正在加载图片...
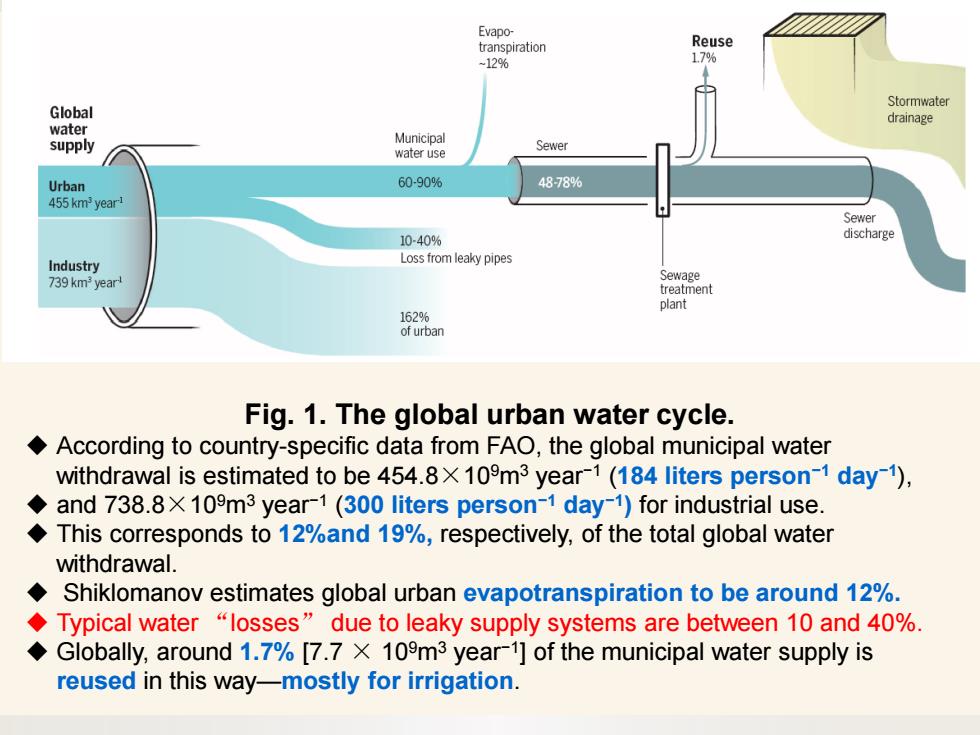
Evapo- transpiration Reuse -129% 17% Stormwater Global drainage water supply Municipal Sewer water use Urban 60-90% 4878% 455 km year Sewer 10-40% discharge Industry Loss from leaky pipes Sewage 739 km year treatment plant 162% of urban Fig.1.The global urban water cycle. According to country-specific data from FAO,the global municipal water withdrawal is estimated to be 454.8x 109m3 year-1(184 liters person-1 day-1), and 738.8X 109m3 year-1(300 liters person-1 day-1)for industrial use. This corresponds to 12%and 19%,respectively,of the total global water withdrawal. Shiklomanov estimates global urban evapotranspiration to be around 12%. Typical water "losses"due to leaky supply systems are between 10 and 40%. Globally,around 1.7%[7.7 X 109m3 year-1]of the municipal water supply is reused in this way-mostly for irrigation.Fig. 1. The global urban water cycle. ◆ According to country-specific data from FAO, the global municipal water withdrawal is estimated to be 454.8×109m3 year−1 (184 liters person−1 day−1), ◆ and 738.8×109m3 year−1 (300 liters person−1 day−1) for industrial use. ◆ This corresponds to 12%and 19%, respectively, of the total global water withdrawal. ◆ Shiklomanov estimates global urban evapotranspiration to be around 12%. ◆ Typical water “losses” due to leaky supply systems are between 10 and 40%. ◆ Globally, around 1.7% [7.7 × 109m3 year−1] of the municipal water supply is reused in this way—mostly for irrigation