正在加载图片...
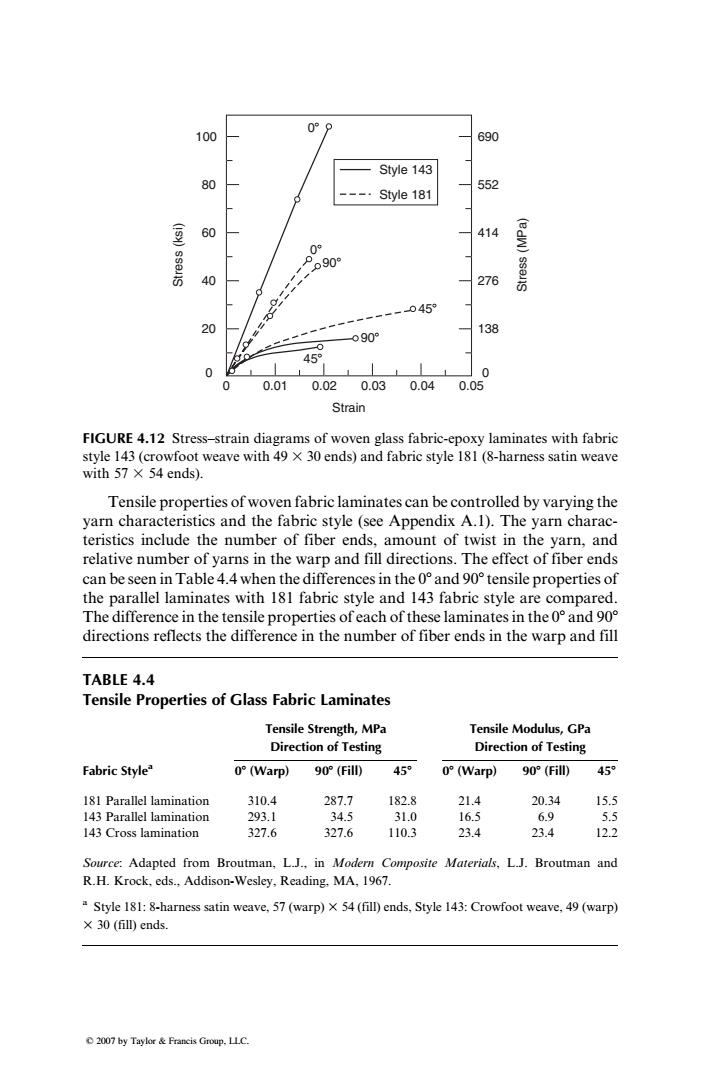
09 100 690 Style 143 80 552 Style 181 60 414 0 p90 40 276 -045 20 138 0909 45° 0 0 0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.040.05 Strain FIGURE 4.12 Stress-strain diagrams of woven glass fabric-epoxy laminates with fabric style 143(crowfoot weave with 49 x 30 ends)and fabric style 181(8-harness satin weave with57×54ends). Tensile properties of woven fabric laminates can be controlled by varying the yarn characteristics and the fabric style (see Appendix A.1).The yarn charac- teristics include the number of fiber ends,amount of twist in the yarn,and relative number of yarns in the warp and fill directions.The effect of fiber ends can be seen in Table 4.4 when the differences in the 0and 90 tensile properties of the parallel laminates with 181 fabric style and 143 fabric style are compared. The difference in the tensile properties of each of these laminates in the0and 90 directions reflects the difference in the number of fiber ends in the warp and fill TABLE 4.4 Tensile Properties of Glass Fabric Laminates Tensile Strength,MPa Tensile Modulus,GPa Direction of Testing Direction of Testing Fabric Style o°(Warp) 90°(Fill) 45 o°(Warp) 90°(Fill) 45 181 Parallel lamination 310.4 287.7 182.8 21.4 20.34 15.5 143 Parallel lamination 293.1 34.5 31.0 16.5 6.9 5.5 143 Cross lamination 327.6 327.6 110.3 23.4 23.4 12.2 Source:Adapted from Broutman,L.J.,in Modern Composite Materials,L.J.Broutman and R.H.Krock,eds.,Addison-Wesley,Reading.MA,1967. Style 181:8-harness satin weave,57(warp)x 54(fill)ends,Style 143:Crowfoot weave,49(warp) ×30(fill)ends 2007 by Taylor&Franeis Group.LLC.Tensile properties of woven fabric laminates can be controlled by varying the yarn characteristics and the fabric style (see Appendix A.1). The yarn characteristics include the number of fiber ends, amount of twist in the yarn, and relative number of yarns in the warp and fill directions. The effect of fiber ends can be seen in Table 4.4 when the differences in the 08 and 908 tensile properties of the parallel laminates with 181 fabric style and 143 fabric style are compared. The difference in the tensile properties of each of these laminates in the 08 and 908 directions reflects the difference in the number of fiber ends in the warp and fill 100 80 60 Stress (ksi) Stress (MPa) Style 143 Style 181 40 20 0 0 0.01 0.02 0.03 Strain 0.04 0.05 690 552 414 276 138 0 0 0 90 90 45 45 FIGURE 4.12 Stress–strain diagrams of woven glass fabric-epoxy laminates with fabric style 143 (crowfoot weave with 49 3 30 ends) and fabric style 181 (8-harness satin weave with 57 3 54 ends). TABLE 4.4 Tensile Properties of Glass Fabric Laminates Tensile Strength, MPa Direction of Testing Tensile Modulus, GPa Direction of Testing Fabric Stylea 08 (Warp) 908 (Fill) 458 08 (Warp) 908 (Fill) 458 181 Parallel lamination 310.4 287.7 182.8 21.4 20.34 15.5 143 Parallel lamination 293.1 34.5 31.0 16.5 6.9 5.5 143 Cross lamination 327.6 327.6 110.3 23.4 23.4 12.2 Source: Adapted from Broutman, L.J., in Modern Composite Materials, L.J. Broutman and R.H. Krock, eds., Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1967. a Style 181: 8-harness satin weave, 57 (warp) 3 54 (fill) ends, Style 143: Crowfoot weave, 49 (warp) 3 30 (fill) ends. 2007 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.������