正在加载图片...
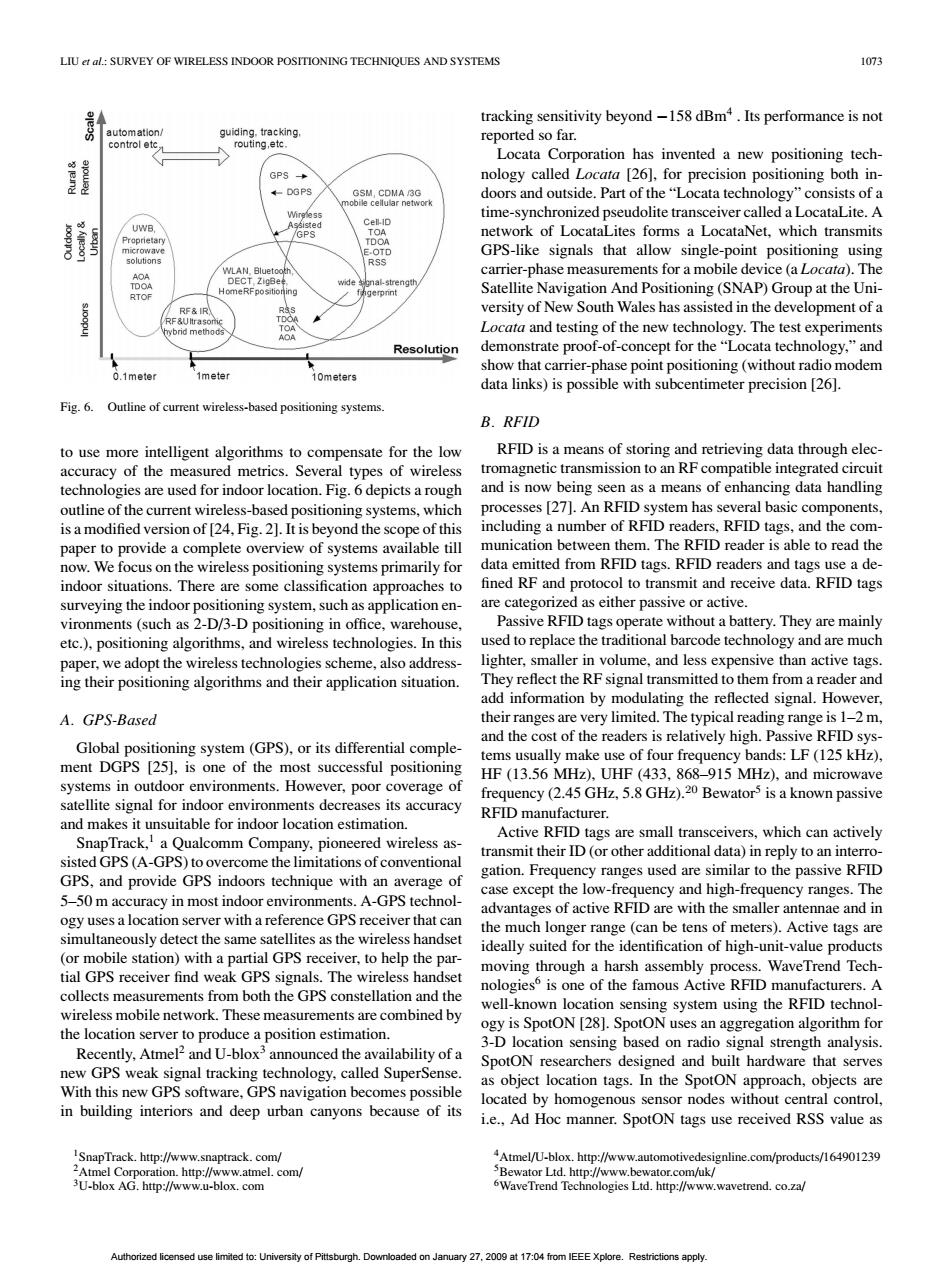
LIU:SURVEY OF WIRELESS INDOOR POSITIONING TECHNIQUES AND SYSTEMS 1073 tracking sensitivity beyond-158 dBm+.Its performance is not automation/ guiding.tracking. control etc. routing,etc. reported so far. Locata Corporation has invented a new positioning tech- GPS nology called Locata [26],for precision positioning both in- DGPS doors and outside.Part of the"Locata technology"consists of a time-synchronized pseudolite transceiver called a LocataLite.A UWB. Cell-ID GPS TOA network of LocataLites forms a LocataNet,which transmits solutions GPS-like signals that allow single-point positioning using RSS WLAN Bluetooth carrier-phase measurements for a mobile device (a Locata).The AOA TDOA DECT,ZigBee al-strength Home RFpositioning Satellite Navigation And Positioning(SNAP)Group at the Uni- RTOF RF&IR versity of New South Wales has assisted in the development of a TOA Locata and testing of the new technology.The test experiments Resolution demonstrate proof-of-concept for the"Locata technology,"and show that carrier-phase point positioning(without radio modem 0.1meter 10meters data links)is possible with subcentimeter precision [26]. Fig.6.Outline of current wireless-based positioning systems B.RFID to use more intelligent algorithms to compensate for the low RFID is a means of storing and retrieving data through elec- accuracy of the measured metrics.Several types of wireless tromagnetic transmission to an RF compatible integrated circuit technologies are used for indoor location.Fig.6 depicts a rough and is now being seen as a means of enhancing data handling outline of the current wireless-based positioning systems,which processes [27].An RFID system has several basic components, is a modified version of [24,Fig.2].It is beyond the scope of this including a number of RFID readers,RFID tags,and the com- paper to provide a complete overview of systems available till munication between them.The RFID reader is able to read the now.We focus on the wireless positioning systems primarily for data emitted from RFID tags.RFID readers and tags use a de- indoor situations.There are some classification approaches to fined RF and protocol to transmit and receive data.RFID tags surveying the indoor positioning system,such as application en- are categorized as either passive or active. vironments(such as 2-D/3-D positioning in office,warehouse, Passive RFID tags operate without a battery.They are mainly etc.),positioning algorithms,and wireless technologies.In this used to replace the traditional barcode technology and are much paper,we adopt the wireless technologies scheme,also address- lighter,smaller in volume,and less expensive than active tags ing their positioning algorithms and their application situation. They reflect the RF signal transmitted to them from a reader and add information by modulating the reflected signal.However, A.GPS-Based their ranges are very limited.The typical reading range is 1-2 m, and the cost of the readers is relatively high.Passive RFID sys- Global positioning system(GPS),or its differential comple- ment DGPS [25],is one of the most successful positioning tems usually make use of four frequency bands:LF(125 kHz), HF(13.56 MHz).UHF (433,868-915 MHz).and microwave systems in outdoor environments.However,poor coverage of frequency(2.45 GHz,5.8 GHz).20 Bewator5 is a known passive satellite signal for indoor environments decreases its accuracy RFID manufacturer. and makes it unsuitable for indoor location estimation. SnapTrack,a Qualcomm Company,pioneered wireless as- Active RFID tags are small transceivers,which can actively transmit their ID(or other additional data)in reply to an interro- sisted GPS (A-GPS)to overcome the limitations of conventional gation.Frequency ranges used are similar to the passive RFID GPS,and provide GPS indoors technique with an average of case except the low-frequency and high-frequency ranges.The 5-50 m accuracy in most indoor environments.A-GPS technol- advantages of active RFID are with the smaller antennae and in ogy uses a location server with a reference GPS receiver that can the much longer range(can be tens of meters).Active tags are simultaneously detect the same satellites as the wireless handset ideally suited for the identification of high-unit-value products (or mobile station)with a partial GPS receiver,to help the par- moving through a harsh assembly process.WaveTrend Tech- tial GPS receiver find weak GPS signals.The wireless handset nologies5 is one of the famous Active RFID manufacturers.A collects measurements from both the GPS constellation and the well-known location sensing system using the RFID technol- wireless mobile network.These measurements are combined by the location server to produce a position estimation. ogy is SpotON [28].SpotON uses an aggregation algorithm for 3-D location sensing based on radio signal strength analysis Recently,Atmel and U-blox'announced the availability of a SpotON researchers designed and built hardware that serves new GPS weak signal tracking technology,called SuperSense. as object location tags.In the SpotON approach,objects are With this new GPS software,GPS navigation becomes possible located by homogenous sensor nodes without central control in building interiors and deep urban canyons because of its i.e.,Ad Hoc manner.SpotON tags use received RSS value as SnapTrack.http://www.snaptrack.com/ 4Atmel/U-blox.http://www.automotivedesignline.com/products/164901239 2Atmel Corporation.http://www.atmel.com/ 5Bewator Ltd.http://www.bewator.com/uk/ 3U-blox AG.http://www.u-blox.com 6WaveTrend Technologies Ltd.http://www.wavetrend.co.za/ Authorized licensed use limited to:University of Pittsburgh.Downloaded on January 27.2009 at 17:04 from IEEE Xplore.Restrictions apply.LIU et al.: SURVEY OF WIRELESS INDOOR POSITIONING TECHNIQUES AND SYSTEMS 1073 Fig. 6. Outline of current wireless-based positioning systems. to use more intelligent algorithms to compensate for the low accuracy of the measured metrics. Several types of wireless technologies are used for indoor location. Fig. 6 depicts a rough outline of the current wireless-based positioning systems, which is a modified version of [24, Fig. 2]. It is beyond the scope of this paper to provide a complete overview of systems available till now. We focus on the wireless positioning systems primarily for indoor situations. There are some classification approaches to surveying the indoor positioning system, such as application environments (such as 2-D/3-D positioning in office, warehouse, etc.), positioning algorithms, and wireless technologies. In this paper, we adopt the wireless technologies scheme, also addressing their positioning algorithms and their application situation. A. GPS-Based Global positioning system (GPS), or its differential complement DGPS [25], is one of the most successful positioning systems in outdoor environments. However, poor coverage of satellite signal for indoor environments decreases its accuracy and makes it unsuitable for indoor location estimation. SnapTrack,1 a Qualcomm Company, pioneered wireless assisted GPS (A-GPS) to overcome the limitations of conventional GPS, and provide GPS indoors technique with an average of 5–50 m accuracy in most indoor environments. A-GPS technology uses a location server with a reference GPS receiver that can simultaneously detect the same satellites as the wireless handset (or mobile station) with a partial GPS receiver, to help the partial GPS receiver find weak GPS signals. The wireless handset collects measurements from both the GPS constellation and the wireless mobile network. These measurements are combined by the location server to produce a position estimation. Recently, Atmel2 and U-blox3 announced the availability of a new GPS weak signal tracking technology, called SuperSense. With this new GPS software, GPS navigation becomes possible in building interiors and deep urban canyons because of its 1SnapTrack. http://www.snaptrack. com/ 2Atmel Corporation. http://www.atmel. com/ 3U-blox AG. http://www.u-blox. com tracking sensitivity beyond −158 dBm4 . Its performance is not reported so far. Locata Corporation has invented a new positioning technology called Locata [26], for precision positioning both indoors and outside. Part of the “Locata technology” consists of a time-synchronized pseudolite transceiver called a LocataLite. A network of LocataLites forms a LocataNet, which transmits GPS-like signals that allow single-point positioning using carrier-phase measurements for a mobile device (a Locata). The Satellite Navigation And Positioning (SNAP) Group at the University of New South Wales has assisted in the development of a Locata and testing of the new technology. The test experiments demonstrate proof-of-concept for the “Locata technology,” and show that carrier-phase point positioning (without radio modem data links) is possible with subcentimeter precision [26]. B. RFID RFID is a means of storing and retrieving data through electromagnetic transmission to an RF compatible integrated circuit and is now being seen as a means of enhancing data handling processes [27]. An RFID system has several basic components, including a number of RFID readers, RFID tags, and the communication between them. The RFID reader is able to read the data emitted from RFID tags. RFID readers and tags use a de- fined RF and protocol to transmit and receive data. RFID tags are categorized as either passive or active. Passive RFID tags operate without a battery. They are mainly used to replace the traditional barcode technology and are much lighter, smaller in volume, and less expensive than active tags. They reflect the RF signal transmitted to them from a reader and add information by modulating the reflected signal. However, their ranges are very limited. The typical reading range is 1–2 m, and the cost of the readers is relatively high. Passive RFID systems usually make use of four frequency bands: LF (125 kHz), HF (13.56 MHz), UHF (433, 868–915 MHz), and microwave frequency (2.45 GHz, 5.8 GHz).20 Bewator5 is a known passive RFID manufacturer. Active RFID tags are small transceivers, which can actively transmit their ID (or other additional data) in reply to an interrogation. Frequency ranges used are similar to the passive RFID case except the low-frequency and high-frequency ranges. The advantages of active RFID are with the smaller antennae and in the much longer range (can be tens of meters). Active tags are ideally suited for the identification of high-unit-value products moving through a harsh assembly process. WaveTrend Technologies6 is one of the famous Active RFID manufacturers. A well-known location sensing system using the RFID technology is SpotON [28]. SpotON uses an aggregation algorithm for 3-D location sensing based on radio signal strength analysis. SpotON researchers designed and built hardware that serves as object location tags. In the SpotON approach, objects are located by homogenous sensor nodes without central control, i.e., Ad Hoc manner. SpotON tags use received RSS value as 4Atmel/U-blox. http://www.automotivedesignline.com/products/164901239 5Bewator Ltd. http://www.bewator.com/uk/ 6WaveTrend Technologies Ltd. http://www.wavetrend. co.za/ Authorized licensed use limited to: University of Pittsburgh. Downloaded on January 27, 2009 at 17:04 from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply