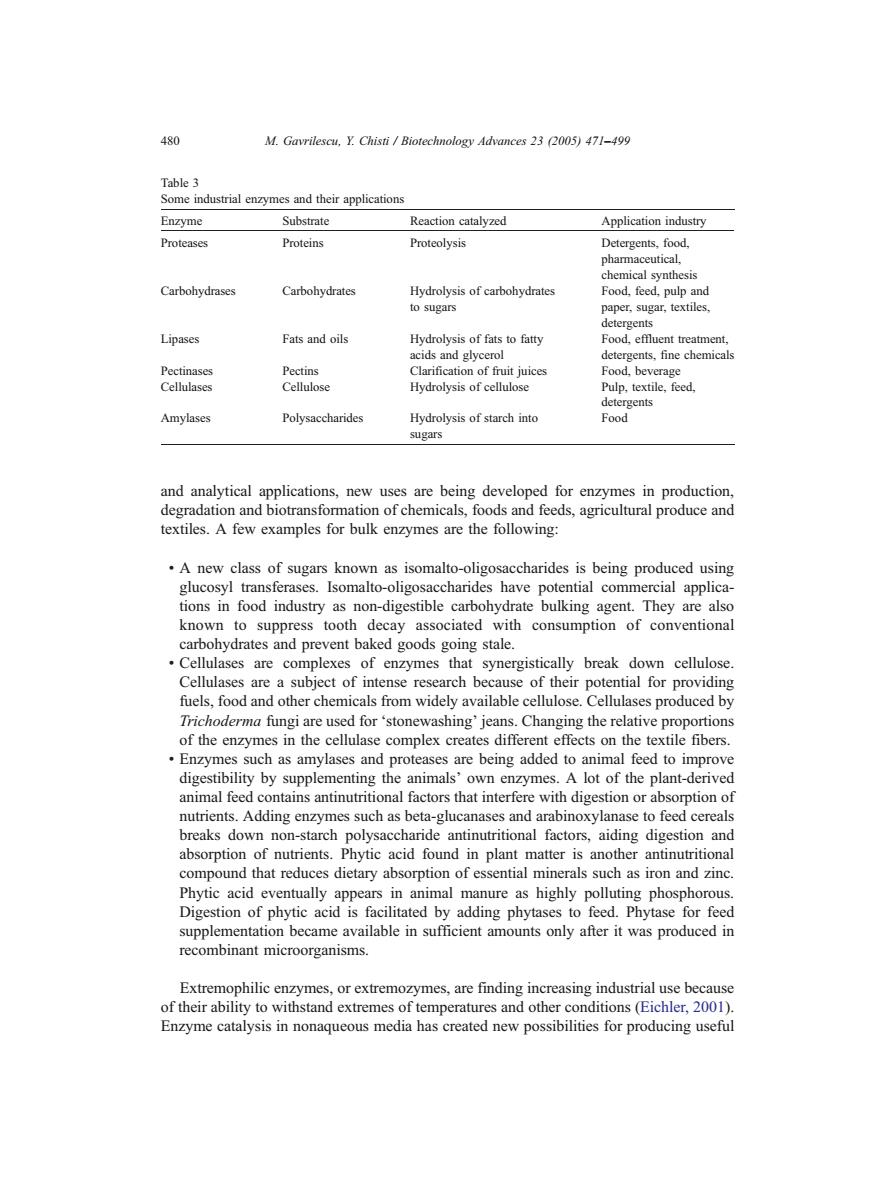
480 M.Gavrilescu,Y.Chisti/Biotechnology Advances 23 (2005)471-499 Table 3 Some industrial enzymes and their applications Enzyme Substrate Reaction catalyzed Application industry Proteases Proteins Proteolysis Detergents,food, pharmaceutical, chemical synthesis Carbohydrases Carbohydrates Hydrolysis of carbohydrates Food,feed,pulp and to sugars paper,sugar,textiles, detergents Lipases Fats and oils Hydrolysis of fats to fatty Food,effluent treatment. acids and glycerol detergents,fine chemicals Pectinases Pectins Clarification of fruit juices Food,beverage Cellulases Cellulose Hydrolysis of cellulose Pulp,textile,feed, detergents Amylases Polysaccharides Hydrolysis of starch into Food sugars and analytical applications,new uses are being developed for enzymes in production, degradation and biotransformation of chemicals,foods and feeds,agricultural produce and textiles.A few examples for bulk enzymes are the following: A new class of sugars known as isomalto-oligosaccharides is being produced using glucosyl transferases.Isomalto-oligosaccharides have potential commercial applica- tions in food industry as non-digestible carbohydrate bulking agent.They are also known to suppress tooth decay associated with consumption of conventional carbohydrates and prevent baked goods going stale. Cellulases are complexes of enzymes that synergistically break down cellulose. Cellulases are a subject of intense research because of their potential for providing fuels,food and other chemicals from widely available cellulose.Cellulases produced by Trichoderma fungi are used for 'stonewashing'jeans.Changing the relative proportions of the enzymes in the cellulase complex creates different effects on the textile fibers. Enzymes such as amylases and proteases are being added to animal feed to improve digestibility by supplementing the animals'own enzymes.A lot of the plant-derived animal feed contains antinutritional factors that interfere with digestion or absorption of nutrients.Adding enzymes such as beta-glucanases and arabinoxylanase to feed cereals breaks down non-starch polysaccharide antinutritional factors,aiding digestion and absorption of nutrients.Phytic acid found in plant matter is another antinutritional compound that reduces dietary absorption of essential minerals such as iron and zinc. Phytic acid eventually appears in animal manure as highly polluting phosphorous. Digestion of phytic acid is facilitated by adding phytases to feed.Phytase for feed supplementation became available in sufficient amounts only after it was produced in recombinant microorganisms. Extremophilic enzymes,or extremozymes,are finding increasing industrial use because of their ability to withstand extremes of temperatures and other conditions(Eichler,2001). Enzyme catalysis in nonaqueous media has created new possibilities for producing usefuland analytical applications, new uses are being developed for enzymes in production, degradation and biotransformation of chemicals, foods and feeds, agricultural produce and textiles. A few examples for bulk enzymes are the following: ! A new class of sugars known as isomalto-oligosaccharides is being produced using glucosyl transferases. Isomalto-oligosaccharides have potential commercial applications in food industry as non-digestible carbohydrate bulking agent. They are also known to suppress tooth decay associated with consumption of conventional carbohydrates and prevent baked goods going stale. ! Cellulases are complexes of enzymes that synergistically break down cellulose. Cellulases are a subject of intense research because of their potential for providing fuels, food and other chemicals from widely available cellulose. Cellulases produced by Trichoderma fungi are used for dstonewashingT jeans. Changing the relative proportions of the enzymes in the cellulase complex creates different effects on the textile fibers. ! Enzymes such as amylases and proteases are being added to animal feed to improve digestibility by supplementing the animals’ own enzymes. A lot of the plant-derived animal feed contains antinutritional factors that interfere with digestion or absorption of nutrients. Adding enzymes such as beta-glucanases and arabinoxylanase to feed cereals breaks down non-starch polysaccharide antinutritional factors, aiding digestion and absorption of nutrients. Phytic acid found in plant matter is another antinutritional compound that reduces dietary absorption of essential minerals such as iron and zinc. Phytic acid eventually appears in animal manure as highly polluting phosphorous. Digestion of phytic acid is facilitated by adding phytases to feed. Phytase for feed supplementation became available in sufficient amounts only after it was produced in recombinant microorganisms. Extremophilic enzymes, or extremozymes, are finding increasing industrial use because of their ability to withstand extremes of temperatures and other conditions (Eichler, 2001). Enzyme catalysis in nonaqueous media has created new possibilities for producing useful Table 3 Some industrial enzymes and their applications Enzyme Substrate Reaction catalyzed Application industry Proteases Proteins Proteolysis Detergents, food, pharmaceutical, chemical synthesis Carbohydrases Carbohydrates Hydrolysis of carbohydrates to sugars Food, feed, pulp and paper, sugar, textiles, detergents Lipases Fats and oils Hydrolysis of fats to fatty acids and glycerol Food, effluent treatment, detergents, fine chemicals Pectinases Pectins Clarification of fruit juices Food, beverage Cellulases Cellulose Hydrolysis of cellulose Pulp, textile, feed, detergents Amylases Polysaccharides Hydrolysis of starch into sugars Food 480 M. Gavrilescu, Y. Chisti / Biotechnology Advances 23 (2005) 471–499