正在加载图片...
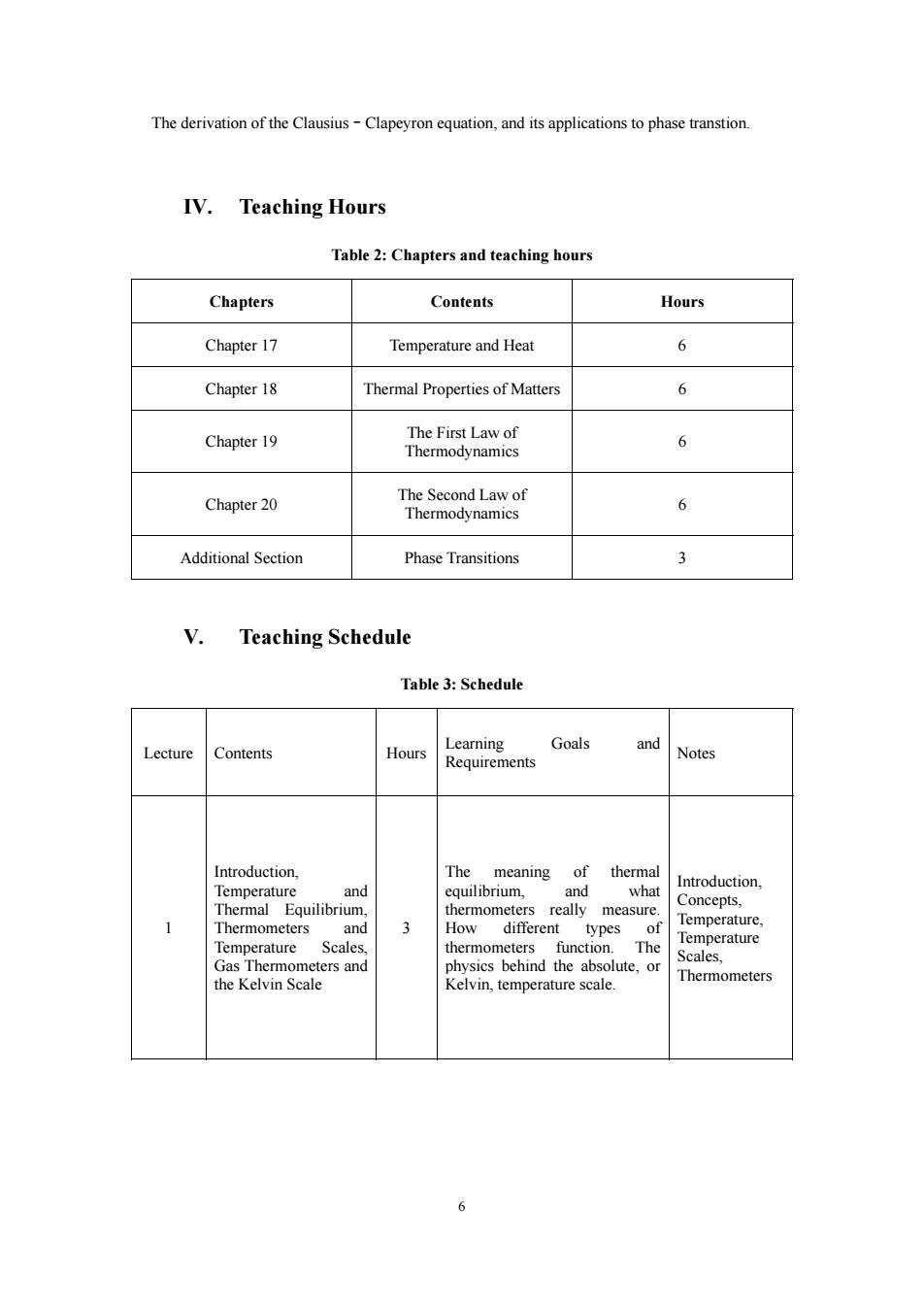
The derivation of the Clausius-Clapeyron equation,and its applications to phase transtion. IV. Teaching Hours Table 2:Chapters and teaching hours Chapters Contents Hours Chapter 17 Temperature and Heat 6 Chapter 18 Thermal Properties of Matters 6 Chapter 19 The First Law of 6 Thermodynamics Chapter20 6 Additional Section Phase Transitions Teaching Schedule Table 3:Schedule Goals Lecture Contents Hours Learning and Requirements Notes of ther and roduction. Thermal really measure. Concepts, rmome 3 feren h The ometers and vsics behind the abs olute.or Thermometers he Kelvin Scale 6 6 The derivation of the Clausius–Clapeyron equation, and its applications to phase transtion. IV. Teaching Hours Table 2: Chapters and teaching hours Chapters Contents Hours Chapter 17 Temperature and Heat 6 Chapter 18 Thermal Properties of Matters 6 Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics 6 Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics 6 Additional Section Phase Transitions 3 V. Teaching Schedule Table 3: Schedule Lecture Contents Hours Learning Goals and Requirements Notes 1 Introduction, Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium, Thermometers and Temperature Scales, Gas Thermometers and the Kelvin Scale 3 The meaning of thermal equilibrium, and what thermometers really measure. How different types of thermometers function. The physics behind the absolute, or Kelvin, temperature scale. Introduction, Concepts, Temperature, Temperature Scales, Thermometers